Ancient Civilizations
advertisement

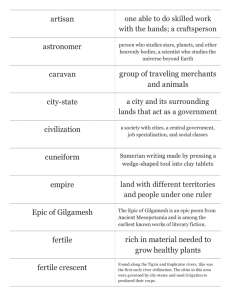
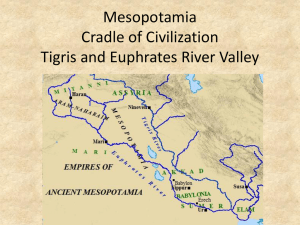
What is a Civilization? The mystery of being human….survival, intelligence, leaders, competition, emotions, greed When did it all begin…putting the pieces together Archaeologists: “Diggers”: scientists who study past human life: putting pieces together for the whole story Artifacts: items from the past such as tools, pottery, bones, arrowheads, shelters. Fossils Anthropologist: “the man”: scientists who study past human life, concentrating on the human himself Historians: people who study the past, use of primary and secondary sources. Primary and Secondary Sources Primary Source: first hand information, “I was there”, witnessed the information: current newspapers/magazines, pictures/drawings, diaries, journals, document, map, autobiography personal correspondence and diaries works of art and literature speeches and oral histories audio and video recordings photographs and posters newspaper ads and stories laws and legislative hearings census or demographic records plant and animal specimens coins and tools More Primary and Secondary Sources Secondary Source: information that comes from research, “after the fact”…passing information on Research papers, biographies, reports…history books, historical magazines, Primary and Secondary Sources: Video Another Look…. How long ago? Use of scientific method: a procedure based on logic and reason…conducted in an orderly manner…looking to find answers 1 method: radiocarbon dating: study the amount of carbon in an item/artifact 2. deoxyribonucleic acid: DNA, genetic make-up of humans The Dig… 1. Let’s look here….a new site 2. create a site grid: the method of dividing the site into sections…easier to keep track of what was found where…level of the find 3. The higher the level find the most recent the item 4. The tools: shovels, trowels, wooden picks, brushes, sifters….(delicate) 5. Every item is a piece of information 6. Environmental information: study soil, plant remains Early Man It is all a theory: an idea of how something may have happened…need to find clues to prove a theory Early human being: Homo sapiens: lived in central east Africa: 100,000 to 200,000 years ago: similar appearance to modern man Movement: modern man moved, migrated, to other parts of Africa, intoAsia…..impact of movement?????? Other early human beings: Homo erectus and Neanderthals: moved throughout Africa and Asia Beringia: area where Asia and North America met…Homo Sapiens move throughout North and South America Just Roaming 1. Early man did not live in organized communities 2. They were hunters and gatherers…wanderers 3. Survival was most important…looking for food 4. Man uses intelligence to survive…began to settle 5. Plants seeds, grow crops, tame animals, build shelters 6. Development of laws…government BEGINNING OF A CIVILIZATION! What makes a Civilization? 1. A civilization is an advanced society with agriculture, division of labor, multiple cities, organized religion, science/technology, some form of government, and a written language. Five Elements of a Civilization A. People learn how to grow crops and domesticate animals B. People build permanent homes…settlements, towns, cities C. People began to develop technology..advanced tools and weapons: wheel, spear, plow D. People made intellectual achievements…use of the mind: THINKING: PROBLEM SOLVING: writing, calendar E. People began to create rules/laws. Need for order. Beginning of a government Today’s Civilization Create a picture of our civilization today including all 5 elements of a civilization. Be creative 15 points In color 10 points Neatness matters 10 points Show details/examples 25 points Give a title 10 points Total Points 70 points Begin by looking, reading, and writing…. A time line: pp 82: write 5 statements based on the information pp 82—83 A map pp 84-85: Write 5 statements based on the information on pp 84—85…what is the title of this map? Let’s read: “Gilgamesh the King”…Response Corner #2 The Land Between Two Rivers Importance of Major River Systems River systems formed valleys Importance of water—uses River valleys location of permanent settlements River Valley…. 4 major river systems….earliest civilizations Tigris-Euphrates: southwestern Asia Nile River: Africa Indus river: southern Asia Huang He: eastern Asia Pictures The Tigris and Euphrates Civilization: Sumer: located in fertile crescent of Tigris and Euphrates River valley Very fertile land Smaller rivers flow into the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers: tributaries Tigris meets Euphrates: flow into Persian Gulf Land between Tigris and Euphrates: Mesopotamia: “land between the rivers” Sumer became first civilization in Mesopotamia Need for Irrigation Flooding: saint and demon…fertile soil but floods could destroy Northern Mesopotamia: enough rainfall Not true of Southern Mesopotamia…hot sun…baked soil Learned to make use of the river…irrigation…water the crops..store water Building of dikes to protect from floods Dams: to control the flow of river water Allowed for farming to become a way of life First Settlement in Sumer First known settlement in southern Mesopotamia: Ubaid: 5000 BC Grew enough crops to survive Use of stone hoes and clay sickles Wheat and barley Lived close to fields in huts of reeds and mud Worshiped gods in one-room temples Changes in Ubaid Culture More advanced irrigation Surplus crops Need for rules and regulations…need for leaders…government Larger homes…larger temples Painted pottery Ubaid culture: foundation for civilization in Mesopotamia Reading a Land/Product Pp 100—101: Read Practice the skill: 1--5 Independent Sumerian City-States The Emergence of Cities Sumerian cities: Ur, Kish, Uruk, Eridu: grew to be powerful..cities of culture and achievement By 3000 BC: 12 cities had developed into citi-states Characteristics of citi-states independent Walled city Land around city Own government Populations of over 5,000..eventually over 60,000 Individual citi-states became part of the civilization Common language, writing, arts, and crafts among the entire civilization Government and Religion Government: made up of small group of leaders and a chief leader Made laws, settled disputes, decided what work had to be done, waged war Need for ONE leader: idea of monarchy, a government ruled by a king or queen Monarchy passed on by blood-line King had complete control: autocracy…rule by one King had power, authority, and legitimacy Sumerians practiced polytheism: belief in many gods: one god for each natural event or element of life: god of agriculture, god of transportation, god of war Gods must be kept pleased…worshiped the gods in temples MesopotamianAchievement Agricultural Techniques: innovations: new ways of doing tasks, problem solving: creative: innovative Example: irrigation From clay…copper….bronze Each new way: innovation: life improved, more productive, benefits Passing on information: almanacs…giving advice: planting, irrigation, crops Measurements Land critical element of Sumerian life How much do we have????...need for measurement iku or ikum: the field: an iku equaled 37,600 square feet From iku to acre: one acre equals 43,560 square feet Measurement for weight/volume: quart Sumerian numbers based on 60….our number system developed FROM the Sumerian number system ( hours, minutes, seconds) Sumerian calendar: 360 day Buildings Use what you have…few trees in southern Mesopotamia but plenty of MUD..make bricks out of mud Building of houses: flat-roofed, built close together, facing an open court, thick walls: cool in summer, warm in winter Higher your rank…higher your house, more detail Ziggurat: temple, highest and tallest building, as wealth and power grew so did ziggurat Top of each ziggurat a shrine for city’s god Other buildings built around the ziggurat..center of activity Transportation Wheels: Sumerians attached wheels to carts: twowheeled/four wheeled Chariots pulled by donkeys or oxen Use of caravans Boat transportation: built like basket made from reeds and covered by animal skins: mast and sail in center; first sailboat Also canoes Writing and Literature Sumerians: first written records: clay tablet in Kish 3500 BC: picture symbols that recorded trade Clay tablets found at Uruk: writing system: cuneiform: wedge shaped symbols: over 700 symbols Scribes: those people who knew how to write; recorded history: very important Your turn Make an alphabet in cuneiform and then write three words using your alphabet. Symbols in color. Daily Life in Sumer Sumerian cities: center of trade, religion, government Key to Sumer: agriculture: meat, fish, grain: surplus: trade: money: power Government and Law: more important/closer to ziggurat Role of government: trade, settle disputes, collect taxes, oversaw temples and monuments Rights given to people, except in time of war Property rights/land and animals taken More taxes to support a war More daily life… Urukagina: ruler of Lagash: laws to prevent government leaders or wealthy from taking advantage of poor Ur-Nammu: leader of Ur…laws written down: if you do…then this will happen 7 laws carved on monument: written government…oldest know record of ancient law Life goes on… Specialization of labor: skills and information to do ONE job WELL Traded services with each other…I give you..you give me Occupations: priests, government officials, scribes, craftsmen, merchants, farmers, fishermen Government officials: building projects, distribution of food, schools, taxes Scribes: records, wrote letters, stories, songs Craftsmen: jewelers: lapis lazuli, carpenters: ships Weavers, potters, stonemasons, bricklayers Trade Merchants: buying and selling Sumerians: wheat, barley, metal tools for wood salt, precious stones, copper and tin Pleasing the Gods Mother nature: storms, insects…impact on life Sumerians worshipped gods: deities…gods who controlled nature Offered gifts to please the gods Worshipped thousands of gods Most important: air god, Enlil…water god, Enki, also god of wisdom Social Structure of Sumer Social classes: a division of the people based on power and wealth Highest rank: king, nobles, priests, military leaders Middle class: merchants, scribes, craft workers, farmers Could move up the “social ladder”: work and effort Lowest rank: slaves: debtors Sumerian women: more rights than most civilization: could own property, divorce, could be priestesses, or scribes The First Empires Akkadian Empire Sumerian city-states: wealth: war Sumerians defeated by Sargon and his army Sargon: defeated…defeated…defeated…across all of Mesopotamia…building an empire Capital city of empire: Akkad/Akkadian Empire Sargon became emperor, ruled by military rule, kept a standing army Governors appointed to control conquered cities, paid tribute to Sargon Empire stretched from what is now Iran to the Mediterranean Sea Empire will fall Hammurabi and the Babylonian Empire 1790—1750 BC: Hammurabi, king of Babylon….united most of Mesopotamia Became the Babylonian empire Encouraged trade, agriculture, irrigation Instituted a fair tax system Code of Hammurabi: one collection of laws for all of Babylonian Empire (national laws) Consisted of 282 laws: family relations, taxes, land and business deals, trade, loans, debts, crimes…”so that the strong should not harm the weak.” “eye for an eye” Babylonian Empire falls around 1600 BC Hammurabi and His Code http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oDALXORbtR 4 Kassite and Assyrian Rule 1600’s BC: Hittites captured and looted Babylon Next came the Kassites…ruled for more than 500 years…adopted Babylonian way of life Next: Assyrian Empire: wanted to control trade routes…new weapons to defeat: battering ram, lance By 700 BC: Assyrian largest empire in world..all of Mesopotamia, present-day Turkey, Egypt, Persian Gulf area Developed paved roads…postal system: united empire…locks that opened with keys, magnifying glass, first libraries Assyrian Empire falls in 600 BC…New Babylonian Empire…ruler Nebuchadnezar: Hanging Gardens of Babylon…one of the Seven Wonders of the World Hanging Gardens Another Picture Skill Time: Map Reading Using the map on page 123 answer the following questions: A. What is the title of the map B. Name 4 bodies of water found on the map C Name 5 cities found on the map D. What information is found in the key? A Review http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ki8S5I83Ccc Mesopotamia Rap http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=84y2q4giihY