Cardiac Monitoring Skills

Module One
Cardiac Monitoring Skills
NRSG450
Goals
• Student Will Be Able To Discuss Cardiac Monitoring And Correctly
Place Chest Leads.
• Student Will Be Able To Interpret A Rhythm Strip For Cardiac Rate,
Wave Morphology, Direction, Duration And Relationships To Other
Waves.
• Student Will Recognize Normal From Abnormal Rhythms.
• Student Will Recognize Basic Sinus, Atrial, Junctional And
Ventricular Rhythm Variations.
• Student Will Identify Lethal Rhythms.
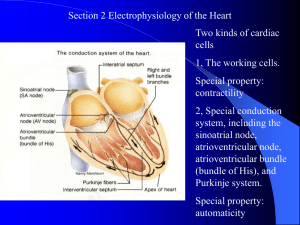
Background of Electrical Flow of the Heart
Electricity stimulates the heart muscle to contract. It spreads through the heart sequentially changing the polarity of the cell’s interior from negative to positive
(depolarization). This causes contraction of the muscle. The internal cell positive polarity changes back to negative
(repolarization) and the muscle relaxes. This process proceeds through cell-to-cell communication and high speed tracts in the atria and ventricles.
www.guidant.com
Anchoring the Information
• Electricity stimulates the heart muscle to contract.
• The internal cell is Negatively charged at rest.
• Stimulating the change of the cell’s internal and external polarity is called Depolarization .
• Depolarization produces Contraction of the muscle.
• Repolarization is the return of the internal cell negative polarity and muscle Relaxation .
• Depolarization and repolarization occur Sequentially.
• These processes proceed through Cell-to-cell communication and high speed tracts.
TAKE THE QUIZ ON THE NEXT SLIDE AND TEST YOUR
KNOWLEDGE OF WHAT YOU HAVE JUST LEARNED.
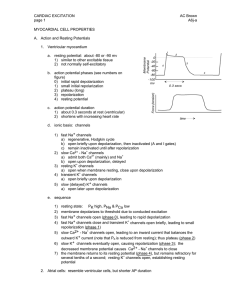
Action Potential Curve
the Heart
Intracellular
Cell wall
Extracellular
Depolarization-repolarization involves the exchange movement of sodium and potassium across the cell wall with calcium modulation. This exchange sets the rate of the electrical spread. This process, including a rest period, is called the action potential curve.
Background of Electrical Flow of the Heart
• Each heart cell is able to start the depolarization process – automaticity.
• Excitability is term given to a cell responsiveness to a electric stimulus.
• The ability of a cell to transmit a stimulus to another cell is contractivity.
• Contractility is a measure of the cell’s ability to contract upon electrical stimulus.
• These processes are influenced by the autonomic nervous systems & medications.
Background of Electrical Flow of the Heart
• The sino-atrial (SA) node is usually the group of cells that trigger depolarization.
This is why the SA node is known as the heart’s pacemaker.
• The SA node usually sets the heart’s rate at 60 – 100 beats per minute.
Anchoring the Information
• Depolarization and repolarization involves the exchange movement of Sodium and Potassium across the cell wall with calcium modulation.
• This exchange sets the Rate of the electrical spread and muscle Contraction .
TAKE THE QUIZ ON THE NEXT SLIDE AND TEST YOUR
KNOWLEDGE OF WHAT YOU HAVE JUST LEARNED.
Anchoring the Information
Automaticity
• Ability to start the depolarization process.
Autonomic nervous system
• Measure of cell’s ability to contract.
Conductivity
• Cell’s responsiveness to a electric stimulus.
Contractility
• Ability of cell to transmit a stimulus to another cell.
Excitability
• These processes are influenced by the autonomic nervous systems & medications
TAKE THE QUIZ ON THE NEXT SLIDE AND TEST YOUR
KNOWLEDGE OF WHAT YOU HAVE JUST LEARNED.