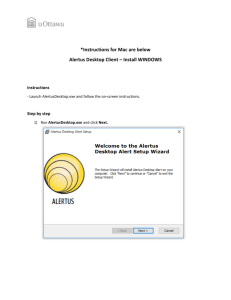
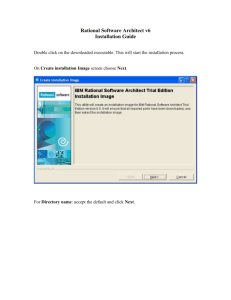
Chapter 10
advertisement

Chapter 10 Installing End-user Computer Systems Learning Objectives • Site preparation steps for computer installations • Tasks to prepare an installation site • Purpose and contents of a site management notebook • Tools needed to install hardware • Steps to install and configure hardware • Steps to install and configure an operating system • Steps to install and configure software software • packages Wrap-up tasks that installers often perform Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 2 System Installation Overview Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 3 Site Preparation • Pre-installation inspection • Checklist of issues • • • • • • • • • • • Space requirements Space constraints Storage requirements Ergonomic issues ADA or OSHA accommodations or issues Adequate power supply accessible Power conditioning required Telephone and/or network access Air conditioning required Lighting problems Fire suppression Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 4 Locating System Components • • Locate computer system and devise strategies to conserve space System Components • System unit • The footprint of a desktop case is its length times its width (measured in square inches) • Keyboard and Mouse • Optimal desk height is 26-28 inches from the floor • Monitor • Optimal user view is straight ahead or slightly down • Printer • Optimal access for loading paper, retrieving print-outs, and clearing jams Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 5 Locating System Components (continued) • Supplies (manuals, ink/toner cartridges, media, printer paper) • Convenient access • Tip: avoid storing paper in damp area • Tip: avoid storing magnetic media near generators, motors, electric and phone equipment • Furniture considerations • Importance of adjustable chair • Adjustable: seat height, seat swivel, tilt, backrest, arm rest • Waterfall seat edge • 5-leg base Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 6 Space Constraint Solutions • Separate computer worktable • Flat panel display screen • Monitor arm for CRT display • Keyboard shelf • Locate system unit and peripherals under or close to, but not on, user’s desk Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 7 Ergonomic Concerns • Ergonomics is the study of how to design computer systems and workspaces to • Minimize health problems • Maximize worker • Safety • Productivity • Comfort • Job satisfaction Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 8 Health Concerns Related to Ergonomic Problems (Overview) • Back or Neck Muscle Pain • Leg Pain • Eyestrain and Headaches • Wrist and Finger Pain • Repetitive strain injuries (RSI) result from continuous use of joints in a limited range of motion • Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common form of repetitive strain injuries that affects wrists and fingers Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 9 Back or Neck Muscle Pain or Numbness Sources Monitor too high Chair too low Poorly designed chair Keyboard too high Inadequate breaks Infrequent change in body position Guide to Computer User Support, 3e Solutions Replace office chair with adjustable one Adjust keyboard height Install adjustable keyboard shelves Recommend frequent breaks and exercises to reduce stress 10 Leg Pain or Numbness Sources Chair too high for feet to touch floor Chair design that impairs leg circulation Too little knee room Guide to Computer User Support, 3e Solutions Replace office chair Place footrest on floor 11 Eyestrain and Headaches Sources Screen glare Glasses or contact lenses inappropriate for distance from display screen Guide to Computer User Support, 3e Solutions Reorient computer to reduce screen glare Adjust office lighting Install display screen antiglare filter Check for proper glasses & prescription Recommend frequent breaks and exercises 12 Wrist and Finger Pain Sources Keyboard too high or too low Guide to Computer User Support, 3e Solutions Adjust keyboard height Install adjustable keyboard shelf Supply keyboard wrist rest Recommend frequent breaks and exercises to reduce stress 13 Workstation Ergonomics Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 14 Devices to Address Ergonomic Problems • • • • • • Adjustable tables and work surfaces Adjustable chairs Footrests Keyboard shelves Alternative (natural/ergonomic) keyboards Alternative pointing devices (trackballs and touchpads) Guide to Computer User Support, 3e • • • • • • • Wrist rests Mouse support rests Document holders Monitor arms Task lighting Antiglare screens Assistive devices 15 Impacts of Ergonomic Problems • Ergonomics are important concerns • Injuries • Permanent disabilities • Legal rules and regulations • • Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) • Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) Tip: Ergonomics is an area where a user support specialist can develop special expertise to add value to their employment or résumé Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 16 Power Requirements Overview • Many small computer systems do not require • special electrical power Special situations: • Outlets • Outlet wiring • Circuit amperage • Shared circuits • Power stability • Multiple computers Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 17 Special Power Requirements 1. Outlets • Old buildings may have two-pronged outlets • Avoid “cheater” plug adapters 2. Outlet wiring • Use LED tester • Test three-prong outlets to make sure the hot, neutral, and ground prongs are wired correctly Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 18 continued Special Power Requirements (continued) 3. Circuit amperage • Determine total amperage to see whether circuit can handle the load of devices 4. Shared circuits • Do not install computer system on a circuit that services devices with heavy motors or generators • A dedicated circuit is preferable Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 19 continued Special Power Requirements (continued) 5. Power stability • Get advice from local electric company • Use metering device to measure quality of power • Power conditioner is a device placed between computer and power source that regulates electrical power to keep it within acceptable limits 6. Multiple computers • Consult electrical contractor to verify that power is adequate and well-conditioned Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 20 Tips on Power • Use an electrical power strip for convenience, but not as • an extension cord Best power strips include surge suppression features • Certification: UL 1449 (second edition) • Peak protection: at least 40,000 amps • Clamping voltage: 330 volts or less • Clamping response time: 1 nanosecond or less • Energy rating (dissipation): 750 joules or more • Status indicator: LED lamps • Warranty against damage to protected equipment Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 21 More power tips • Avoid • Stressed cables • too tight • hard bends • Cables on floor or under carpet • Use • Wall-mounted cable conduits (runways) • Protective rubber conduits • Plastic ties to bundle cables Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 22 Telephone and Network Access • Determine location of access points before installation • in case extension lines are necessary to reach installation site Identify type of network access • • • • • • • Dial-up modem DSL Cable modem ISDN Satellite T1 or T3 Wireless Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 23 Air Conditioning • May be required in locations where a large number of computer systems will be installed close together • Small office • Training room • Computer lab facility • Mainframe and minicomputer facilities • Consult an HVAC specialist • Determine BTUs of air conditioning capacity required Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 24 Lighting Problems • Light intensity • Reduce lighting in over-lit areas • Light source • Position display screen to avoid glare on screen • Light type • Florescent bulbs may flicker at same rate as CRT-type monitor Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 25 Fire Suppression • Electromechanical equipment can cause fires, • primarily due to power supply problems If no fire extinguisher system exists: • Use portable fire extinguishers rated for electrical fires (Class C) • Use Halon-substitute in gas extinguisher Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 26 Site Management Notebook • A site management notebook consolidates important information about a computer system • Useful to operate, diagnose, troubleshoot, reconfigure, upgrade, and repair system and its components • Critical in multiple-computer situations where many support staff are likely to work on various components Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 27 • • • • • • • • • Contents of Site Management Notebook Hardware configuration Operating system configuration Network configuration Software licenses Application software configuration Special operating procedures Warranty and repair information Problem log Backup media log Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 28 Basic Hardware Installation Tools • Screwdriver set • • • • • Slotted • Phillips Nut driver Pliers • Regular • Needle-nose IC chip extractor/inserter Parts-picker Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 29 Additional Hardware Installation Tools • Pocketknife • Small parts container • Mirror • Small flashlight • PC Pocket Reference • Isopropyl alcohol Guide to Computer User Support, 3e • Lint-free cloth or foam • • • • • tip brush Antistatic wrist strap Electrician’s tape Compressed air Circuit tester Multi-meter 30 Typical Hardware Installation Toolkit Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 31 Common Hardware Installation Steps • Following hardware installation safety precautions: • Unpack the system • Connect power and signal cables, basic components • Install upgrades • Test the system Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 32 Common Operating System and Network Installation Steps • Make backup copies of existing system and data • Install operating system software • Configure network connectivity • Install client software • • Dial-up networking LAN networking • • User accounts Access rights • Perform network administrative tasks Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 33 Common Steps to Install Application Software • Determine whether software is compatible with hardware and network • Make backup copies of user data files • Choose type of installation • Install special devices drivers • Configure application to meet user needs • Install organization-specific utilities, templates, or style sheets • Reboot and test all applications Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 34 Application Software Compatibility Issues • CPU types the software runs on • Amount of memory the software requires • Amount of hard drive space the software requires • • for full installation Whether the software is compatible with hardware peripherals Whether the software is compatible with the user’s network environment Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 35 Installation Media • Distribution media is the original vendor copies of software • CD-ROM • Floppy disk • Internet download Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 36 Installation Types • Express (typical or common) • Most commonly used features • Custom (special or expert) • User selects specific features to install • Minimal (laptop or space-saver) • For users with little hard drive space available • Smallest set of functions and features possible • Full (maximum or complete) • All program features • Takes maximum amount of hard drive space Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 37 Tips on Applications Software Installation • Close all open programs prior to installation as a • • precaution Retain license information, installation key codes (in Site Management Notebook), and distribution media To reduce staff time to install and maintain application software: • Download or launch software upgrades from server • Use an application service provider (ASP), which is a vendor that sells or rents access to applications software Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 38 Wrap-up Tasks • Document system settings • Back up critical files • Create rescue disks • Fill out warranty and registration cards • Document problems • Address ergonomic concerns • Make sure user can use the system Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 39 Chapter Summary • Basic steps to install a computer system • • • • • Site preparation Hardware installation and configuration Operating system and network installation and configuration Application software installation and configuration Wrap-up tasks • • • • • • • Location Ergonomic concerns Power requirements Network connectivity Air conditioning Lighting Fire suppression precautions • Site preparation steps for computer installations Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 40 continued Chapter Summary (continued) • • • • • A Site Management Notebook organizes information about a system in a convenient location Hardware installers need a variety of mechanical tools to aid with installation tasks Hardware installers follow several safety precautions when working inside the system unit Installers develop check lists of installation procedures for • • • • Hardware Operating system and network software Application software Wrap-up tasks The ultimate measure of installation success: Is the user satisfied? Guide to Computer User Support, 3e 41