CSCI-1305 Introduction To Information Technology
advertisement

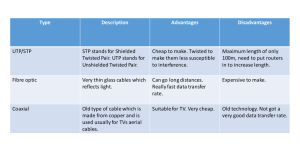
Introduction to Networks What is a Network? • A network is an interconnected system of things or people • • • • • • • • Religions Business contacts Snail Mail Social Media Broadcasting - NBC, CBS, ABC, PBS Transportation (air traffic control, highways & rail) Cellular phone service …and of course computer based (internet) • Networks let people share resources, devices, information, software, and data. • Networks can be simple, or complex, and network components can interact in different ways. Computing before Networks • In the early years of the computer revolution, most computers functioned as stand along units. • And then . . . Bob Metcalfe had an Idea • In 1976, Bob Metcalfe had an idea for transporting data between computers. • His idea has become a key element in just about every computer network including the Internet. • He called his idea Ethernet. And so . . . • In the global society we live in, networks connect people and resources • Hardware and software are required to make this happen • Networks can be simple or complex • The Internet is the largest network in the world Ethernet Technology • Ethernet is the most widely used standard for wired networks. This standard controls how adapter cards, routers, and modems share access to cables and phone lines. The standard also dictates how devices transmit data. Cables, Connectors, Ports Wired networks have cables that connect network devices through ports. Networks could use the following types of cables. • Twisted pair (lowest rate of data transfer) • Coaxial • Fiber optic (fastest rate of data transfer) Are all Networks the Same? • Networks exist in many variations because each one is constructed from a collection of technologies. • Networks can be classified according to their size and geographic range or scope. Wired Networks • Data in a wired network travels from one device to another over cables. Wired networks tend to be more secure and transmit data faster than wireless networks. Wireless Networks • Data in a wireless network travels through the air. Wireless networks are more convenient, but can be less secure. In information technology, a network is the combination of hardware, software, cables, and signals that allows people and computers to communicate with each other and other electronic devices. Nodes What is a Node? • In a network, a node is a connection point. In general, a node has programmed or engineered capability to recognize and process or forward transmissions to other nodes. Computer Networks – Nodes • Node – Client • • • • • • • Printers Desktops Laptops Copiers Network storage devices Routers Anything that can connect to a network • • • Cell phone GPS device IPOD/PSP/XBOX/PS3/Tivo/DVR/Slingbox… Identify Nodes Networks Need Hardware and Software to Make Connections • Simple software built into a computer will connect a home network • Sophisticated software is needed for larger and more complex networks Network Interface Card (NIC) • A circuit board with special electronic circuits that connects a computer to a network • Smaller laptops or tables may use a wireless network card Communications Hardware • To connect to a network, your computer will need a network interface card (NIC), which can be wired or wireless Hub or Switch • A device that provides a central point for cables in a network. Most networks today use switches, which transfer data only to the intended recipient. • Switches are more commonly used than hubs because switches transfer data only to the intended devices. Communications Hardware Hubs and switches provide a central point for network cables. Hubs transfer all data to all devices, and switches transfer data only to specified recipients. Most modern networks use switches rather than hubs. Router • A device that connects two or more networks and directs, or routes, the flow of information along the networks. Communications Hardware A router manages network traffic by evaluating messages and routing them on the best path to their destination. Communications Hardware • A digital modem sends and receives data and information to and from a digital line. Many modems today include built-in Wi-Fi connectivity. Network Hardware Devices • Wireless access point – Lets wireless device connect to a wired network • Router – Sends data between networked computers • Broadband modem – Connects a computer to the Internet Mobile Computing Smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other handheld devices can connect wirelessly to networks to share data and services, which is known as mobile computing. Identify NICs, Switch, Wireless Access Points, Mobile Computing, and Router Why no modem? Network Architecture Network architecture determines how networked computers interact with one another. Typically, one of two architectural models are used: • Peer-to-peer • Client/Server Domain vs. Peer Networks can be domain-based or peer-to-peer. • Domain-based networks have a domain controller such as a server, that regulates access to the network. • In a peer-to-peer network each computer is equal on the network and controls access to its own resources. Peer-to-Peer is best suited for networks with 10 or fewer computers Individual computers may maintain their own files, but share resources such as printers and scanners. Client Server Each computer or device on the network is called a client. The clients make requests of the server for services, like access to a software program, a database, the Internet, or a printer. A client server is one central computer (the server) controlling access to network resources. Wireless Networks In addition to domain vs. peer-to-peer, networks can be wired and wireless. Wireless networks communicate via signals through the air, connecting devices without the use of cables. Wi-Fi Hotspot A Wi-Fi (wireless fidelity) network uses radio signals to connect computers and devices. Tethering and Mobile Hotspots You tether (connect) your mobile phone to your computer, using a USB cable or Bluetooth, and then turn on your mobile phone’s tethering feature. Client/Server or Peer-to-Peer? Identify Hotspots, and Tethering Areas PAN (Personal Area Network) • Is a network that connects personal digital devices within a range of about 30 feet. PANs work without the use of wires or cables. Bluetooth is an example of a PAN. Where could a PAN be located in this diagram? Networks May Use a Combination of both Wired and Wireless Technologies Identify wired and wireless Types of Networks • In communication networks, a topology is a schematic description of the arrangement of a network, including its nodes and connecting lines. • The topology of a network is a diagram of the network and the way it physically connects. Network Topology Network topology is the physical system of interconnections of the elements of a computer network (Links, Nodes, Clients, etc.) The system of interconnected things on a computer network are referred to as nodes. Star Topology Star topology is the most common topology used in today’s workplace. North Greenville University in Tigerville uses star topology. Bus Topology Bus topology is where in a computer network, a bus is a transmission path on which signals are dropped off or picked up at every device attached to the line. Ring Topology A ring is a network topology or circuit arrangement in which each device is attached along the same signal path to two other devices, forming a path in the shape of a ring. Mesh Topology Wireless Topology A wireless Internet service provider (WISP) is an Internet service provider (ISP) that allows subscribers to connect to a server at designated hot spots (access points) using a wireless connection such as Wi-Fi. Identify Ring Topology, Star Topology, and Wireless Topology LAN – Local Area Network • A local area network (LAN) connects computers and devices in a limited area, such as a home, an office building, an office complex, or a school • Each computer or device on the network is called a node • Networks help companies save money by facilitating resource sharing. WAN – Wide Area Network • A wide area network (WAN) covers a large area. A WAN is appropriate for a state, country, or other large area where data needs to be transmitted over significant distances. • WANS combine multiple connection technologies, such as telephone lines, cables, and radio waves. • A WAN can be one large network, or a WAN can consist of a series of interconnected LANs. • Multi-nations companies, governments, retail chains might all use WANS. • The Internet is the world’s largest WAN. LAN or WAN? The Internet . . . • Is a collection of personal, local, regional, national, international, and multinational computer networks. It is the largest network in the world. The Internet is Many Networks all Linked Together. • They share data and tasks. The Internet carries voice, data, video, and graphics. Artist rendering of the Internet The Internet Backbone . . . • The essential infrastructure of the Internet, is owned by several telephone and communications companies around the world such as AT&T and Verizon. Network Service Providers • Backbone links and routers are maintained by network service providers (ISPs). No single entity controls or owns the Internet. Internet Service Provider (ISP) • Is a company that offers Internet access to individuals, businesses, and smaller ISPs. Connecting to a Network • Computers need specific network hardware, services, and standards to connect to a LAN or a WAN • Connecting to the Internet often requires services from an Internet service provider • All communication technologies need global standards so they can understand one another Network Standards • Computers need a common language to communicate over networks. Network hardware and software must work together, regardless of who made them or where they are located. • To ensure that any computer in any part of the world can connect to any network, organizations such as ANSI and IEEE propose, develop, and approve network standards Network Standards Network standards specify the way computers access a network, the types of hardware used, data transmission speeds, and the types of cable and/or wireless technology used. Current Network Standards How Networks Work • • • Networks connect computers and digital devices to share resources and data. Networks need hardware to transmit data Networks let you share resources and data to get your work done Bandwidth Networks transmit data using the information “Roads” and “highways.” Smaller roads carry less information than the larger highways. Bandwidth is the common term used to describe information carrying capacity. Broadband refers to high-capacity channels (like the superhighways.) Narrowband refers to slower channels with less capability such as dial-up (like the back roads.) Networks can also be described by their geographical area PAN Personal Area Network • PAN refers to the networking of personal digital devices within a range of about 30 feet. For example, a PAN can transmit data wirelessly from a notebook computer to a media player. LAN Local Area Network • A local area network (LAN) connects computers and devices in a limited area, such as a home, an office building, an office complex, or a school • Each computer or device on the network is called a node • Networks help companies save money by facilitating resource sharing. NAN Neighborhood Area Network • A NAN provides connectivity within a limited geographical area, such as in a city’s downtown area. MAN Metropolitan Area Network • A MAN is a public high-speed network capable of voice and data transmission within a range of about 50 miles. • Examples of MANs include local ISPs, cable television companies, and local telephone companies. WAN Wide Area Network • A WAN covers a large geographical area and typically consists of smaller networks, which might use different computer platforms and network technologies. • Networks for nationwide banks and large retailers are classified as WANs. Other Types of Computer Networks • Intranet • An organizations restricted computer network • Private, yet using WWW software • Extranet • Part of a organization‘s intranet that is extended to users • outside the organization – usually via WWW. Customer access • VPNs • A virtual private network (VPN) is a private, secure path across a public network that allows authorized users secure access to the company network. What is the Internet? • Internet • A worldwide computer network using TCP/IP protocol to transmit and exchange data. • (TCP/IP is a set of communication protocols used by networks.) Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. • The Internet is a worldwide system of computer networks - a network of networks in which users at any one computer can, if they have permission, get information from any other computer. World Wide Web • The web consists of Web pages and documents connected through links that include text, graphics, sound, and video. E-commerce • E-commerce refers to buying and selling products using the Internet. Net Neutrality • The idea that every Web site SHOULD have the same value or priority as other Web sites. Net neutrality supports the Internet’s core principle that its networks should be neutral. Computer Networks – Benefits • Simultaneous Access • • Software/Programs Data • Device Sharing • • Printers NAS – Network Access Storage • Communication • • Email VOIP – Voice over internet protocol (Skype) • Archiving • Backups of multiple clients by a single server • This is a huge benefit, saving time and effort