CScope Academic Voc. Drama 1
advertisement

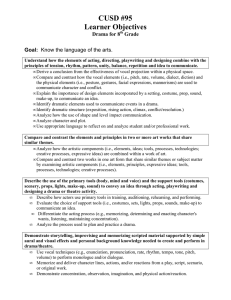
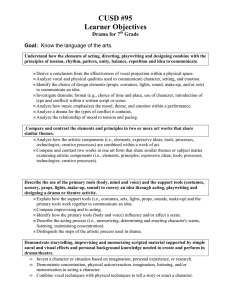
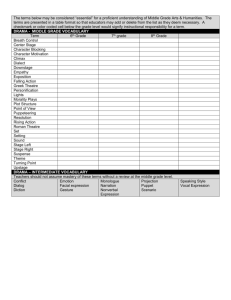
CScope Key Academic Vocabulary DRAMA a story told in front of an audience PLAYWRIGHT the author of a play THEATER where a play takes place Three types of Drama Elements Literary Technical Performance Literary Elements Script Plot Character Story organization Setting Dialogue Monologue Conflict script the written words and directions of a play acts the units of action scenes parts of the acts plot the storyline or arrangement of action character a person portrayed in a drama story organization the storyline or arrangement of action – beginning, middle, and end setting where the action takes place Dramatic Speech dialogue – conversation between or among characters Dramatic Speech monologue – long speech by one single character (private thoughts) conflict The internal or external struggle between opposing forces, ideas, or interests that create dramatic tension (man/man, man/nature, man/self) Technical Elements Scenery Costumes Props Sound and Music Make-up set/scenery theatrical equipment on the stage that shows time/place (curtains, backdrops, platforms, etc…) stage directions found in brackets describe scenery and how characters speak C, center stage L, stage left R, stage right U, upstage or rear D, downstage or front props small movable items that the actors use to make actions look real sound and music sound- the effects an audience hears during a show music – songs you hear during a show make-up the use of costumes, wigs and body paint to transform an actor into a character Performance Elements (What do the actors do on the stage to make a character come alive?) Acting Speaking Non-verbal expression acting how speaking and moving help to create characters speaking vocal expression, projection, speaking style and diction non-verbal expression includes gestures, facial expressions, and movement