Urban Settlement Patterns & Hierarchy Presentation
advertisement
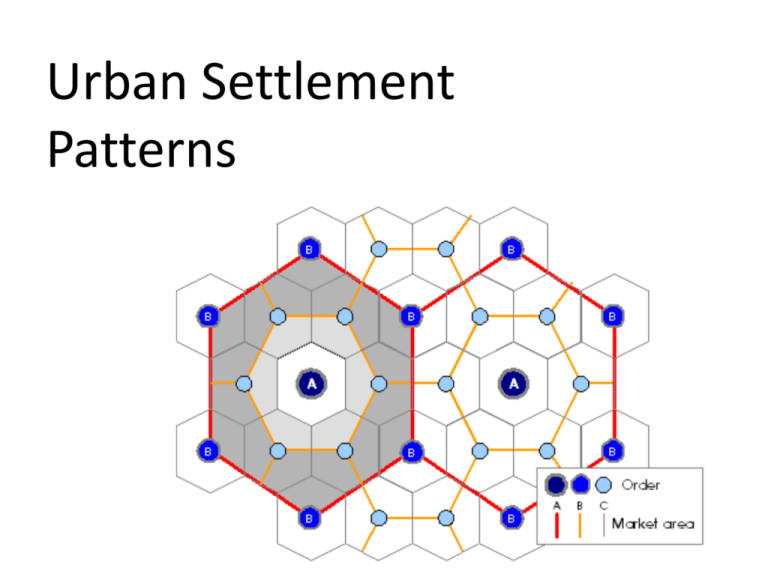
Urban Settlement Patterns Urban and Rural Interactions • Agricultural Revolution – cultivation of plants and animals. • More time to specialize in non-farming practices such as making things they could sell. • People wanted to live in closer proximity to other people (towns). • Improvement of technology allowed more people to move into urban places to work in manufacturing jobs. • Villages grew into town, towns into cities, etc. • Rural areas – hamlet, village, or town. • Urban areas – suburb, city, or metropolis. • Urban hierarchy (each one is a larger settlement going up the line than the one before it). hamlet village town suburb city metropolis Urban Hierarchy Basic Industry – activities that bring money into an urban place. Eg. Hotels, Restaurants, Factories Non-Basic Industry – activities that do not bring in ‘outside’ money, but circulate existing money. Eg. Local grocery stores, Variety stores. Urban Hierarchy Hamlet – less than 200 people Village – 200-800 people – offer low-order goods and services Town – 1000–10 000 – offer middle-order goods and services City – more than 10 000 – offer high-order goods and services Census Metropolitan Area – more than 100 000 – Consists of one or more adjacent municipalities centred on a large urban core. Offer specialized services Low Order Goods or Services – goods that are needed for everyday living and purchased frequently. Eg. food, clothing, hardware, post office. Middle order Good or Services – goods or services only needed from time to time. Eg., doctor’s offices and hair salons. High Order Goods and Services – goods or services that are not needed for everyday living and not purchased often. Eg., cars, furniture, Sick Kids Hospital Urban Hierarchy • Walter Christaller – Central Place Theory, based on the number of people needed to keep a store in business. • The minimum number of customers is known as a threshold population. Lake Huron Lake Ontario Lake Erie Lake Huron Mississauga Kitchener-Waterloo Cambridge Oakville Burlington Lake Ontario Hamilton London Lake Erie Types of Urban Places Transportation Hubs – Where ship, train, and truck routes connect. Eg., Winnipeg – major hub for railways across the country. Tourist Cities – Where people vacation to as a result of a unique physical or human feature. Eg., Banff – Skiing, scenery, hot springs. Types of Urban Places Resource Based Communities – Where there is a presence of a rich natural resource. Eg., Sudbury = Nickel. Manufacturing Cities – Where goods are mass produced. Eg., Sarnia – oil refining. Types of Urban Places Government Centres – Where local, regional and national government services are provided. Eg., Ottawa. Urbanization • Urbanization – movement of people UP the urban hierarchy. People general move to cities because of: – reduced need for farm labour due to farm modernization (e.g. tractors) – improvements in mobility (better transportation systems reduces need for local stores) – consolidation of goods & services (most things one needs has relocated to urban areas) Year % Urban % Rural 1853 15 85 1908 50 50 2001 85 15











