Kingdom Protista - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

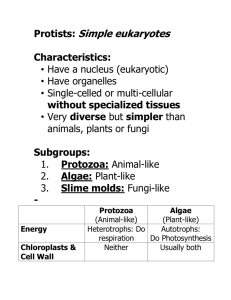
Kingdom Protista Most diverse kingdom Characteristics • • • • • • Eukaryotic (has a nucleus) Unicellular/ Multicellular Autotrophic/Heterotrophic Can be Animal-like, Plant-like, and Fungus-like First Eukaryotes on planet (Name in Greek means ‘the very first’) May reproduce using binary fission, conjugation, or sexual reproduction. Animal-like Protists – Protozoans (Zoa = Animal) • They feed on other organisms or dead matter (heterotrophs). • Protozoans consists of Ciliates, Flagellates, Sporozoa, and Sarcodina. Ciliates • • • • • • • Ciliates use cilia for movement and feeding. Found in freshwater and seawater They are free-living Phylum: Ciliophora Example: Paramecium Reproduce asexually through mitosis or ‘sexually’ through conjugation. They can use contractile vacuoles to control water flow. Flagellates • • • • • • • Flagellates use flagella to move. Phylum Zoomastigina They absorb nutrients through the cell membrane. Found in lakes and streams; some live in the bodies of other organisms Example: Trichonympha (live in the stomachs of termites) Helps termites break down cellulose that is found in the wood. Trypanosoma is a parasite that causes sleeping sickness (Get from the bite of a tsetse fly) Sporozoa • • • • • Sporozoa are non mobile. These are parasitic and produce spores. Some are free living, some are parasites. Reproduce by sporozoites. Example: Plasmodium which causes malaria in humans. It is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito. • • • • • • • • • Sarcodina Sarcodina use pseudopodia (false feet) for feeding and movement. Their movements are called ameboid movements. Found in freshwater, oceans and some in soil. Phylum Sarcodina Reproduction through mitosis They can capture and digest food in food vacuoles; A few are parasitic – Entamoeba hystolitica (causes dysentery) Example: Amoeba Foraminiferans – shells of calcium carbonate form chalk deposits on the ocean floor – Cliffs of Dover Magnification: x65 Plant-like Protists • They make their food by photosynthesis (autotrophs). • All are water dwellers – most found near the water’s surface. (??) • From microscopic (diatoms) to large, multicellular forms such as kelp. • Cells are eukaryotic. • Some move by flagella while others are non-motile. Euglenophyta Example: Euglena •They are plant-like (have chloroplasts), but move around with flagella (animal-like). •Both autotrophic and heterotrophic. •Eyespot helps Euglena detect light. (eyespot) • Algae are classified into 5 groups according to the pigments they contain. • The pigments give the algae their characteristic color. • Despite the pigments, all algae have chlorophyll. Chrysophyta: (Golden algae) Example: Synura Primarily found in freshwater. Have pigments that give them a yellow, golden color. Some can form algal blooms that can kill fish. 2. Bacillariophyta Example: Diatoms • Unicellular • Cell walls are made of silica • Store food in the form of oils. • Used to make toothpaste and metal polish. • When they die, their shells accumulate on the ocean floor to form diatomaceous earth. Pyrrophyta: (fire protists) are luminescent and glow. Sometimes look like a fire smoldering in the water. Example: Dinoflagellates Blooms of dinoflagellates can cause red tide which release poisons that kill thousands of fish. Rhodophyta: Red algae Example: Seaweed • Found in marine and some in fresh water. • Can absorb blue light which penetrates water more deeply – therefore red algae grow deeper under the ocean. Phaeophyta: Brown algae • Example: Kelp • Kelp has air-filled structures called air bladders that help keep the photosynthetic parts of the algae near the water’s surface. • Used by humans for food, cosmetics. • Chlorophyta: Green algae • Example: Chlamydomonas ,Volvox (live as a colony), Spirogyra • • • • Most diverse of all the algae. Some single celled, others are multicellular Contain the same pigments that are found in plants. Phytoplankton is a huge group of producers in the marine food web. • Produce O2 Fungus-like Protists • All are heterotrophic • Recyclers of organic matter/rotting (saprophytic) • Example: Slime Molds and Water Molds • Some are parasites and can infest crops for example potato famine caused by potato blight Dog vomit slime Red raspberry slime