Unit 4: Chapter 7
advertisement

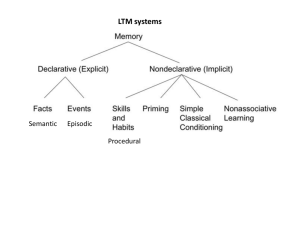
Unit 4: Chapter 7 Memory Warm Up 03/14 ● Do you remember what you had for breakfast? ● Do you remember what you had for breakfast 2 weeks ago? ● Explain why these two answers might differ. FIRE AND ICE Robert Frost Some say the world will end in fire, Some say ice. From what I’ve tasted of desire, I hold with those who favor fire. But if it had to perish twice, I think I know enough of hate To say that for destruction ice Is also great And would suffice. Acquainted with the Night - Robert Frost I have been one acquainted with the night. But not to call me back or say goodbye; I have walked out in rain -- and back in rain. And further still at an unearthly height, I have outwalked the furthest city light. A luminary clock against the sky I have looked down the saddest city lane. I have passed by the watchman on his beat And dropped my eyes, unwilling to explain. I have stood still and stopped the sound of feet When far away an interrupted cry Came over houses from another street, Proclaimed the time was neither wrong nor right. I have been one acquainted with the night. Three Kinds of Memory – indication that learning has persisted over time ● Three kinds of Memory ● Memory ◦ Episodic ◦ Semantic ◦ Implicit Three Kinds of Memory ● Episodic ◦ Memory of events ◦ Flashbulb memory – vivid memories where you generally remember exactly what happened like a photo ⚫The day JFK was shot ⚫September 11, 2001 Three Kinds of Memory ● Semantic ◦ Information that does not have a specific time stamp ⚫The alphabet ⚫George Washington ◦ Explicit Memory – specific information Three Kinds of Memory ● Implicit ◦ Skills or procedures ⚫Riding a bicycle ⚫Driving ◦ Not likely to be forgotten Processing your memories ●3 processes of memory ◦ Encoding ◦ Storage ◦ Retrieval Encoding ● Putting information into form easily stored ● Visual – mental pictures ● Acoustic – stores info as sequence of sounds ● Semantic – trying to make sense of the info ◦ Meaningful codes Storage ● Maintenance of encoded info over time ● Maintenance rehearsal – repeating info many times to keep from forgetting ● Elaborative rehearsal – relating new info to things you already know ● Organizational systems – meaningful grouping of info ◦ Can have errors Retrieval ● Recalling stored info ● Context-dependent memory - situation reminds you ● State-dependent memory – mood the memory was encoded in was recreated Chapter 7 Vocab ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● memory episodic memory flashbulb memory semantic memory explicit memory implicit memory encoding storage maintenance & elaborative rehearsal ● schemas ● recognition ● state- and contextdependent memories ● sensory memory ● iconic memory ● eidetic memory ● echoic memory ● primacy & recency effect ● chunking ● interference ● long-term memory ● relearning ● decay Memory Mural/Collage ● ● Either draw or cut out from magazines things that represent some of your most powerful memories. They can be happy or less than ◦ ◦ you are not presenting these, but you do have to explain what you included on the back of the mural/collage label as episodic, implicit, semantic Warm Up 03/17 ● Describe an episodic memory you have. ● Would this be considered a flashbulb memory? Read/Collage Warm - Up Review 03/18 1. 2. 3. How can we determine cause-andeffect relationships? (correlations, surveys, etc.) Which psychological perspectives deals primarily with groups of people? (ethnic groups) What type of psychologists studies how people change over their lifetimes? Activity ● ● Watch TED Memory Answer the following questions: a. b. c. What is a memory Palace? How is it used to improve memory? How could you use this technique in your life? Stages of Memory ●3 stages of Memory ◦ Sensory ◦ Short-term ◦ Long-term Sensory Memory ● Initial recording of info ◦ Based the senses and decays quickly memory – extremely short snapshots of events ● Eidetic imagery - longer iconic memory ● Echoic memory – sounds last longer in the sensory memory ● Iconic Short-term Memory ● Working memory ◦ Longer than sensory memory ◦ Still fades within minutes ● Primacy Effect – remembering the first items of a list better ● Recency Effect – being able to better remember the last few items of a list ● Chunking – long lists of data into smaller units ● Interference – new info takes the place of what is already there Long-term Memory ● Stored for long periods of time ● Less likely to decay ● Schemas – organization of information into knowledge Are you forgetting something? ● ●Amnesia ◦ infantile, anterograde, and retrograde ● Improving Memory ◦ make it meaningful to you! ◦ mnemonic device - ex. Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally – fabricated memories that you believe are real memories ● Confabulation Let me Tell you a story ● Once upon a time… Thinking…. ● Multiple intelligences ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Verbal/linguistic visual/spatial musical logical/mathematical interpersonal naturalistic body/kinesthetic intrapersonal Please Keep in Mind... ● ● ● ● You may also take this time to pick groups. We will be creating a children’s book for the next project. This will be based on language development. Please determine the following: ◦ ◦ Age group aspect of language you will be informing...look in the book Warm up 1. What is a memory of an event? 2. What is a memory of a skill? 3. What is a memory of information? Notebook Check 1. Warm ups 2. memory vocab 3. Quizzes from operant conditioning (don’t worry about actual grade just make sure it is there)