Vertebrates
advertisement

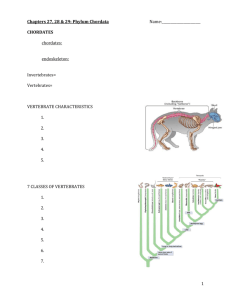
• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • What features the vertebrates? Four features define chordates – – – – A notochord A dorsal hollow nerve cord A pharynx with gill slits A tail extending past the anus All features form in embryos – May or may not persist in adults Invertebrate chordates Ancestors Tunicates and lancelets (marine filter-feeders) Adult and larva Craniates Another ancestor Chordates with a braincase of cartilage or bone – Hagfish (jawless fish): Simplest modern craniate Vertebrate evolution Key innovations laid the foundation for adaptive radiations of vertebrates – – – – Vertebral column of cartilaginous or bony segments Jaws evolved in predatory fishes Gills evolved in water, then lungs for dry land Paired fins were a starting point for other limbs Jawed fishes Jawed fishes – – Cartilaginous fishes (sharks and rays) Bony fishes Gills present • • • • • • • • • • • • • – Not free Body plans adapted to life in water – – Streamlined shape reduces drag Swim bladder (in bony fishes) adjusts buoyancy Bony fishes The most diverse vertebrates – – – Lungfishes Lobe-finned fishes (coelacanth) Ray-finned fishes Amphibians Frogs, toads, and salamanders – – – – Carnivorous vertebrates First to evolve from aquatic Devonian tetrapods Adapted to life on land (lungs, 3-chambered heart) Nearly all return to the water to reproduce Vanishing amphibians Many amphibians now face extinction due to pollution and habitat loss Amniotes First vertebrates able to complete their life cycle on dry land – – – Water-conserving skin and kidneys Amniote eggs (four membranes) Active life-styles Some amniote groups Sauropsids – Reptiles (including extinct dinosaurs) and birds Anapsids – Turtles Synapsids • • • • • • • • • • • • • • – Modern mammals and mammal-like species Modern reptiles Major Groups – – – – – Turtles (shell attached to skeleton) Lizards (the most diverse reptiles) Snakes (limbless) Tuataras (some amphibian-like traits; third eye) Crocodilians (closest relatives of birds) Reptile characteristics General characteristics – – – – Live on land or in water Cold-blooded Have a cloaca (opening for wastes and reproduction) Eggs are fertilized in the body, usually laid on land Birds Birds are the only modern animals with feathers Birds are warm-blooded amniotes Adaptations for flight and migration Feathers, lightweight bones, and highly efficient respiratory and circulatory systems Mammals Animals with hair, females that nourish young with milk from mammary glands, a single lower jawbone and four kinds of teeth Modern mammals Three major lineages – – – Egg-laying mammals (monotremes) Pouched mammals (marsupials) Placental mammals (eutherians), the most diverse and widespread mammals • • Primate evolution Key trends – – – – – – Better daytime vision Upright walking (bipedalism) More refined hand movements Smaller teeth Bigger brains Social complexity (extended parental care; culture evolved in some lineages)