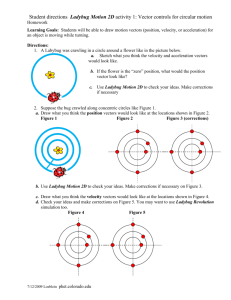
A Look at Ladybugs
advertisement

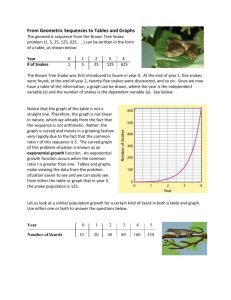
Table of Contents Ladybug Facts……….….page 2 Ladybug Larvae……..…...page 11 Ladybug Habitats …...page 3 Ladybug Pupa ………….....page 12 Ladybug Diet …………...page 4 Ladybug Adults ……......page 13 Ladybugs in Flight …..page 5 Ladybugs in Space ..….page 14 Ladybug Predators ….page 6 Ladybug Acrostic ……..page 15 Ladybug Protection …page 7 Ladybug I Poem ………...page 16 Ladybugs in Winter …page 8 Ladybug WOW Facts ..page 17 Ladybug Life Cycle . .page 9 Glossary ………………………page 18 Ladybug Eggs …………page 10 Index ……………………..……page 19 Illustrated by Mayrani Ladybug Facts Ladybugs are insects. They belong to the beetle family. There are about 5,000 different kinds of ladybugs in the world. Most ladybugs are red with black spots, but they can also be orange, yellow, or black. They may have stripes or no designs at all. Illustrated by Brittney Ladybug Habitats Ladybugs live all over the world. They live on every continent except Antarctica. Ladybugs can be at home in many different habitats. They can live in cities or suburbs, grasslands or gardens, forests or fields, mountains or marshes. Illustrated by Macy Ladybug Diet Ladybugs are helpful to farmers. They eat aphids which are tiny insects that devour and destroy crops. Ladybugs have a voracious appetite and can eat over 5,000 aphids in a lifetime. They will also consume moth eggs, pollen, and other small insects. Illustrated by Camille Ladybugs in Flight A ladybug's wings are hidden under the wing covers. When they want to fly away, they must hold up the covers and unfold their wings. Their wings must move very fast before they can take off. When the ladybug lands, it must fold its wings back under the wing covers. Illustrated by Reagan Ladybug Predators Ladybugs have predators or enemies that try to eat them. Their main predator is a bird. Other attackers are frogs, wasps, spiders, dragonflies, and praying mantises. When a ladybug sees one of these creatures, they know to watch out. Illustrated by Ethan Ladybug Protection Ladybugs can fly away from some predators, but they are not fast flyers. They have two other forms of protection. First, ladybugs can play dead. When they are frightened, they topple over, lie on their backs, and roll up their legs. They can also defend themselves by oozing a yucky, evil-smelling liquid from their legs. This disturbing stench drives away enemies. Illustrated by Lucas Ladybugs in Winter Ladybugs are busy during the spring, summer, and fall. But when the weather turns cold, it is time for them to hibernate. They search for a place to hide from the cold winter winds. They may hibernate under leaves, stones, or tree trunks or even in barns or homes. Thousands of ladybugs can be found sleeping together until warm weather returns. Illustrated by Ameshia Ladybug Life Cycle Illustrated by Henry Ladybug Eggs A mother ladybug searches for a good place to lay her eggs. She looks for a plant that has aphids so her babies will have food. She lays about 20 eggs on the bottom of a leaf then flies away. The eggs are orange and oval-shaped. After about a week, the eggs turn brown and hatch the next day. Illustrated by Jessica Ladybug Larvae The tiny creatures that emerge from the eggs are called larvae. They are bluish-gray with yellow spots and have long, thin bodies. They are covered with spiky bristles. The larvae are ravenous and immediately devour their egg shells. Then, they hunt for aphids to eat. As they eat, they grow and as they grow, they must shed their skins. This is called molting. They will molt three times. After three or four weeks, the larvae are completely grown. Illustrated by D. J. Ladybug Pupa When the larvae are finished growing, they attach themselves to a leaf and hang upside down. They molt for the last time. The new skin turns into a hard case called a pupa. The pupa looks like bird poop. This keeps it from being eaten. Inside the pupa, the larva is going through a spectacular change. Illustrated by Salma Ladybug Adults After about a week, the pupa splits open and a new creature crawls out. It is a ladybug! The new ladybug must rest and stretch its wings. Then it's ready to fly. A ladybug spends most of its time searching for food and eating. Illustrated by Jeremiah Ladybugs in Space In 1999, four ladybugs and a bunch of aphids traveled to outer space on the space shuttle. Scientists named the insects John, Paul, Ringo, and George. They were trying to see if ladybugs could catch their food in space. The ladybugs enjoyed their outer space picnic and ate all the aphids. The astronauts decided that ladybugs do great in outer space! Illustrated by Brandon Ladybug Acrostic Ladybug I Poem I am a lovely ladybug I wonder if I will find enough aphids I hear other ladybugs’ wings humming I see my friends in the rose garden I want to join them for a meal I am a lovely ladybug I pretend that I will live for hundreds of years I feel old although I am only a few weeks old I touch my eggs for the last time I worry that my babies will not survive I cry when I realize I will never meet my children I am a lovely ladybug I understand that birds want to eat me I say “Stay away - I taste yucky” I dream that I can fly faster than a bird I try to play dead before my predators I hope that bring luck to many people I am a lovely ladybug Illustrated by Briana Ladybug WOW Facts A lady ladybug will lay around 2,000 eggs. There are over 5,000 different species of ladybugs. The most common ladybug in North America is the seven-spotted ladybug. One ladybug will eat over 5,000 insects in its lifetime. Some people believe that ladybugs bring good luck. A ladybug in flight beats its wings over 85 times per second. Six states have a ladybug for its official state insect - Delaware, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, & Tennessee. Illustrated by Mrs. Hicks Glossary Aphid – A small insect that feed by sucking juice from plants Beetle – A group of insects with strong, biting jaws and hard wing covers. Insect – A creature that has 3 body parts and six legs. Larva – The second stage of an insect’s life cycle. Molt – To split and shed the skin to allow for new growth. Predator – An animal that hunts and eats other animals. Pupa – The hard case that forms around a larva before it becomes an adult. Illustrated by Litzy Index aphid – 4, 10, 14 larva – 9, 11,12 adult - 13 life cycle - 9 beetle - 2 molt - 11 diet - 4 predator – 6 eggs – 10, 11 protection – 7 farmers - 4, 15 pupa – 9, 12, 13 hibernate – 8 wings - 5 Illustrated by Dalton Sources Ladybug, Ladybug, Fly Away Home Written by Judy Hawes Illustrated by Ed Emberley Ladybugs: Red, Fiery, and Bright Written and Illustrated by Mia Posada Starting Life Ladybug Written by Claire Llewellyn Illustrated by Simon Mendez National Geographic Kids Ladybug Website Enchanted Learning Ladybug Website About the Authors and Illustrators We are second graders at Forbush Elementary School in East Bend, N.C. We have enjoyed researching and writing about ladybugs. We are also excited about the ladybug habitat that our teacher bought. We will use it to observe the stages of the ladybug life cycle and will learn even more about these interesting insects.