Marketing
advertisement

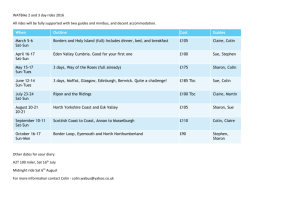
North Arctic Federal University Marketing Building a Customer-Driven Business © professor colin egan, 2012 Marketing Session Introduction © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 2 Marketing Theory & Practice: Corporate Experience • Royal Philips International – Philips Marketing Academy • IBM – IBM Marketing University • BP & Castrol – BP Sales & Marketing Academy • YKK – Marketing Excellence Programme • Coca-Cola – Coca-Cola Chair in Marketing, IEDC – Bled School of Management, Slovenia © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 3 Marketing Theory & Practice: UK Higher Education Experience • University of Bradford Management Centre – Research, MBA & Executive Education • University of Warwick: Warwick Business School – Research, MBA & Executive Education • Leicester Business School: De Montfort University – Professor of Strategic Management; Director of Research, Department of Corporate Strategy; Advisor to Senate on New University Strategy • Universities of: Strathclyde; Lancaster; Aston; St. Andrews – External Examiner © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 4 Marketing The Central Principles of Marketing © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 5 Marketing A Themed Approach Delivered Stakeholder Value Strategic Clarity Operational Excellence Organizational Design © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 6 A Tall Order: Defining Marketing A number of processes designed to analyze, anticipate and create customer needs & preferences. To create a compelling value proposition to meet these needs & preferences fully and better than rivals. To capture the imagination of customers and to secure their loyalty. To organize all the firm’s assets and resources to maximize the customer experience and the company’s profitability along with that of selected business partners. © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 7 The Central Principles of Marketing Management Customer Value © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 8 The Many Dimensions of Customer Value Customer Value © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 9 Driving Customer Satisfaction: Delivering Value • • • • • • • • • • • Economic (EVC) Psychological (PVC) Customisation Product functions Product durability Product reliability Delivery reliability Delivery time Pre-sale service Post-sale service Price Financial terms Etc. • Relationship image © professor colin egan, 2012 • • • • • • • • • • Slide 10 Previous relationship Trust Helpfulness Contactability Help in crises Order responsiveness Advice & information Complaints processing Harmonious dealings Etc. Delivering Value in B2B Markets • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Customisation Forward linkages Lending equipment Lending staff Joint R&D Dual selling Help in crises Free trials After-sales service Pre-sales advice © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 11 Free installation Returns service Electronic linkages Keep in touch service JIT delivery Any order size ok Consultancy Countertrade Satisfaction studies Etc. The Central Principles of Marketing Management Customer Value © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 12 Dimensions of Strategic Marketing Management Market Environments Opportunities Threats, KSFs Strategy Capabilities Objectives, Markets, Differential Advantage Processes, Systems, Skills, Culture, etc. Process Leadership Functions & Finance Networks © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 13 A Logical TOWS (SWOT) Analysis Sequence for Marketing Success 1 Analyse Environment 4 Analyse Organization 2 Identify Threats & Opportunities 5 Identify Strengths & Weaknesses 3 Deduce Key Success Factors 6 Identify Distinctive Capabilities 7 ‘Fit’ Leads to Superior Competitiveness & Performance in Marketing Strategy © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 14 Scanning & Sensing: Analysing The Marketing Environment Demographic Cultural Physical Customers The Firm Social Publics Shareholders Marketing Strategy Competitors Internal & Immediate Environment (Micro) © professor colin egan, 2012 Economic Suppliers Regulators Intermediaries Technological Slide 15 Political Legal External Environment (Macro) General Environment Changes & Organizational Implications I Changes Implications Affluence & quality expectations Quality offerings Service expectations Tailored offerings Micro markets Customisation Fashionisation Speed to market Consolidating competition Acquisitions, alliances, networks & partnerships © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 16 General Environment Changes & Organizational Implications II Changes Implications Intensive competition Differential advantage Commoditisation Innovation & branding Erosion of brands Partnerships & strong branding New channels Selective adoption Technology First and/or fast © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 17 General Environment Changes & Organizational Implications III Changes Implications Legislation Conform / exploit Green concern Conform / exploit Demography Selective targeting Globalisation Standardisation with adaptation Economic Strategic fit © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 18 The Central Principles of Marketing Management Customer Value © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 19 The Market Segmentation Process Segment Markets Select Target Markets Group markets with similar needs and separate them from others with different needs & preferences Select the most attractive markets given key success factors, organizational capabilities, risk assessment and long term profit potential Decide how many markets to target and with how much marketing strategy standardisation (for efficiency) and adaptation (for effectiveness) where © professor colin egan, 2012 Establish Competitive Positioning Standardise Or Adapt Ensure that customers in each market perceive that we can satisfy their needs better than rival offerings how Slide 20 Categories & Significance of Market Segmentation Criteria Macro Background Significance - Geography - Demographics - etc. Informs the supplier about who the customer is Benefits BenefitsSought Sought Significance - Needs & Preferences - Supplier selection criteria Guides the supplier’s Value Proposition design Behavioural Significance - Psychographics - Channels - Buy Class - Loyalty - DMU - Usage © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 21 Guides the supplier’s Marketing Plan design Market Segmentation for Organizational Markets • Demographic Geography • • • • • • Industry • • • • • Retailing Financial services Manufacturing Etc. • • • Lifestyle characteristics of employees • Health & Safety • Diversity & Inclusion Customer Size • • Country Region City Climate Topography • • • • Large, Medium, Small Key Account Profile • Strategic, A+, B+, served through distributors etc. © professor colin egan, 2012 Behavioural Usage Rates Adopter Groups Distribution versus Direct Decision Making Unit (DMU) Influences Loyalty Status Psychographic • Demanding versus Tolerant • BENEFITS SOUGHT Slide 22 The Central Principles of Marketing Management Customer Value © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 23 Differential Advantage • Definition: – Being superior to rivals and/or unique at supplying the mixture of benefits valued by customers in a specific market segment • Can be the product, the availability, the price, the service, the brand associations, strong relationships etc. • Can be one, but preferably many, competitive factors • Should be sustainable • Should be improved on an ongoing basis • Should be profitable in the short and/or long term, i.e., differentiation investments (technology, brand etc.) should be covered by better market positioning and/or stronger prices to reflect the enhanced customer value delivered © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 24 Differential Advantage Factors Knowledge Advantage Features & Performance Service Support Intensity (Advertising / Sales Force) Information Processes Power! Superior Technology Content Human Resource Competencies Personnel Rules & Procedures © professor colin egan, 2012 Inputs Quality Slide 25 Technology Support The Central Principles of Marketing Management Customer Value © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 26 The Strategic Marketing Mix Definition: The mixture of controllable variables that the organization blends to provide customer benefits and differential advantage in the target market segment Combines: • Value Proposition • Communications (marcomms) © professor colin egan, 2012 Quality Features Options Packaging Etc. Cost/Price Value Terms Internet Etc. After Sales Installation Training Supports Etc. Segment Channels Locations Logistics Internet Etc. Slide 27 Selling Advertising Sales Promo. Internet Etc. Marketing Organizational Analysis © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 28 The Logical TOWS (SWOT) Analysis Sequence for Marketing Success 1 Analyse Environment 4 Analyse Organization 2 Identify Threats & Opportunities 5 Identify Strengths & Weaknesses 3 Deduce Key Success Factors 6 Identify Distinctive Capabilities 7 ‘Fit’ Leads to Superior Competitiveness & Performance in Marketing Strategy © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 29 Organizational Capability Analysis Organization for Marketing Strategic Capabilities - Marketing orientation Functional integration Adequate budgets Marketing info, planning & control systems - R&D, production & distribution processes - Marketing skills levels & training - Awareness of KSFs - Distinctive capabilities - Effective objectives - Segment selection - Differential advantages - Innovation - Marketing assets - Generic strategy - Balanced portfolio © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 30 Organizational Distinctive Capability Factors • • • • • • • • • Market share Customer share Customer loyalty Market knowledge Image Innovation Flexibility Technology Internet savvy © professor colin egan, 2012 • • • • • • • • • • Slide 31 Networks Financial strength Costs Prices Quality Services Customisation Channels Product range Etc. Customer-Based Marketing Assets (Liabilities) Tied-in Clients Satisfied Clients Superior Image Customer Based Assets Superior Price / Value Quality Fit Superior Products Superior Service © professor colin egan, 2012 ‘Thought’ Leadership Slide 32 Organization-Based Marketing Assets (Liabilities) Planning & Systems Deep Pockets Marketing Culture Organization Based Assets Operational Excellence Employee Knowledge Advanced Technology Flexible Operations © professor colin egan, 2012 Managerial Knowledge Slide 33 The TOWS (SWOT) Summary Threats Market KSFs Opportunities Weaknesses Company DCs Strengths © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 34 Marketing Organization & Implementation of Marketing Strategies © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 35 Evaluating a Marketing Strategy • Validity: Reliability of information and assumptions • Distinctive: Differentiated from competition, industry breakout • Suitability: Given corporate strategy, objectives, etc. • Feasibility: Given resources/competences • Acceptability: Given company culture, ethics and values • Consistency: Are the marketing elements balanced? • Vulnerability: Given risks and contingency plans • Flexibility: Can we adapt fast enough? • Rewardability: Payoff versus risk © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 36 And Finally… Explaining Superior Marketing Performance Employee Engagement A long term perspective Understanding buyer behaviour Marketing Excellence Balanced portfolio Innovation © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 37 Market environment sensitivity Asset-based marketing philosophy Striving for competitive advantage The Role of Employee Engagement in Organizational Success (McKinsey) Strategy Skills (Competencies) Staff Shared Values Style (Leadership) Systems Structure © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 38 Shared Values: The Vector Metaphor Desired Direction 1 Resultant Force © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 39 Shared Values: The Vector Metaphor Desired Direction 1 Resultant Force Desired Direction 2 Resultant Force © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 40 Marketing North Arctic Federal University Workshop Activities © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 41 Workshop Activity I: NAFU Customer-based Assets & Liabilities Analysis Objective To evaluate NAFU Strengths / Weaknesses / Distinctive Capabilities from a Customer Assets & Liabilities Perspective. Team Mixed teams. Media Flip Chart. Preparation Using the template which follows, note the assets from the next slide, discarding those which you think lack direct relevance and adding those which you believe are more pertinent to NAFU. Feel free to add additional sector-specific categories. Execution For each item rate NAFU performance on an eleven point scale (-5 thru 0 to +5). Negatives are liabilities (weaknesses); positives are assets (strengths). The magnitude of the score reflects strengths, distinctive capabilities, weaknesses, big weaknesses. List the high scoring distinctive capabilities and big weaknesses. Feedback NAFU customer-based capabilities insights and performance improvement actions. © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 42 NAFU Customer-Based Marketing Assets (Liabilities) Tied-in Clients Satisfied Clients Superior Image Customer Based Assets Superior Price / Value Quality Fit Superior Products Superior Service © professor colin egan, 2012 ‘Thought’ Leadership Slide 43 NAFU Assets (Liabilities) Analysis: Customer-based Strengths/Weaknesses/DCs Use 11 point Scale -5 (W) thru 0 (N) to +5 (S) Customer Based Superior Image Thought Leadership Quality Fit Superior Products Superior Service Superior Price / Value Satisfied Clients Tied-in Clients Etc… © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 44 NAFU Improvement Proposals Workshop Activity II: NAFU Organization-based Assets & Liabilities Analysis Objective To evaluate NAFU’s Strengths / Weaknesses / Distinctive Capabilities from an Organization Assets & Liabilities Perspective. Team Mixed teams. Media Flip Chart. Preparation Using the template which follows, note the assets from the next slide, discarding those which you think lack direct relevance and adding those which you believe are more pertinent to NAFU. Feel free to add additional sector-specific categories. Execution For each item rate NAFU’s performance on an eleven point scale (-5 thru 0 to +5). Negatives are liabilities (weaknesses); positives are assets (strengths). The magnitude of the score reflects strengths, distinctive capabilities, weaknesses, big weaknesses. List the high scoring distinctive capabilities and big weaknesses. Feedback NAFU Organization-based capabilities insights and performance improvement actions. © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 45 NAFU Organization-Based Marketing Assets (Liabilities) Planning & Systems Deep Pockets Marketing Culture Organization Based Assets Operational Excellence Employee Knowledge Advanced Technology Flexible Operations © professor colin egan, 2012 Managerial Knowledge Slide 46 NAFU Assets Analysis: Organization-based Strengths/Weaknesses/DCs Use 11 point Scale -5 (W) thru 0 (N) to +5 (S) OrganizationBased Marketing Culture Managerial Knowledge Employee Knowledge Advanced Technology Flexible Operations Operational Excellence Deep Pockets Planning & Systems Etc. © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 47 NAFU Improvement Proposals Workshop Activity III: Competitive Positioning / Marketing Actions Analysis • The final activity leads to the creation of a customer-based marketing mix – Prepare a differential advantage profile (Value Proposition/Communications Gaps) for one key segment – List Specific Marketing Mix Actions arising from this analysis • Use the following guidelines and framework for guiding your discussion and preparing your presentation © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 48 Differential Advantage/ Marketing Actions Analysis • This process identifies ‘Value Proposition Gaps’ and ‘Communications Gaps’ in a business unit’s marketing programme • Start by identifying a target market segment and evaluate its needs in terms of a ranked list of benefits. Identify a ‘best-in-class’ rival who is currently or potentially competing in this segment • Undertake an objective evaluation of how the business unit thinks it performs in meeting these benefits versus the named best-in-class rival. Assume an external independent analysis • The aim of the process is to benchmark against a ‘best-in-class’ rival and all other competitors in the segment from: (i) A Value Proposition perspective; (ii) A Customer Perception perspective. © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 49 This exercise has six stages • Stage 1 – Name a clearly defined target market segment • Stage 2 – Name a ‘best-in-class’ rival who competes in this segment • Stage 3 – Identify eight key benefits sought by customers in the target market segment. Rank them in order of stated customer priority © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 50 Exercise stages cont… • Stage 4 – Rate how well your business performs in meeting these customer benefits – As a benchmark, use the ‘best-in-class’ rival – Use a seven point measurement scale ranging from – 3 through zero to +3 – A score of zero states that you are no better or worse than the named rival on each customer benefit – A negative score suggests you are worse, while a positive score indicates superior performance © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 51 Exercise stages cont… • Stage 4 (cont.) – Use the full seven point scale and measure for each customer benefit identified in Stage 3 – The magnitude of a positive score is a measure of the sustainability of the advantage – The magnitude of a negative score shows how difficult and/or costly it would be to close the gap with the rival – Assume that the exercise would be undertaken every six months © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 52 Exercise stages cont… • Stage 5 – Rate how well customers perceive that your business performs in meeting the benefits they seek – Use the same seven point scale and benchmark against the same rival – A score of zero means that you are perceived as no better or worse than your rivals in meeting the customer benefits sought – A negative score indicates that you are perceived to be worse in meeting the customer benefits sought – A positive score indicates that you are perceived to be superior in meeting the customer benefits sought – Measure for each customer benefit identified in Stage 3 © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 53 Exercise stages cont… • Stage 6 – Evaluate the gaps between the company’s objective evaluation of its own performance and the perception of its customers in how well their sought benefits are met, in both cases versus the same best-in-class rival – The output of the exercise will be in the form of a matrix as shown in the next slide © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 54 Exercise Output: Competitive Positioning Matrix Target Market Best-in-Class Rival Customer Benefit (Ranked) Column Totals © professor colin egan, 2012 BU Value Proposition: Customer Perception of Performance in Meeting BU's Performance Customer Benefit -3-2-1 0 +1+2+3 -3-2-1 0 +1+2+3 0 0 Slide 55 Action Analysis Competitive Positioning Value Proposition & Integrated Marcomms MARKETING MIX Customer Needs & Preferences • • • • • • • • • • • Quality Features Options Style Brand Name Packaging Sizes Services Warranties Returns Internet ‘Cost’ of Ownership • • • • • • • • • ‘Sticker’ Price Economic Value Psychological Value Discounts Allowances Payment Types Payment Period Credit Terms Internet Convenience & Lifestyle • • • • • • Channels Intensity Locations Logistics Mode Internet Service • • • • • • • Value Proposition © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 56 Pre-sales Installation After Sales Tech Support Training Consultancy Internet Communications (passive/interactive) • • • • • • • • • • Advertising Personal Selling Sales Promotion Sponsorship Publicity Public Relations Exhibitions Direct Mail W.O.M. Internet Marcomms Communications Objectives: Low scores in Column 3 • • • • • • • Create Awareness Inform Persuade Demonstrate Educate Generate Publicity W.O.M – – – – Editorial Reference Endorsement Testimonial © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 57 Communications Objectives: High Scores in Column 3 • • • • Remind Reassure Re-inforce Relationship Management: – Brand Communications in Consumer Markets – Key Account Management in Organizational Markets – Effective Combination in Business-to-Business-toConsumer Markets • Similar to New Market Segment Communications to Encourage Brand Switching © professor colin egan, 2012 Slide 58