The Heart
advertisement

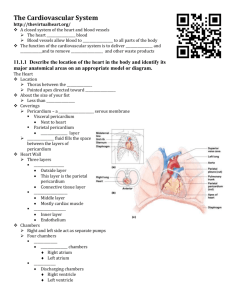
The Heart SBI 3U Ms. Raper The Heart • Is a pump • Actually it is TWO pumps • One pump deals with blood to the lungs, the other pump deals with blood to the body. • Heart is made of Cardiac Muscle • The two sides are separated by a thick wall of muscle called the SEPTUM • The blood for the two pumps is kept separate in mammals. Fetal Heart circulation • Because the fetus is not using its lungs, the blood is “shunted” between the right and left atria through a hole called the foramen ovale. This usually closes shortly before birth. • Babies who do not have the foramen ovale closed are born with a “hole in the heart” This diagram shows the path taken by the blood through the heart. Use the following link to label the heart. http://www.bishopstopford.com/f aculties/science/arthur/Heart%2 0drag&drop.swf http://academic.kellogg.cc.mi.us/herbrandsonc/bio201_McKinley/table22-3_blood_flow_th.jpg Cardiac Muscle The synchronous beating of the cardiac muscles are controlled by bundles of nerves. http://learninglab.co.uk/headstart/ Structure of the Heart. • Four chambers, 2 upper called ATRIA 2 lower called VENTRICLES • The Right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava. • The Left side receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the Pulmonary veins Valves of the Heart • The atria and ventricles are separated by one way atrioventricular valves. • Between the right atria and right ventricle is the TRICUSPID valve • Between the left atria and left ventricle is the MITRAL valve. • SEMILUNAR valves are found at the base of the PULMONARY artery and AORTA. • The purpose of the valves is to prevent blood flowing backwards. • Leaking of these valves can result in a heart murmur Watch the heart valves at this link • http://www.wellesley.edu/Biology/Courses/111/HeartValves.MOV Cardiac Cycle - Heart Beat. • Phase 1 SYSTOLE – Contraction “Occurs when the Ventricles contract, closing the AV Valves and opening the SL Valves to pump blood into two major vessels leaving the heart.” • Phase 2 DIASTOLE – Relaxation “Occurs when the Ventricles relax, allowing the back pressure of the blood to closed SL Valves and opening AV valves.” (Mr. Johnson) http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/circulation.html http://www.biologymad.com/HeartExercise/HeartE3.gif http://academic.kellogg.cc.mi.us/herbrandsonc/bio201_McKinley/f22-11_cardiac_cycle_c.jpg Check out the following link. http://www.owensboro.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat2/notes/Notes5%20Cardiac%20Cycle.htm EKG - electrocardiogram • • • • • • • Records the electrical activity of the heart. S-A node generates an electrical impulse that spreads over the two atria causing them to contract. S-V node causes the ventricles to contract. P to Q represents the small electrical voltage increase due to depolarization when the atria contract. The large spike Q-S represents the contraction of the ventricles. As the ventricles recover, a small spike at T precedes the next firing of the S-A node Check this link http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookcircSYS.html Chemical Regulators of the Heart • Noradrenaline: increase in CO2 stimulates receptors in the blood vessels. The Medulla oblongata sends impulses to produce noradrenaline, this chemical causes the S-A node to fire more rapidly • Acetylcholine: increase in blood pressure causes receptors in the blood vessels to send the information to the medulla oblongata which in turn causes the release of acetylcholine. This chemical slows the firing of the S-A node. Other chemicals that affect the heart…. • • • • • Nicotine – increases heart rate Caffeine - increases heart rate Amphetamine – increases heart rate Cocaine – increased heart rate Anabolic steroids – increased blood pressure. • Barbiturates – slow pulse • Alcohol - decreases heart rate • http://www.nida.nih.gov/DrugPages/DrugsofAbuse.html Cardiac Output & Fitness • Like all muscles, the heart needs exercise • The volume of blood pumped out by the heart is known as the CARDIAC OUTPUT. • Factors that affect cardiac output are heart rate and stroke volume • Cardiac output = heart rate X stroke volume Average person data • • • • • Stroke volume = 70mL Heart rate = 70 beats/minute Cardiac cycle = 70mL X 70beats/min = 4900mL/min There is a correlation between heart health and fitness Relationship between stroke volume, heart rate & and cardiac output Individual Cardiac output Stroke Volume mL/beat Heart Rate Beats/min A 4900 70 70 B 4900 50 98 C 4900 140 35 D 9800 70 140 •C is exceptionally fit has a high stroke volume and maintain a low hear rate. •B is less fit •Regular cardiovascular exercise increases the resting stroke volume. •Fitness is measured by how quickly the heart rate returns to the resting rate before exercise began. http://www.owensboro.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat2/notes/Notes5%20cardiac_equations.htm Resources that you need to review • • • • • Text – Chapter 9 Mr. Johnson’s biology –chapter 46. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/circulation.html Professor Fajer – Circulation, Heart & Blood http://fajerpc.magnet.fsu.edu/Education/2010/20 10_INDEX.HTM • Online Biology Book: Circulation http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BI OBK/BioBookcircSYS.html Check out these • Biology animations: http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/index.html • Anatomy & Physiology II http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/ap2.html • Science animations: http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/animatio.htm • And especially http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/ap2int.htm • Check out the section on cardiovascular. • Anatomy of the Heart: http://www.owensboro.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat2/notes/No tes5%20Anatomy%20of%20the%20Heart.htm