BI11_LG_U13 - BC Learning Network
advertisement

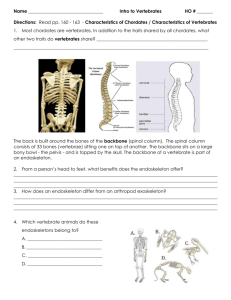
BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Unit 13 ~ Learning Guide Name: _______________ INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit test. Do your best and ask questions about anything that you don't understand BEFORE you write the unit test. 13.1 NOTES: CHORDATES General Characteristics of Phylum Chordata Although not the largest, Chordates are the most diverse phylum in the animal kingdom. Chordates have _____________________________ at some stage of the life cycle and have __________________________ made from an outgrowth of the digestive tube. All chordates are deuterosomes and the blastopore during embryonic development forms the anus. They show body segmentation and other characteristics present in the more advanced animals. In order to be classified as a chordate an animal must have the characteristics listed below. Although it may seem as if many chordates do not possess these characteristics, they do at some point during embryonic development. 1. Notochord __________________________ __________________________ _________________________. The function of the notochord is to provide support and protection to the nerve chord. In the higher chordates, the vertebrates, the notochord is present in embryonic development and __________________________ _______________________________________________________________. Page 1 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 2. Dorsal Tubular Nerve Chord The _________________________________________________ is exactly what its name suggests. The term dorsal means it is on the back side of the animal. The term tubular means it is hollow. It is the nerve chord of the animal. The hollow portion of the nerve chord is filled with fluid that nourishes the nerve cells. ___________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ _______________________________. 3. Pharyngeal Pouches ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________. In water-breathing animals the pharyngeal pouches become the gills or gill slits. In air- breathing animals the pharyngeal pouches take on a number of functions. None of the pharyngeal pouches are involved in respiration in humans. 4. Post Anal Tail The ______________________________________ is simply an extension of the nerve chord and body ___________________________________. There are three sub-phyla that will be discussed in the lessons to follow: 1. Subphylum Urochordata 2. Subphylum Cephalochordata 3. Subphylum Vertebrata Endoskeletons All of the chordates have an _______________________________________. The skeleton of chordates varies greatly from the ________________________________ _________________________________ to the ______________________________ ___________________________________ and the bony skeletons of humans. The endoskeleton possesses advantages and disadvantages to the previously studied exoskeleton of Arthropods. The endoskeleton doesn't provide the overall protection to the body that the exoskeleton does. Where protection of a certain internal organ is very important it is well protected by the endoskeleton. In humans, the skull, spine, and rib Page 2 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 cage would be examples of bones that are providing effective protection for organs like the brain, spinal cord and heart. The endoskeleton has a ________________________________________________ __________________________________________. Likely, the most important improvement over the exoskeleton is its _____________________________________. The exoskeleton must be periodically shed and regrown. This leaves the animal vulnerable for a short time while it is re-growing its exoskeleton and is also very costly in terms of energy. With the endoskeleton's ability to grow along with the animal, these animals can grow much larger and energy can be expended on the development of other organs. 13.1 PRACTICE: CHORDATES 1. In the diagram below, identify and label the 4 characteristics that are common to all chordates. (4 marks) Page 3 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 2. Members of Phylum Chordata have ______________________ symmetry and a _______________________ (which means they have a body cavity which is completely lined with mesoderm). (2 marks) 3. In Chordates the blastopore becomes the anus: a. Organisms that develop this way _________________________________. (1 mark) are termed b. Identify at least one other animal phylum, studied in Biology 11, that has a similar developmental pattern. (1 mark) 4. All chordates have an endoskeleton: a. Define endoskeleton. (1 mark) b. Explain two ways that an endoskeleton might provide a selective advantage over either lacking a skeleton altogether or over an exoskeleton. Remember to answer this question properly you must compare the exoskeleton to the alternatives. (2 marks) Page 4 of 30 13.2 NOTES: PROCHORDATES General Characteristics of Prochordates ____________________________________________________ ___________________________ are those animals in which ___________________________________________________ __________________________________ during development. The two subphyla of prochordate are the ________________________ (subphylum Cephalochordata; pictured top right) and the ____________________ (subphylum Urochordata; pictured bottom right). 1. Lancelets _________________________ (subphylum Cephalochordata) _______________ ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________. The ________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________. A lancelet is very mobile and powers its way through the water with muscles that use the notochord as a point of attachment. The tentacles around the mouth are for searching through mud for microscopic food particles that will filter out of the constant water stream that is moving through the animal. Page 5 of 30 PLEASE LABEL THE ANATOMY OF A LANCELET DIAGRAM BELOW BEFORE PROCEEDING ANY FURTHER! 2. Tunicates _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________. There are an estimated 2000 species of tunicates that are commonly called “Tunics” meaning tough covering. _______________________________________________ ___________________. Tunicates are hermaphrodites. The adult tunicate (subphylum Urochordata) looks more like an invertebrate than a chordate since the only retained trait from the larval stage are the gill slits. Tunicate larva possesses all of the chordate characteristics. The tadpolelike larvae is bilaterally symmetrical and free swimming which is ideal for the dispersal stage of the tunicate life cycle. __________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________. Page 6 of 30 The sessile tunicate will filter feeder by drawing in water thought its incurrent siphon and past the gill slits to filter out oxygen and food. The larvaceans (class Appendicularia) are a group of tunicates that remain in the larval form and do not become the sessile adult. ____________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________. 13.2 PRACTICE: PROCHORDATES 1. What is the defining characteristic of a prochordate? (1 mark) 2. The lancelet is considered the prototypical chordate. a. Define prototypical. (1 mark) b. Why is the lancelet considered the prototypical chordate? (1 mark) 3. It is difficult to recognize an adult tunicate as a chordate. a. Explain why. (1 mark) b. Explain why scientists classify it as chordate. (1 mark) Page 7 of 30 13.3 NOTES: VERTEBRATES Diversity of Vertebrates The anatomy and physiology of humans is the focus of Biology 12. For this reason, the study of the vertebrates in Biology 11 will be an introduction to the diversity of the classes within the phylum. The vertebrates are the animals that are more typically used to represent the chordate phylum. With ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ vertebrates are the most advanced of all organisms. Vertebrates are distinguished from other chordates by: 1. _____________________________________________________________ that surround and protect the dorsal nerve cord. The vertebrae form a vertebral column or spine. 2. A cranium or _____________________________________________________ 3. An _____________________________________________________________ Features of Vertebrates Vertebrates also have: 1. A living endoskeleton with vertebral column that can grow. 2. __________________________________________________ 3. Paired appendages. 4. Efficient respiration and excretion. 5. __________________________________________________ 6. Adapted to active lifestyles. Page 8 of 30 Proposed Vertebrate Lineages Fishes Vertebrates first appear in the fossil record ______________________________________. Today there are an estimated 45,000 species of vertebrates. More than 24,000 of these are fish species. _______________________________ ______________________: 1. _________________________________ _________________________________ 2. _________________________________ _________________________________ 3. _________________________________ ________________________________ General Characteristics of Fishes Fish have a stream-lined shape for to reduce drag with paired fins that allow movement left or right. Secretion of a mucus layer helps to reduce friction. Fish have an air bladder Page 9 of 30 which stores carbon dioxide to control their buoyancy in the water. Gills allow for gas exchange between the blood stream and water. Fish also have a lateral line or row of sensory structures along the side of the body that can detect vibrations in the water. 1. Jawless Fishes It is predicted that the ______________________ ________________________________________ since they are the most similar to the prochordates and are the oldest known vertebrate fossils. Jawless fishes have ____________________________________________ _____________________. They rely on external fertilization for reproduction. Examples of these fishes include the ___________________________________. Both of these fishes rely on symbiotic relationships. _______________________ are deep sea bottom dwellers named for their slimy coat. They take part in a commensalistic relationship as _______________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ___________________________________________. The circular rasping teeth of the lamprey attach to a fish. Rasping at the flesh of the host fish the lamprey will feed off of the blood. Lampreys are an exotic species introduced into the Great Lakes through the discharge of ballast tanks from ships. They devastated native fish populations in the 1970's and 1980's. 2. Cartilaginous Fishes The next group of fishes are the ____________ ______________________________________. This class includes sharks, skates and rays. ______________________________________ ______________________________________. The cartilaginous fishes are all marine and all are carnivorous except the whale shark. They have jaws, paired appendages, visceral arches, three semi-circular canals, paired nasal cavities, and placoid scales that feel like sandpaper, and a wellPage 10 of 30 developed sense of smell. As their name suggests they have an endoskeleton made entirely of cartilage. Other features include no swim bladder or lung, a heterocercal or asymmetrical tail, and respiration by means of five to seven pairs of gills with gill slits. These fish have separate sexes and utilize several reproductive strategies. Some species are oviparous (eggs hatch outside the body), others are ovovivparous (eggs hatch inside the body), and others are viviparous (young are cared forcompletely internally). ____________________ have very well developed senses that are used to locate prey. In fact, they actually have seven senses. The two extra senses are the ability to detect slight electric currents in water which could be caused by the muscle contractions of another animal and the ability to detect changes in pressure in water currents with their lateral line. Sharks have 6-20 rows of teeth that are continually being replaced and may use over 20,000 teeth in a lifetime. The paired pectoral fins in sharks are located just behind the head and jut out from the body like wings on a plane to provide lift when swimming. ______________________________________ have flattened bodies, paired wing like pectoral fins, and some species have a whip like tail. Rays have diamond shaped bodies while skates have triangular shaped bodies. Both are bottom dwellers and their flat shape and color camouflage them with the ocean floor. 3. Bony Fishes _____________________________________________ have a ________________________________________ _____________________________________. Bony fish are characterized by three key features; bone, lungs or swim bladder, and scales. The tail is usually homocercal or symmetrical on the top and bottom. They have skin with mucous glands and embedded dermal scales. The operculum, a bony plate that protects the gills, is found in bony fishes. Page 11 of 30 These are the fishes that we generally think of when we think of fish. From the fish that we eat to the ones we keep as pets in a fish tank. One of the most unique organs in the bony fishes is the swim bladder. This is a relatively large air sac within the fish that increases in size when the fish wants to go up and decreases in size when the fish wants to go down. Most of the bony fishes are ray-finned fish. However, a very important group of fish in terms of evolution are the lobe-finned fishes. __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ _________________________________. These fishes not only had fleshy appendages instead of flat fins, but they also had a lung that could be used for respiration. Lobe-finned fish were long thought to be extinct, but in 1938 a lobefinned fish called a coelacanth was caught off the coast of Madagascar. These are the only known living lobe-finned fish. Bony fish all have a very similar internal anatomy. The circulatory system consists of a ________________________________________ with separate arterial and venous systems and four aortic arches. The nervous system consists of a well-developed brain with well-developed olfactory and optic lobes. Most species are oviparous and fertilization is external. Life in the Water Scales found in fishes prevent diffusion through body tissues so gills are needed for gas exchange. In marine fish water is continually leaving the body by osmosis and ions are continually entering. To keep from dehydrating they must drink large amounts of water and produce a small amount of concentrated urine. Their gills are also adapted to lose salt. In freshwater fish water is continually entering the body of the fish by osmosis so they do not drink water and produce large amounts of dilute urine. Page 12 of 30 Amphibians Amphibians are the most primitive of the animals to possess true limbs and are tetrapods with four legs. Other features are _______________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________. Frogs, toads, newts and salamanders all undergo metamorphosis from a ___________ __________________________________________________________. Amphibians must lay their eggs in a place where they will hatch in water. Respiration occurs in the _____________________________________________________________________. Amphibian/vertebrate Adaptation to Land There are two hypotheses: 1. Aquatic vertebrates first moved onto land as shallow pools of water began drying up. This theory is no longer accepted. 2. More likely that ancestors of amphibians left the water to escape predation, competition and gain access to the abundance of resources on land. Characteristics of Early Amphibians Amphibians ___________________________________________________________. Four strong limbs developed from fins. The adaptations for living on land included sense organs for detecting scents and sound. 360-286 million years ago early amphibians split into two main evolutionary lines that led to modern amphibians and reptiles. Diversification of Amphibians Today there are an estimated 4,500 species of amphibians in three Orders. Modern amphibians share the five key characteristics of metamorphosis, __________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ Page 13 of 30 Amphibians – Order Anura The Order Anura includes frogs and toads. They are found worldwide except in polar climates. Frogs and toads live in a variety of habitats. The term “toad” is commonly used for any anuran that has rough bumpy skin. The term “frog” is commonly used when anurans have smooth moist skin. Frogs and toads spend part of their life in water (if not all). They are characterized by a body adapted for jumping and are carnivores (some have a sticky tongue). Many return to the water to reproduce where their eggs hatch into larvae called tadpoles. Amphibians – Order Urodela The Order Urodela includes salamanders that are characterized by elongated bodies, long tails, and moist skin. Most salamanders have four limbs and are aquatic and terrestrial. They are carnivores who are mainly active at night. Most of them live in North America and Central America. The Family Plethodontidae or ________________________________________ with more than 300 species is the largest group of salamanders. _____________________ ____________________________________________________________________ Page 14 of 30 ___________________. Fertilization is internal and they lay eggs in water (larval stage) or in moist land environments (no larval stage). Amphibians – Order Apoda The Order Apoda includes caecilian or legless amphibians as the name suggests. They resemble small snakes and are often blind. Caecilians are rarely seen and little is known about their ecology and behavior. Most of them burrow in soil and some are aquatic. All species have teeth and eat worms and other invertebrates that they detect using chemosensory tentacles on the side of their head. They can be found in Asia, Africa and South America. Reproduction in Amphibians The reproductive system of the male frog includes two bean shaped testes located near the kidneys. During the breeding season sperm develop in the testes and pass through the tubes to the kidneys and urinary ducts. During mating sperm leaves the body through the _________________________ opening. The reproductive system of the female frog includes a pair of large, lobed ovaries containing thousands of tiny immature eggs that lie near the kidneys. During the breeding season the eggs enlarge, mature and burst through the thin ovarian walls into the body cavity. Cilia move the egg forward into a funnel like opening of the oviducts. As eggs pass through the oviduct they are coated with jelly like material. The eggs exit through the cloaca to the external environment where fertilization occurs. Page 15 of 30 Amphibian Courtship and Fertilization In early spring frogs emerge from hibernation and migrate to ponds and slow moving streams. Males call to attract females and warn off other males. Each species has its own mating call. When a mating pair find each other, the male frog climbs onto the females back in an embrace called amplexus that may last for days. The female leases legs into the water and the male discharges sperm over them called direct external fertilization. Amphibian Metamorphosis Increasing levels of a hormone called thyroxine which circulates throughout the bloodstream stimulates metamorphosis. Within a few days of fertilization tadpoles emerge. They live off the yolk stored in their body. Tadpoles grows larger and develop three pairs of gills. Eventually the mouth opens and allows it to feed. A process of change called metamorphosis results in the legs growing and the tail and gills disappearing. The mouth broadens and develops teeth and jaws. The lungs then become functional. Amphibian Parental Care Parental care is common among amphibians. Eggs and larvae are vulnerable to predators so parental care increases the likelihood that offspring will survive. Most often the male remains with eggs to guard them. Darwin’s males take young into their mouth. Female gastric-brooding frogs swallow their eggs. Both appear to have become extinct!! Page 16 of 30 Reptiles Reptiles are ___________________________ ______________________________________ by the Permian period. Reptiles have a ______________________________________ that is keratinized and __________________ ___________________. They are usually tetrapods and have ______________________ _____________________________________. Reptiles have evolved to be completely terrestrial in many cases and are no longer dependent upon water for the laying of eggs. This is because of the ____________________ _____________________________. This egg is developed from _______________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________. Reptiles, fish and amphibians are cold blooded or ________________________. This does not mean that their blood is cold. The body temperature of an ectotherm is ____________________________________________________________. Therefore, ectothermic animals regulate their body temperature by regulating their surroundings. They will lie in the sun if it is cold out, and shade themselves if they are hot. Ectotherms must still regulate their body temperature in order for normal internal body functions to take place. The above right image above shows the American Alligator, Garter snake close up, Gopherus polyphemus, and the Collared Lizard. Birds Birds are __________________________________. Often referred to as __________________________________, birds and other endothermic animals regulate their body temperature internally. By maintaining a constant internal body temperature bodily functions occur at optimum levels of efficiency. This self-regulation is known as ______________________________. This is important for animals such as birds that require a Page 17 of 30 great deal of energy for flight. Birds also have other adaptations for flight such as ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________. Since we can see a bird’s beak, we can easily hypothesize what it might eat. We can watch birds catch, handle, and swallow different foods to test our hypotheses based on the shape of the bill. The sharp thin bill of herons and egrets spear fish. The hooked bills of hawks and owls grab and rip apart prey and the short conical bills of sparrows crack seeds. Flight is very efficient but requires a lot of energy. Flying birds have 5-20 times their resting metabolic rate while running mammals only have 2-4 times their resting metabolic rate. To produce the level of energy required for flight, birds have incredibly efficient and ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________. These systems allow both fast flight and long distance migration. In addition, ___________________________________________________________ _________________________ that greatly aid in flight. Page 18 of 30 __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ ________________________. Air passes through bird lungs ___________________ _____________ into posterior __________ __________________________________ ___________________ by a different route. As a result, there are two passes of air in each respiratory cycle and because of countercurrent flow the oxygen extraction is very high. Birds have a _______________ __________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________. This efficiency of respiration and circulation enables birds to fly over the Himalayans at the altitude of Mount Everest. Mammals Mammals are thought to have evolved during the Mesozoic Era from therapsids. The mammalian skull accommodates a larger brain relative to its body size and differentiated teeth. Mammals are characterized by having __________ _____________________________ __________________. Mammals have a high level of infant care, because the young are fed by means of the mammary glands. The adults must expend a lot of energy in the young, but it increases the chances of having successful offspring. This high-energy load on the mother means fewer offspring are produced. Mammals share other characteristics with birds. For example, efficient circulatory and respiratory systems, a ____________________________________ and being ______________________________ are characteristic shared by both. Page 19 of 30 Mammals are divided into three groups; 1. monotremes 2. marsupials 3. placental mammals 1. Monotremes The _________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________. They are different from the other mammals in that they ____________________________ __________________________ and have a cloaca. Interestingly, the platypus lacks a true stomach and digests its food in an enlarged area of the esophagus. 2. Marsupials Marsupials (like the wombat above) are found mainly in Australia, but some marsupials are found in South and Central America as well. The only marsupial living in North America is the opossum. These opossums, although not native to the area, are found as far north as Hornby Island, British Columbia. In Australia, marsupials have filled many of the niches held by placental mammals in the rest of the world. Marsupials spend comparatively less time with pregnancy and they are born very immature. Once born they enter a pouch on the mother. Fed by the mammary glands the newborn will remain in the pouch until mature. The vast majority of marsupial fossils have been found in Australia including those of a huge ten foot tall kangaroo ancestor. 3. Placental Mammals Due to the presence of the __________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________, a longer pregnancy is possible. Page 20 of 30 The increased gestation time allows more energy to be used for the development of the nervous system. As a result of this development, placental mammals have the largest brain to body weight ratio. Even after the lengthy pregnancy brain development continues under parental care. The larger brain has resulted in social development and communication in many mammals. Placental mammals are very widely distributed around the world and have members in almost every niche. Bats have taken to the air, whales to the water, and many examples exist on land. Placental mammals can be ___________________________________ _______________________________________. Major Orders of Placental Mammals include: Perissodactyla = Horses Artiodactyla = Deer Carnivora = Cats Primates = Monkeys Cetacea = Whales Chiroptera = Bats Rodentia = Mice Proboscidea = Elephants Lagomorpha = Rabbits 13.3 PRACTICE: VERTEBRATES 1. What three characteristics distinguish vertebrates from prochordates? (3 marks) 2. There are three main classes of fish, listed in proposed evolutionary order, they are: a. Class _____________________________ which include jawless fish such as the lamprey and _______________________. (2 marks) b. Class _____________________________ which includes cartilaginous fishes such as __________________, rays and skates. (2 marks) Page 21 of 30 c. Class _____________________________ which include bony fishes such as the ones we eat and keep as pets. (2 marks) 3. Lobe-finned fish from Class Osteichthyes are thought to be the evolutionary forerunner to __________________________. (1 mark) 4. Amphibians live both in water and on land. a. What features of their respiratory system make them well-adapted for such a life style? (3 marks) b. Using our current understanding of Darwin's theory of evolution, please explain how such adaptions likely came to be. (4 marks) Page 22 of 30 5. Reptiles are hypothesized to have evolved from ________________________ ancestors. (1 mark) 6. Reptiles lay leathery shelled amniotic eggs. a. Define amniotic egg. (1 mark) b. Identify two selective advantages associated with an amniotic egg. (2 marks) 7. Reptiles, fish and amphibians are ectothermic. a. Explain what ectothermic means (cold-blooded is not a sufficient or correct answer). (1 mark) b. How does being ectothermic impact an organism's behavior? (1 mark) Page 23 of 30 8. Birds and mammals are endothermic. a. Explain what endothermic means (warm-blooded is not a sufficient answer). (1 mark) b. What is the term for when an organism self-regulates its internal conditions such as temperature? (1 mark) 9. Identify and explain at least four adaptations that enable birds to meet and/or limit the metabolic demands of flight. (4 marks) Page 24 of 30 10. Mammals are characterized by having ___________ and __________________ _________________________ as well as having a larger _________________ relative to body size. (3 marks) 11. Three main groups of mammals include: a. The ______________________________ which include the duck-billed platypus and echidna and which are unique in that they lay hard-shelled amniotic eggs. (1 mark) b. The ______________________________ which include kangaroos, wombats and opossums which are all have pouches for rearing their young. (1 mark) c. The ____________________________________________ which include humans, bats and whales, all characterized by having a __________________________ that assists in exchange of nutrients between a mother and her developing fetus(es). (1 mark) ~ END OF BIOLOGY 11 UNIT 13 LEARNING GUIDE ~ Page 25 of 30 UNIT 13 ANSWER KEY 13.1 PRACTICE: CHORDATES 1. In the diagram below, identify and label the 4 characteristics that are common to all chordates. (4 marks) 2. Members of Phylum Chordata have ______________________ symmetry and a _______________________ (which means they have a body cavity which is completely lined with mesoderm). (2 marks) 3. In Chordates the blastopore becomes the anus: a. Organisms that develop this way are termed _________________________________. (1 mark) b. Identify at least one other animal phylum, studied in Biology 11, that has a similar developmental pattern. (1 mark) - Echinoderms Page 26 of 30 4. All chordates have an endoskeleton: a. Define endoskeleton. (1 mark) - internal skeleton b. Explain two ways that an endoskeleton might provide a selective advantage over either lacking a skeleton altogether or over an exoskeleton. Remember to answer this question properly you must compare the exoskeleton to the alternatives. (2 marks) - an endoskeleton is advantageous in many situations compared to no skeleton as it serves to protect organs and it acts as levers for muscles and movement - an endoskeleton is advantageous in many situations compared to an exoskeleton as it grows with the organism and thus, does not need to be shed such that the organism is periodically vulnerable and because it is lighter than an exoskeleton and thus, does not limit the potential size of an organism 13.2 PRACTICE: PROCHORDATES 1. What is the defining characteristic of a prochordate? (1 mark) - the notochord remains intact throughout development as opposed to being replaced with a vertebral column 2. The lancelet is considered the prototypical chordate. a. Define prototypical. (1 mark) - representing the original form after which all other related organisms are patterned b. Why is the lancelet considered the prototypical chordate? (1 mark) - the lancet is considered prototypical as it clearly displays all 4 characteristics of a chordate (notochord, dorsal tubular nerve cord, pharyngeal slits and post anal tail) throughout its entire life cycle - all other chordates go through an embryonic state that closely replicates the adult lancet form 3. It is difficult to recognize an adult tunicate as a chordate. a. Explain why. (1 mark) - as larva, tunicates clearly possess the 4 key characteristics of chordates but as the tunicate matures to adult stage these characteristics are no longer apparent Page 27 of 30 b. Explain why scientists classify it as chordate. (1 mark) - based on the fact that their larval stage has the four key characteristics of chordates 13.3 PRACTICE: VERTEBRATES 1. What three characteristics distinguish vertebrates from prochordates? (3 marks) - have vertebrate made of bone or cartilage that surround and protect the dorsal nerve cord - have a cranium (skull) to protect brain - have an endoskeleton of bone or cartilage 2. There are three main classes of fish, listed in proposed evolutionary order, they are: a. Class _____________________________ which include jawless fish such as the lamprey and _______________________. (2 marks) b. Class _____________________________ which includes cartilaginous fishes such as __________________, rays and skates. (2 marks) c. Class _____________________________ which include bony fishes such as the ones we eat and keep as pets. (2 mark 3. Lobe-finned fish from Class Osteichthyes are thought to be the evolutionary forerunner to __________________________. (1 mark) 4. Amphibians live both in water and on land. a. What features of their respiratory system make them well-adapted for such a life style? (3 marks) - can exchange gas via moist skin, gills and/or lungs enabling them to survive on both land and water b. Using our current understanding of Darwin's theory of evolution, please explain how such adaptions likely came to be. (4 marks) - As per previous answers to similar questions… o random variation (via mutation and genetic recombination) o if variation is beneficial it helps organism to survive natural selection o if organism survives natural selection and reproduces it passes on the random, beneficial variation Page 28 of 30 5. Reptiles are hypothesized to have evolved from ________________________ ancestors. (1 mark) 6. Reptiles lay leathery shelled amniotic eggs. a. Define amniotic egg. (1 mark) - Egg that is surrounded by amniotic fluid b. Identify two selective advantages associated with an amniotic egg. (2 marks) - allows embryo to develop on land independent of water and thus, opens up an entirely new niche for reptiles as compared to amphibians which must reproduce near or in water - allows embryo to be well-developed and relatively independent of water when hatched again opening up a new niche (dry land) 7. Reptiles, fish and amphibians are ectothermic. a. Explain what ectothermic means (cold-blooded is not a sufficient or correct answer). (1 mark) - Ectothermic = refers to animals whose body temperatures fluctuate with that of the surrounding environment…if in shade their body temperature lowers and if in sun their body temperature rises b. How does being ectothermic impact an organism's behavior? (1 mark) - metabolic rates are typically influenced by body temperature with warmer temperatures resulting in greater metabolic rates, ectothermic organisms will regulate their body temperature and thus, their metabolic rated by either seeking out cold or hot locations in their environment 8. Birds and mammals are endothermic. a. Explain what endothermic means (warm-blooded is not a sufficient answer). (1 mark) - Endothermic = refers to animals whose are able to internally regulate their body temperatures b. What is the term for when an organism self-regulates its internal conditions such as temperature? (1 mark) - homeostasis Page 29 of 30 9. Identify and explain at least four adaptations that enable birds to meet and/or limit the metabolic demands of flight. (4 marks) - light, hollow bones = less energy required - efficient circulatory system = rabid delivery of O2 to and removal of CO2 from muscles - efficient respiratory system allows for continual flow of oxygenated air through the system - feathers to maximize lift - strong muscles 10. Mammals are characterized by having ___________ and __________________ _________________________ as well as having a larger _________________ relative to body size. (3 marks) 11. Three main groups of mammals include: a. The ______________________________ which include the duck-billed platypus and echidna and which are unique in that they lay hard-shelled amniotic eggs. (1 mark) b. The ______________________________ which include kangaroos, wombats and opossums which are all have pouches for rearing their young. (1 mark) c. The ____________________________________________ which include humans, bats and whales, all characterized by having a __________________________ that assists in exchange of nutrients between a mother and her developing fetus(es). (1 mark) Page 30 of 30