STUDY OUTLINE FOR EXAM 2
advertisement

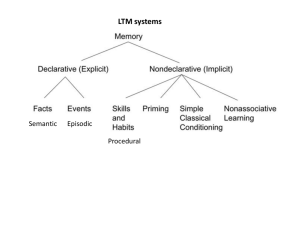
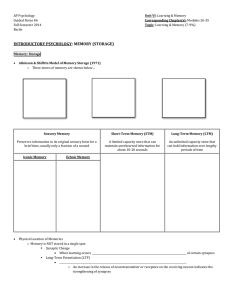
Exam 2 Study Outline SHORT-TERM MEMORY A. B. C. D. The cases of H.M., Clive Wearing, H.K., Shereshevskii Dualist Theories and Serial Position Curve Atkinson-Shiffrin Modal Model of Memory 3 Stages of Processing E. Capacity Issues 1) Memory span technique 2) Miller (1956) magic number + - 2 3) Brown-Peterson task F. Coding information into short-term memory 1) 2) 3) 4) Auditory code (Conrad experiment) Pronunciation rate Visual code (Posner letter matching experiment) Semantic code (PI and release from PI) G. Retrieval from working memory 1) Sternberg memory scanning task (3 possibilities for how scanning occurs) H. Baddeley’s model of working memory 1) 2) 3) 4) Phonological loop Visuospatial sketch pad Episodic buffer Central executive I. Cognitive neuroscience and working memory (pp. 156-158) 1) Cases of H.M. and K.F. LONG-TERM MEMORY A. Types of long-term memories 1) Episodic (characteristics) a. Autobiographical b. Flashbulb 1. National events (Brown & Kulik, Talarico & Rubin) a. Types of information remembered (Brown & Kulik) 2. Personal events (Rubin & Kozin, Conway) a. 4 types of events recalled the most c. Constructive Episodic Simulation Hypothesis 2) Semantic 3) Procedural 4) Schematized a. Restaurant script b. Repisodic memory problem 5) Memory for action a. 4 factors that can cause absentmindedness 6) Very Long Term Memory studies (Spanish, Cognitive class) B. Levels of processing model (Craik & Lockhart) 1) 3 levels of processing 2) 2 types of rehearsal processes C. Effects of context on encoding 1) Encoding specificity principle 2) Physical and mental context 3) Emotion and mood a. Memory for items varying in emotion (Pollyanna principle) b. Mood congruence c. Mood-dependent memory (match of mood at time of exposure and time of test) D. Implicit vs. explicit memory 1) implicit memory tasks 2) explicit memory tasks E. Models of memory 1) Tulving’s model 2) Squire’s model 3) PDP model F. Eyewitness Testimony 1) Loftus studies 2) “Misinformation Effect” 3) 3 factors affecting eyewitness testimony FORGETTING AND MNEMONICS A. Failure to encode, store, retrieve B. Retrograde vs. anterograde amnesia; Korsakoff’s, Alzheimer’s C. False Memories 1) Recovered-memory vs. false-memory perspective 2) False memory syndrome 3) Planting false memories (word lists, "lost in the mall") D. Mnemonics 1) Visual Imagery Techniques a. Method of Loci b. Pegword Method 2) Organizational Techniques a. b. c. d. e. Chunking Hierarchies and outlines Acronyms/Acrostics Rhymes and sayings Narrative technique 3) External memory aids, effects of practice, the multimodal approach REPRESENTATION OF KNOWLEDGE A. Declarative vs. Procedural knowledge; Natural vs. artifact concepts; semantic memory B. Feature Comparison Model (Smith et al.) 1. General characteristics 2. Defining vs. Characteristic Features 3. Sentence Verification Task (SVT) C. Prototype/Exemplar theory 1. Prototypes 2. Exemplars 3. Advantages/disadvantages D. Network Models 1. Collins Model a. General characteristics b. ISA and M links c. spreading activation 2. Anderson’s ACT Model a. General characteristics b. Propositions E. PDP/Connectionist Models 1. Characteristics 2. Spontaneous generalization + default assignment; graceful degradation 2. Advantages