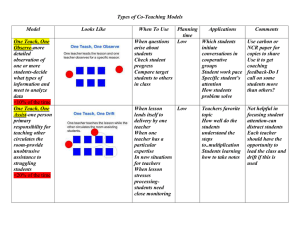
Learning Targets, Change Rationale
advertisement

Learning Targets, Change Rationale The Task at Hand ► Challenging times call for people to step forward - try new things, lead new innovation, look at the world in a “fresh” light Education - a changing landscape Senge (1990) ► Perhaps for the first time in history, humankind has the capacity to create far more information than anyone can absorb, to foster far greater interdependency than anyone can manage, and to accelerate change far faster than anyone’s ability to keep pace (Senge, p. 69). Xerox’s CEO – David Kearns “ Schools are admirably suited to the economy & culture of the 1950s and spectacularly unsuited to the high-tech future of the next century” Education - a changing perspective ► Traditionally - two things separated education from the “real world” of business Profit Competition What will the world look like? ►Interactive technology – anytime/ anywhere ►Evolving workplace ►Globalization – adaptability, flexibility, critical thinking, ‘systems thinking’understanding Begin with the end in mind! ► What is the reality we’re preparing our students for? ► Change must begin at the top ► What innovations or changes in structure or practice are we modeling to accomplish the goals for this new “reality”? Times have changed ► In this age of “accountability” – we must turn a “profit” and we now have competition ► http://www.flvs.net/ Operational Definitions What is effective instruction? What is ineffective instruction? Learning Targets & Standards ► Goals, objectives, & targets ► Standards ► Sources of learning targets & standards ► Criteria for selecting targets & standards ► Types of learning targets Learning Targets ► Commonly thought of as: Goals, objective, competency, standard or expectation Goals ► Broad, general statements that cover a block of instructional time ► Lay groundwork for specific learning objectives ► May be closely related to defining the mission of a school or school system ► Ex: Learning to think critically - citizen Objective ► Usually more specific statement of student performance - to be demonstrated at the end of an instructional unit Global objective Instructional objective Global Objective ► Often goal interchanged with the definition of a Instructional Objective ► Intended learning outcome ► Specific, observable, and measurable ► Begin with action verbs (state, define, list, etc) ► Specific behavior, audience, criterion, and condition ► May be stated in general terms Standards Based Education ► National/State standards have been developed for most content areas ► Content Standards - Statements about what students should know, understand, and be able to do ► Performance Standards - level of proficiently to be demonstrated Criteria ► May be called scoring criteria, rubrics, or scoring guidelines ► Key - what is excellence in comparison to simple proficiency ► Establishing rubrics, expectations and sharing them with students is helpful Expectations ► Communicate the level of performance you think they can demonstrate ► Based upon student’s previous achievement, aptitude, motivation, etc ► Differentiate instruction and have understanding of level of performance Types of Learning Targets ► Knowledge and Simple Understanding ► Deep Understanding ► Skills ► Products ► Affective Knowledge and Simple Understanding ► Student mastery of substantive subject matter and procedures ► Some simple recall and mastery of basic facts ► More than rote memory - implies some level of understanding or application Deep Understanding & Reasoning ► Use of knowledge to solve problems ► Problem solving, critical thinking, analysis, synthesis, compare/contrast, higher order thinking Skills ► Requires student to perform - demonstrate use of skill - significantly different than just knowing the right answer to a question ► There is an assumed background skill involving procedures that must be effectively performed ► Presentation, speaking a second lang. Products ► Samples of student work - demonstrate the ability to use knowledge ► Project, portfolio, artwork, etc ► Performance based assessments are examples of how product learning targets are measured Affective Learning Targets ► Include emotion, feelings, beliefs - different than cognitive learning ► Hope to develop positive affect - positive attitude towards school, proper motivation, ► Character ed Sources of learning targets ► Bloom’s Taxonomy Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation Sources of learning targets ► Professional Preparation - TEP, Certification ► Textbooks - provide objective - usually don’t go far enough ► Professional organizations ► State Department (alsde.edu) ► Local systems (curriculum maps, etc) Criteria for Selecting Learning Targets ► Grade Level ► Represent all types of learning from recall to application ► Teacher, school, system, and state goals should be included in targets ► Should be challenging, yet feasible ► Current, motivational, applicable