KPMG Talkbook template

Governance, Risk &
Compliance (GRC) –
Vendor Landscape and
Implementation
Considerations
Sean Winekauf – Director
Enterprise Risk Management &
Governance, Risk & Compliance, KPMG
04/07/15
Agenda
• What is GRC?
• GRC Marketplace today
• GRC Software Vendors
• Why GRC?
• Areas of Organizations that benefit from integrated GRC
• Tangible and intangible benefits
• Roles of technology
• Technology selection – do’s and dont’ s
• Closer look at Internal Audit
• Lessons learned
• How KPMG is helping clients
• Q&A
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
1
What is GRC ?
“
An approach to align the organization’s governance, risk and compliance processes to its strategy, allowing for convergence and transparency of information to drive performance and resilience in a dynamic economic business environment.
KPMG’s Definition
”
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
2
What is going on in the GRC Software Market?
Software GRC Market Outlook
• Software GRC market is expected to grow from: 2014
~
$34.5B
Source: IDC
2010
$19.3B
CAGR:
~16%
54 % of compliance officers at public companies expect a spending increase in compliance and ethics in 2014
Source: Thomson Reuters
• GRC market growth will accelerate as regulations and technology environments grow more complex
Software GRC Growth
$60,0
$50,0
$40,0
$30,0
$20,0
$10,0
$19,4
$23,0
CAGR:
~16%
$27,8
$32,1
$34,5
$0,0
2010 2011 2012
GRC Market Size ($B)
2013 2014
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
“
$2B + in additional expenses in our overall control effort will have been made since 2012 through the end of 2014”
Jamie Dimon
Chairman and CEO
J.P. Morgan Chase & Co.
• 2014 Annual Letter to
Shareholders
Source: Competitive Enterprise Institute, Thomson Reuters.
3
Current GRC Spend – Survey results
Annual Cost of Federal Regulation
Over the next 12 months
67% o f compliance professionals expect the compliance team budget to be more than today 67%
The estimated compliance and economic cost burden of federal regulation and oversight in 2012
$1.8T
2013 Compliance Executive Survey Results
800 compliance practitioners, including heads of compliance and chief executives, were surveyed:
6%
Less than Today
2%
Same as Today More than Today
27%
18%
Over the next 12 months
80% o f compliance professionals expect the regulatory focus on managing regulatory risk to be more than today
80%
3%
67%
30%
Over the next 12 months
67% of compliance professionals expect the cost of senior compliance staff to be to be more than today
Source: Competitive Enterprise Institute, Thomson Reuters.
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
4
GRC – What we are seeing in the Marketplace today
• Increased regulations and a more rigorous compliance environment
• Siloed approaches in responding to these requirements leading to duplication of functions and multi-layered Governance, Risk and Compliance processes
• Board executives and senior management struggling to see the value generated by these activities and view them as cost of doing business rather than an investment to improve corporate performance
–
–
–
Company Characteristics
– Are relatively large in terms of employees or revenues
Have multiple divisions/SBUs
Present in highly-regulated industries or markets
Have acquired or are in the process of acquiring businesses within or across regions
–
–
Are present in several regions/countries and therefore need to comply with regulations across all the regions
Do not have a clear owner for GRC across the firm
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
5
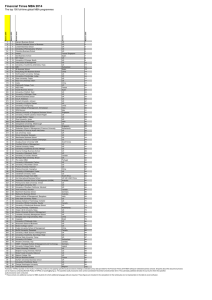
GRC Software Vendors
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Forester Wave 2014
6
Why GRC?
Increases accountability for risks, controls, and issues
Automation of
Control Testing workflow
Consolidated and real-time reporting of cross-functional risks and issues
Automation of 302
Certification
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Single view of controls across the organization
7
What drives Corporate Directions in Governance, Risk and Compliance?
Increasing regulatory requirements have resulted in complex business and risk management processes
Internal
Internal
External
External
Reporting &
Disclosure process
Oversight functions and analysis
Business
Units
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
8
Why GRC? >> What does a GRC enabled Organization look like?
Legal Entities
Geographical Regions
Legal Entities
Geographical Regions
Business and
Controls
ERM Compliance
Internal
Audit
Other
Assurance
Groups
Board/
Committees
Business and Risk Management Information
Internal
Executive/
Senior
Management
Stakeholders
External
Auditor Regulator
Rating
Agency
Desired
State eGRC Foundation Transformation
CONTROL
REPORTS
QUARTERLY
DEFICIENCY
SOX
REPORTING
ERM
REPORTS
COMPLIANCE
REPORTS
FIRM
QUARTERLY
ASSESSMENT
CRMP
AUDIT
REPORTS
ISSUE
MANAGEMENT
REPORTS
AUDIT PLAN OPEN ISSUES
AUDIT
COMMITTEE
EXTERNAL AUDIT
REPORT
PAST DUE
ISSUES
CLOSED ISSUES
Board/
Committees
Business and Risk Management Information
Internal
Executive/
Senior
Management
Stakeholders
External
Auditor Regulator
Rating
Agency
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
9
What areas of an Organization can benefit from an integrated GRC program?
SOX
• Control Testing
(test of design, test of operating effectiveness)
• Control test scheduling
• Link controls to risks, control objective, assertion
• 302 certification survey
• Testing documentation storage
• Deficiency Management
Compliance
• Compliance Test Scheduling
• Compliance Risk Assessment
• Control testing
(test of design, test of operating effectiveness)
• Management of policies
• Exception / Issue Management
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Internal Audit
• Annual Audit Planning
• Audit Planning & Risk Assessment
• Audit Resource & Scheduling Management
• Audit fieldwork execution
(Controls Test of Design,
Test of Operating Effectiveness)
• Audit Reporting
• Audit Finding Remediation Management
Risk / ERM
• Risk Assessment
• Risk Scoring
• Risk Reporting and Dashboards
• Storage of risk data
10
Benefits of an Enterprise GRC Program
Across the marketplace, we see Enterprise GRC initiatives enable companies to more effectively manage risk and compliance activities in an aligned manner. Establishing a common language and converging multiple, independent risk and compliance initiatives into an integrated approach can result in many intangible and tangible benefits. We have highlighted some benefits below:
Benefits:
Improved Gap
Detection and
Mitigation
Reduced
Operating Risk
Reduced Risk of Penalties,
Fines Due to
Noncompliance
eGRC
Convergence
Improved
Reporting
Reduced Risk
Assessment
Effort
Rationalized IT
Systems and
Support
Reduced
Compliance
Effort
Optimized
Business
Processes
Automated
Security Controls
Monitoring
Potential reduction in overall risk and compliance management effort due to integrated eGRC activities
– Dashboarding providing executives their risk profile across value chain and risk category
Improved gap detection and mitigation through automation of remediation plans and deficiency analysis
Efficiencies as a result of automation of eGRC activities
–
–
Scoping at the account level creating a linkage between account and control
Testing workflow
– 302 Automation
Business process controls optimization due to integration and automation
Increased accountability helping embed risk management into BAU activities instead of making it a check the box exercise.
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
11
How does Technology enable an integrated GRC program?
•
Move away from those old spreadsheets
•
Have the necessary information be pushed to you
•
Technology facilitates dynamic GRC connections
•
Empower the broader GRC community with proactive insight
GRC TECHNOLOGY
REGULATORY & LEGAL INSIGHT
• Regulatory News and Analysis,
Legal and Business Research
INTERNAL ASSURANCE
• Internal Audit, Risk Management,
Internal Controls, Policy
Management
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
• Regulatory Disclosure, ICFR
Certification, Board Management
SCOPE OF GRC SOLUTION SETS
• Business Law
Solutions
• Board Solutions
• Disclosure
Solutions
• Due Diligence
Solutions
• Regulatory
Intelligence
Solutions
• Training Solutions
• Screening Solutions
• Policy Management
Solutions
• Internal Audit
Solutions
• Risk Management
Solutions
• Internal Controls
Solutions
• Enterprise GRC
Solutions
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
12
What to look for when selecting a GRC tool
Allow sufficient time for the process
Look to the future as well as the past
Understand the business needs and relevant requirements before judging the quality of competing package solutions
Consider the relative priorities and importance of the different aspects, in particular, which ones are critical to the success of the chosen solution
Avoid selecting individual departmental solutions
Narrow down the number of suppliers to evaluate in detail
Put in writing the organization's needs and requirements so that the package supplier is obliged to state (in writing) whether and how the package can meet those needs
Seek independent views from users of the packaged solutions
Balance the size of the solution with the size of the problem, i.e., accept minor shortcomings if the organization can achieve better overall business benefits
Bear in mind the supplier is potentially going to be a permanent partner in the business solution
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
13
Cautions and pitfalls of GRC tool selection process
Window shop, selecting a package based on recommendation or looks alone
Send large Requests for Proposal to every possible supplier – instead use simple, key criteria to identify the most probable candidates
Class everything as ‘mandatory’
Just ask the salesman if the requirements can be met
Let different team members follow different packages
– there will be inconsistencies
Rely upon the supplier to identify references
Just go to the supplier’s standard demonstration
Automatically take the highest scoring solution
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
14
Audit Lifecycle: Key Internal Audit Areas
KPMG views these as key areas across industries in the
Internal Audit
Lifecycle
Resource
Management
Time
Management
Audit
Universe
Board Reporting and Quality Metrics
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
15
Setting your Internal Audit Foundation Using GRC Concepts
•Perform a Risk Assessment, that aligns with ERM and the Company’s strategic objectives (ensure in-line with 1 st
2 nd lines of defense) and
•Consider building out a Continuous Risk
Assessment Program to gain efficiencies and increase scope of coverage
•Use of a single Risk Taxonomy throughout the Company
•Position Internal Audit to focus on the riskiest areas and add the greatest amount of value to the Company
Risk Profile
Governance,
Infrastructure and
Organization
•Develop an Internal Audit Methodology and Audit Approach (i.e. end to end process reviews) tailored to the needs of the Company
•Determine a governance structure and set up lines of communication to Senior
Leadership, and Audit Committee including escalation procedures
•Consider Efficient Audit techniques (i.e.
Data Analytics and KPI’s)
•Consider use of technology to automate and streamline the Audit process (i.e.
GRC systems)
•Understand and leverage monitoring/testing/assurance activities within the 1 st and 2 nd lines of defense
•Align testing efforts with the 2 nd line of defense to avoid duplicate efforts and gain efficiencies
•Integrate reporting with 2 nd line of defense to Senior Leadership, Board of
Directors and Audit Committee
•Develop an Issue Resolution Tracking process to ensure findings are remediated timely.
Enterprise
Assurance
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Culture
•Develop Internal Audit’s mandate to meet stakeholder expectation and position IA to be a value added function
•Set and communicate expectations (i.e. timelines and responsibilities) with
Management early in the process
•Maintain lines of communication throughout the life cycle of the audit process to keep Management engaged and aware of progress.
16
GRC, Internal Audit and Enterprise Assurance
GRC
FOUNDATIONAL
ELEMENTS
Understanding of and
Alignment with other assurance efforts
SOX, Compliance,
Quality, Safety,
Environmental Groups
RISK-BASED
INTERNAL AUDIT
METHODOLOGY
What should we focus our audit efforts on?
Risk Assessment &
Internal Audit Plan
How do we keep Risk Info
Current?
Risk Assessment Risk Evaluation
Risk Qualification
& Measurement
Data Collection
Advanced
Analytics
Reporting
Risk Definition and
Taxonomy
Prioritization Criteria review for CRA
Metric Analysis and Selection
Gather and Analyze
Information
Automated Analysis
KPI / KRI
Risk Identification
Detailed Risk Review /
SAR Comparison
Risk Appetite and
Tolerance
Data Transfer
Evaluate, Interpret and Report results
Updates
Input/Refresh IA
Plan
Risk Assessment and Prioritization Top Risk Selection
Linkage to
Strategic
Objectives
Review Assurance
Mapping
What approach or techniques should we use to audit?
Value Add Insights Stakeholder
Requirements
Continous Risk
Assessment
Value Added
Specialists &
End-to-end process reviews
Performance
Audits
How do I enable efficient workflow, data storage and
Risk Assessment, Audit workflow, data repository and reporting
Data analytics, continuous auditing & monitoring
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
17
Some Key Questions to consider when selecting an Internal Audit tool
Internal
Audit Point
Solutions
Business Process Adaptation: Does the tool support YOUR business processes. What is the level of configuration and customization that is going to be required?
Flexibility : How flexible is the tool to meet your needs. Conversely , how flexible are your processes to adapt to tool limitations?
The Vision: Does your long term vision look at process efficiencies, integration, cost effectiveness and a horizontal view of risk across the
Organization?
Time to Implement: What is driving the timeline for implementation?
Strategic initiatives, Regulatory requirements, expired licenses for current tools?
Cost: What are the budget constraints given the short term and long term vision for implementation of the tool
GRC
Key Point: Consider an Internal Audit software tool that allows for integration with technology that supports other risk and compliance functions within your organization to support a long term vision of a horizontal view risk across your Organization
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
18
Internal Audit Tools - Key Considerations and Benefits
Functions Key Considerations for Internal Audit Technology
Enterprise Wide
Foundational
Elements /
Core Data
Audit Universe and
Risk Assessment
Audit Planning
Support of common structure and language for: Organizational Structure,
Process Hierarchy, Risk Hierarchy, Control Hierarchy, Issue Classifications
Ability to capture and standardize criteria for risk assessments, audit planning (annual, audits and special projects) and creation of key documentation
Supports individual audit risk assessment, planning tools (identification of risks and controls), definition of scope/objective of audit, meetings and capturing planning approvals.
Audit Execution
Audit Reporting
Assignment of audit procedures, testing and documentation of controls, walkthroughs, storage of testing evidence, review/approval process and issue identification.
Generate status reports (including graphical representation) on a variety of topics/criteria.
Benefits
Horizontal view of risks and issues across the organization empowers Management to make informed decisions
Effective risk assessment process and set up of audit universe
Aligns schedule, anticipated scope, and risk assessment
Streamlines and organizes the audit process
Provides a clear picture of the review status
Ability to create a valid depiction of the audit status
Issue Management
& Remediation
Tracking of issues and action plans through to resolution, ownership of issues, status of issue remediation activities, and retesting by internal audit
Board Reporting &
Quality Metrics
Resourcing
Management
Annual Audit Plan Status, Tracking of Audit open Issues, IA Performance
Scorecard
Management of resources within the IA group, allocating resources to project/audits based on other projects/audits, time off/conflicts, skills, and certifications.
Time Management Tracking of time and expenses for each audit or special project
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
Used to track, schedule testing, and evaluation of overall company status in regards to open/closed findings.
Ability to provide snapshot reports as to the progress and effectiveness of Internal Audit
Group
Capability to ensure the utilization and capabilities of auditors is being met.
Provides a snapshot of the overall budget
19
Internal Audit Technology – What should you be looking for?
Support of audit charter, vision and strategies
Systematic and structured way of aligning an organization’s approach to risk with its strategy
Ability to capture and link org, processes, risks
Develop or adoption of a risk framework
Link to historical data to understand entity, environment, previous audits
Assess material risk, link to SOX, materiality thresholds, account balance info from G/L develop and maintain risk register, risk and controls
Assign the “scope” of each business process, risk, and control to identify whether applicable to Audit,
Compliance, ERM, IT etc
Capture test scripts,
Recommended Internal Audit Technology
Capabilities
(COSO)
Capturing and assessment of the most significant risks to achieving the objectives and opportunities test results
Capture, matrix identification of future growth opportunities and strategic objectives for the business context (e.g. facilitated sessions or surveys)
Capture of attributes – dates, stakeholders, assertions, fraud scenarios, inherent/residual risk etc.
Process, risk, control, issue, owners, date info
Attach evidence and supporting documents and work paper repository
Configuration of Risk assessments factors, weights, risk scores
Change a risk assessment, as well as show changes year over year
Audit Universe &
Risk Assessment
Workflow management for each audit-related
“document”, including audit, audit program,
Automated alerts for items in tasks, outstanding due dates and reporting checklists, audit process, audit risks, audit controls, and audit work papers
Standard checklists for planning, postaudit and other standard activities
Creation of issues from failed tests
Hyperlinks within reports to forms enabling users to edit information realtime
Planning &
Scoping
Attach predefined templates, copy prior audits
Document, link issues and attributes (e.g..
Process, control, owner, dates)
Creation of a risk summary report that describes key risks, how they are being managed and monitored, remediation of key issues, and accountability
Automated Out-ofthe-box reports
(e.g..: SAD, Audit
Export to
PDF, XLS
Committee) etc.
Execution &
Fieldwork
Drill down
Open issue,
Report on
KPIs and
KRIs
Audit reports for metrics (e.g.. completed audits, outstanding tasks)
Link to official repository of contractor information
Internal Audit Lifecycle
Issus Mgmt. &
Reporting
Provide business areas with a comprehensive view of all of their issues reported by Internal
Retention and reporting of certifications, background
Resource Mgmt.
Staff time tracking capability, including audit and non-audit hours charge time by day
Track time and expenses against contingent worker contract.
characteristics of audit personnel such as job classification, information, special skill sets, and training completed and plannedall levels and task
Store charge rates
Define & maintain time tracking codes
Close out time periods to prevent auditors from charging additional time, in addition to allowing the administrator to reopen a period
Security Search Functions Audit Trail System Integration
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
20
Vendor Landscape: Internal Audit Solutions – Key Differentiators & Highlights
[MetricStream]
■
Built-in remediation workflows, time tracking, emailbased notifications and alerts, risk assessment methodologies, and offline functionalities for conducting internal audits at remote field sites Structured process for managing audit work papers and documentation including supporting evidence, findings, analysis, and results for each audit program. The tool provides approval workflow, check-in, check-out features, version control, document preparation workflows, comments, powerful work paper organization, and search capabilities.
■ Record qualitative or quantitative findings along with detailed observations and recommendations in predefined formats,
■ Graphical executive dashboards and flexible reports with drill-down capability provide statistics on a variety of parameters such as by audited entities, audit schedule and calendar, finding reports, and corrective and remediation actions triggered
[Thompson Reuters]
■ Centralized data capture, risk assessment, reporting and documentation similar to SharePoint folder structure
■ Ability to share risks and risk assessments, audit findings, key risk areas and recommendations across the internal audit department and provide quantifiable evidence of compliance through real-time dashboards and reports; Workflow and notifications. Resource scheduling are also key features
■ Flexible deployment options - On-premise perpetual license, ondemand or hosted perpetual license options mean that Accelus
Audit Manager will fit into your current audit and risk processes, providing you with maximum benefit with minimum disruption.
[RSA Archer]
■ RSA’s GRC & IA content includes pre-mapped policies, control standards, procedures, authoritative sources and assessment questions
■
Audit Management enables the identification and risk assessment of the audit universe. Work papers with configurable workflow are generated by the solution to allow audit staff to document the results of procedures associated with an audit project. Has email notifications and alerts
MetricStream
RSA Archer
Thomson
Reuters
Nasdaq
BWise
IBM
OpenPages
[Nasdaq BWise]
■ Ability to capture and store audit data and results in logical folders, which are automatically created based on the audit work program/work papers
■ Offers a flexible Data Model, providing a way of
■ relating elements of the audit framework in many-tomany relations between elements such as processes, risks, controls, control objectives, etc
■
Automatically create multi-year audit plans, based on audit rating, risk rating and cyclical audit frequency
■ Audit Analytics assisting in reducing data collection efforts with both standard and ad hoc analysis
■ Findings and Recommendations with configurable workflows to review and monitor on a one time basis
Basic scheduling functionality
[IBM OpenPages]
■ Supports top-down and bottom-up approaches to risk assessment and creation of multiple-year audit plans
■ Maintains a centralized library of electronic work papers, and automates work paper review and approval.
■ Manages auditor time and expenses to avoid versioning conflicts and promote consistency
■ Integrated with financial controls management, IT risk and compliance management, general regulatory compliance efforts, and operational risk management programs
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
21
Internal Audit Technology Implementation Success Factor:
Interlinked with Other Assurance Areas – A long term vision
SOX/Internal
Controls
Internal Audit
Management’s
View
Other Assurance
Areas
(ERM, Compliance,
Policy Mgmt. etc)
Better Practices across industries show that the success of Internal Audit tool implementations is greatly increased when the implemented in such a way that it is able to interlink with technology utilized by other assurance areas – giving Management a view of risk and issues across the
Organization
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
22
Internal Audit Technology – Key Consideration Areas
Time to
Implement
Flexibility,
Configurability, &
Customization
Maturity &
Sophistication of
Modules &
Capabilities supporting inscope areas
Client Specific
Requirements & why they selected it
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
23
Lessons Learned in GRC Technology Implementations
Include all relevant stakeholders at the start of the project
Define and agree upon the functional and business requirements
Establish a clear project plan inclusive of change and risk management
Develop a deployment plan
Establish a clear change management plan
Perform System Testing and User
Acceptance Testing
Develop and provide training tailored to the end user
Don’t let a tool drive the process
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
24
Enterprise Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) Considerations
GRC Vision
Guiding Principles
Executive Buy-in
Functional Commitment
Roadmap
1
Strategy
2
Convergence
& Foundational
Elements
Foundational Elements
Future State Process Flows
Convergence Opportunities, Alignment of Shared Functionality, and Integration
Points with GRC Tool
High-level Business, Functional, and
Technical Requirements Definition
Link between Business
Requirements and
Business Process Design
Requirements to System
Mapping /Proof of Concept
Data Conversion
Testing Strategy,
Performance and User
Acceptance Testing
6
Technology
Enablement
Enterprise GRC
Considerations
Components
GRC Business requirements design & documentation
Fit-Gap Analysis
Process, Risk, Transactional level dashboards & reporting
Business Requirements
&
Reporting
5
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
People &
Change
Program
Management
4
3
Project Governance
Project Plan, Timeline and Budget
Project Risks/Issue Tracking
Project Resource Management
Stakeholder Analysis
Roles and Responsibilities
Communication Plan
Learning, Development and
Training
Adoption Plan/Roll-out
25
KPMG vs. GRC Technology Vendor – Division of Roles and Responsibilities
GRC Technology Vendor
2
1
3
Strategy
Convergence &
Foundational
Elements
Program
Management
•
• Participate, as needed, in Steering Committee meeting
• Participate in meetings to determine duration and staging of user groups for strategic GRC roadmap/
GRC Journey
• Provide list of configuration options to be defined for initial product setup
• Create a sandbox environment to facilitate workshop sessions and design decisions
• Assist with facilitation of targeted demonstration
(walkthrough of technology and future state process)
Provide project plan for activities assigned for GRC
Technology Vendor to lead (i.e. tool installation, configuration, unit/functional testing, etc)
• Participate in project status meetings
• Provide project status updates, per agreed upon project plan, to PMO
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
• Assist with the development of a GRC Strategy, mission statement, guiding principles, and success criteria
• Assist with the identification of current and potential future stakeholders and perform potential future usage for enterprise-wide solution
• Provide support in forming GRC Steering Committee and establishing roles and responsibilities for the initiative
• Participate in and help facilitate as needed GRC Steering Committee meeting
• Provide guidance with obtaining executive buy-in
• Perform maturity assessment for each stakeholder group and oversight/assurance activity to serve as input to roadmap
• Assist with the development of strategic and tactical roadmap for GRC Journey
• Assist with creation of support model and governance board to provide direction on changes to the tool both during and after the project
• Assist with defining the baseline set of taxonomies/values required to setup the tool (such as organizational structure, process list, and risk categories)
• Assist with gaining agreement for common definitions of terms and ratings criteria to be shared by users
• Review/document future state process flows for use as starting point for business requirements
• Identify and map GRC Technology Vendor tool integration points in future state processes
• Identify gaps and facilitate discussions for process changes required due to tool capability/functionality
• Assist with creation of support model and governance board to provide direction on changes to the tool both during the project
• Develop integrated GRC project plan, incorporating each workstream and GRC
Technology Vendor timelines
• Facilitate/participate in project status meetings
• Provide detailed project plan, budget, risk and scope tracking
26
KPMG vs. GRC Technology Vendor – Division of Roles and Responsibilities,
(continued)
4
People &
Change
GRC Technology Vendor
• Provide super user training guides, screen shots and hold initial standard tool functionality training
• Provide standard ‘out-of-the-box’ training guides
• Create a training strategy and rollout plan by user group and level (i.e. admin, super user, lite user)
• Develop and train UAT testers
• Create user group specific training guides, presentations, and quick reference guides using client-specific GRC
Technology Vendor screen shots to enable the business process
• Coordinate and instruct training sessions specific to client’s usage of GRC Technology Vendor
5
Business
Requirements &
Reporting
• Provide attributes/criteria to consider for process mapping
• Provide detailed advice on tool capabilities based on
(such as mandatory fields, pick list values, etc.)
• Help facilitate sessions with client and GRC Technology Vendor to identify business/functional requirements
• Review/document detailed future use and functional requirement documents client contract
• Participate in business requirements work sessions, to record areas of the tool that require configuration
• Assist in reviewing/documenting business requirements and Gap document including navigating dedicated client sandbox to determine field attributes and approval workflows
• Document business requirements in the Gap document
• Determine users access rights, user groups, and user profiles
• Facilitate sessions to document landing page views, reporting requirements including quick reports to view daily and those processes nightly in batch
• Develop mock reports and requirements for integrated reporting needs
6
Technology
Enablement
• Perform technical installation
•
•
Provide on site support to UAT testers for timely root cause analysis
Develop testing strategy for System Integration Test (SIT), and resolution of defects
• Assist IT with system integration and interfaces with other systems
• Perform any configuration changes, software updates, or technical
User Acceptance Testing (UAT), and regression testing
• Assist with the creation of detailed test cases and scripts to ensure business requirements, functional requirements, and modifications to the software
• Provide on-going technical support technical requirements are being met
• Perform UAT testing, including detailed defect tracking and validation with GRC Technology Vendor
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
27
Q&A – Open
Discussion
Contact Info
Sean Winekauf - Director, ERM & GRC swinekauf@kpmg.com
Phone: 402-672-0126
© 2014 KPMG LLP, a Delaware limited liability partnership and the U.S. member firm of the KPMG network of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International
Cooperative (“KPMG International”), a Swiss entity. All rights reserved.
The KPMG name, logo and “cutting through complexity” are registered trademarks or trademarks of KPMG International.