Fertilization. Conception. Complications.
advertisement

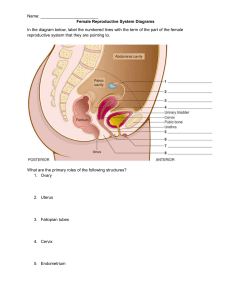
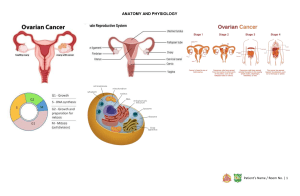
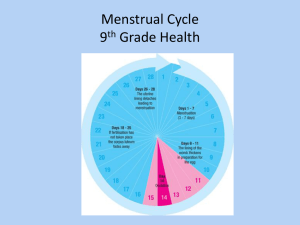
Fertilization. Conception. Complications. 4 Phases of the Menstrual Cycle Phase 4: Premenstural phase. Hormones used to thicken walls. If not fertilized shedding occurs and repeat process. Phase 1: Menstrual Phase. Shedding of the unused uterine lining from pregnancy/ fertilization not occurring. Flow is typically 5-7 days. After menstruation stops, preparation for reproduction begins again. Phase 2: Post Menstrual Phase. This is a resting stage since endometrium and uterine lining is thin. Low levels of estrogen and progesterone signal the pituitary to send large amounts of FSH to the ovaries that cause the one egg to mature. Phase 3: Intermenstrual phase: Ovaries Fromathis point on, till about release hormone estrogen that causes day 26 or 27 the ovum may endometrium to thicken. Matured egg accept the sperm in breaks from to the sac and leaves the ovary. introduced system, Thisresulting is called Ovulation pregnancy can now in pregnancy. occur by male sperms cells swim to fallopian tubes. Name: Hour: Phase 1: ____________ 4 Phases of the Menstrual Cycle Phase 2: ____________ Phase 3: ____________ Phase 4: ____________ STOP HERE!!! Work on book assignment….. Complication Terms: • Sometimes the system or process of reproduction can be flawed, or not work correctly. • When this happens conception is more difficult and may not occur. Breast Cancer • Abnormal growth of breast tissue. • #2 killer among women. • Detected by a lump in the breast. • Self- Exams should be done MONTHLY!! Circumcision: To cut off the foreskin of the penis. If not done, males have Higher risk and harmful effects of of STD’s , infections, and harder time in the ejaculation process. Video Time! • Routine Infant Circumcision Endometriosis • When the endometrium (lining of the uterus,) backs up into the fallopian tubes instead of being released outside the body. • Causes scare tissue and other complications. Estrogen • Hormone that develops many various female characteristics. Hernia • When part of the intestine protrudes down the canal into the scrotum. • It is caused by increased exterior pressure of the intestine against a weak spot in the abdominal wall. Joey’s Hernia https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZjpPJ4M-3-k Hysterectomy Surgical procedure in which the uterus is completely removed. Total Hysterectomy Surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. Radical Hysterectomy Surgical removal of the uterus, cervix, Ovaries, and Fallopian tubes. EVERYTHING IS TAKEN OUT!! PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome) • Condition that occurs 7-10days BEFFORE the menstrual period begins. • Symptoms include headaches, backaches, weight gain, breast tenderness, water retention, food cravings, fainting, and clumsiness. • Symptoms generally improved on with the onset of bleeding. Progesterone A hormone of the ovary that prepares the uterus to receive the fertilized ovum. Prostate Cancer • Abnormal cell growth in the prostate gland. • It can be slow or fast growing. • 1/3 of all men in their sixties have some slow growing cancerous cells in their prostate. Prostatitis Bacterial infection of the prostate Prostatotis • Undiagnosed penis pain that may be caused by a stressed urinary sphincter, muscle valve, or stress. • Sometimes it is aggravated by diet. Testosterone: • Male sex hormone made in the testicles. • It is responsible for puberty and sperm cell production. Tubal Ligation The tying or binding of the fallopian tubes as a methods of sterilization. Uterine or Cervical Cancer • • abnormal growth of cell in the uterus or cervix. Symptoms include: • Abnormal bleeding • Vaginal discharge • Or the appearance of a tumor. • Detected by PAP Smear and treated wit surgery or radiation. Vaginitis • Any vaginal infection or inflammation characterized by a change in vaginal discharge. • Examples • Yeast Infections • Monilia Infections Vasectomy • Male sterilization operation performed under local anesthesia. • It involves cutting the vas deferens. • Surgery can be reversed in half the cases.