BMed TBI & Degenerative Conditions
advertisement

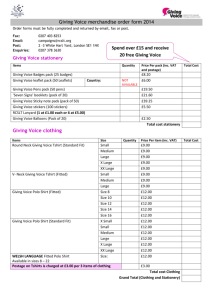
TBI & Degenerative Conditions Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c-W_o-pMDXQ TBI • TBI affects 186,000 people per year (Headway 2009) • TBI can affect all areas of life • TBI can affect: learning ability, attention, memory, language, voice, fluency, speech and swallowing • Cognitive-communication disorders: cognitive difficulties and their effect on language processing, language use and communication behaviour (RCSLT, 2006) • TBI can greatly impact on an individuals social communication and therefore effect relationships ‘Don’t cut me out!’ • Access to vital support services is being reduced due to funding cuts • “…making it harder for brain injury survivors to access the help and support they need...lead independent lives ”. Communications Manager at Headway SLT value • Early assessment in the acute setting to enable early identification of intervention for communication and swallowing needs • Goal orientated rehabilitation by a coordinated interdisciplinary team • Well planned and flexible discharge to community living to improve longer term outcome and self management (RCSLT, 2006) The National Service Framework for long term neurological conditions. (March, 2005) • To improve the treatment and long term support of people with neurological conditions by 2015. • 11 quality standards - health and social care • • • • 3 qualities most relevant to individuals with TBI (Headway) - person-centred service - community rehabilitation and support - supporting families and carers Dementia • Approximately 800,000 people are diagnosed with the condition today • Prediction: - increase to 1 million by 2021 - 1.7 million by 2051 1 in 25 over 65 1 in 6 over 80 Only 43% receive diagnosis (Alzheimer’s Society 2014) Dementia • http://www.telegraph.co.uk/health/10511920/A-cure-fordementia-could-be-found-within-twelve-years-DavidCameron-has-said.html Dementia 80% of people living in care homes have a form of dementia (Alzheimer’s Society 2013) Global action – there is “no solution to the dementia crisis without research” (G8 summit) Carers are vitally important (NICE) – funding is needed to adapt care homes, train carers and adapt wards to be facilitating communication (Defeating dementia campaign) Communication is key • For individuals to maintain a quality of life – communication is important • The RCSLT Dementia Campaign: • Early intervention to monitor changes over time • Help relatives and carers communicate with individuals with dementia more successfully and for longer • Funding will allow training days to be set up to train individuals in communication strategies • Feeding assessments – allow them to keep their independence concerning eating and drinking Parkinson’s Disease • 1 in 500 people suffer with Parkinson’s disease • 127,000 currently have Parkinson’s in the UK • Stem cell research – working towards a cure – new funding March 2014 (Britain and Israel) • Palliative care needed at all phases of the condition (Parkinson’s UK 2013) • 90% of individuals with diagnosed Parkinson’s experience dissatisfaction with how they communicate (Miller, et al, 2010) Parkinson’s Disease • Lee Silverman Voice Therapy has been shown to be effective in improving communication in individuals with the condition • The majority of individuals with Parkinson’s found SLT had a positive effect, helping breathing, speech rate, loudness and confidence, as well as strategies to help swallowing (Miller, et al, 2010) Motor Neurone Disease • Majority of people aged 50-70 years • Incidence – 2 people in every 100, 000 • Prevalence – 7 people in every 100,000 (MNDA 2014) • Incidence of motor neurone disease is increasing as people live longer and more accurate diagnosis • No cure – manage symptoms to improve quality of life Motor neurone disease • Standards of care developed by MND association – work together to maintain these standards • MND Year of Care Pathway to help the NHS and Social Services improve the provision of services for people with MND • SLT input – dysphagia and dysarthria – important for individuals to still be able to communicate with friends and family (Resource manual for commissioning and planning services for SLCN– dysarthria, RCSLT 2009) Multiple Sclerosis (MS) • 20-50 years old • Incidence: 4 per 100,000 (MS Society 2006, cited in RCSLT 2006) • Prevalence: 144 per 100,000 (MS Society 2006, cited in RCSLT 2006 ) MS Challenges as an organisation and SLT clinician • variable condition: Relapse/ remission Slow progressive increase in symptoms. • Prognosis unpredictable • SLT role in rehabilitation (NSF) A case for speech and language therapy and MS • ‘Key element of successful home care’ (The National Service Framework for Long-term Conditions, 2005. Department of Health) Recommendations (NICE Guidelines on MS): • Dysphagia • Communication: Dysarthria AAC Advice and training for circle of support LOCAL IMPLEMENTATION POINTS: • which speech and language therapist should see people with dysarthria • who may assess for and recommend augmentative equipment and adaptive technology to • communication • funding arrangements for augmentative aids to communication (AACs). We need your funding!! Useful links • https://www.headway.org.uk/home.aspx • https://www.headway.org.uk/news/dont-cut-me-out.aspx • https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/qualitystandards-for-supporting-people-with-long-term-conditions • http://www.alzheimers.org.uk/ • http://www.rcslt.org/governments/docs/dementiacampaign_ bulletinmay2013 • http://www.mssociety.org.uk/sites/default/files/Documents/ Governance%20docs/Misc%20resources/Annual%20report%2 0and%20accounts%202006.pdf • http://www.rcslt.org/docs/freepub/TBI_reading_list_Feb_07__2_.pdf • http://www.nice.org.uk/ References • Miller, N., Noble, E., Jones, D., Deane, K. H. O., Gibb, C. (2010). Survey of speech and language therapy provision for people with Parkinson’s disease in the United Kingdom: patients’ and carers’ perspectives. International Journal of Language and Communication Disorders, Online 23 June 2010 • Motor neurone disease association (2014). Brief guide to MND. Retrieved March 17th, from http://www.mndassociation.org/what-ismnd/Brief+guide+to+MND.htm • Parkinson’s UK (2013). NICE guidelines for Parkinson’s. Retrieved March, 12, 2014, from http://www.parkinsons.org.uk/content/nice-guideline-parkinsons • RCSLT (2006). Communicating quality 3. London: RCSLT. • RCSLT (2009). RCSLT resource manual for commissioning and planning services for SLCN; dysarthria. Retrieved 14th March, 2014, from http://www.rcslt.org/speech_and_language_therapy/commissioning/dysarthria _plus_intro • RCSLT (2009). RCSLT resource manual for commissioning and planning services for SLCN; TBI. http://www.rcslt.org/speech_and_language_therapy/commissioning/brain_injur y_intro • http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/live/14355/66330/66330.pdf