Benchmark #1 Study Guide – CE.11-14 Group #1 _____ 1. Value of
advertisement
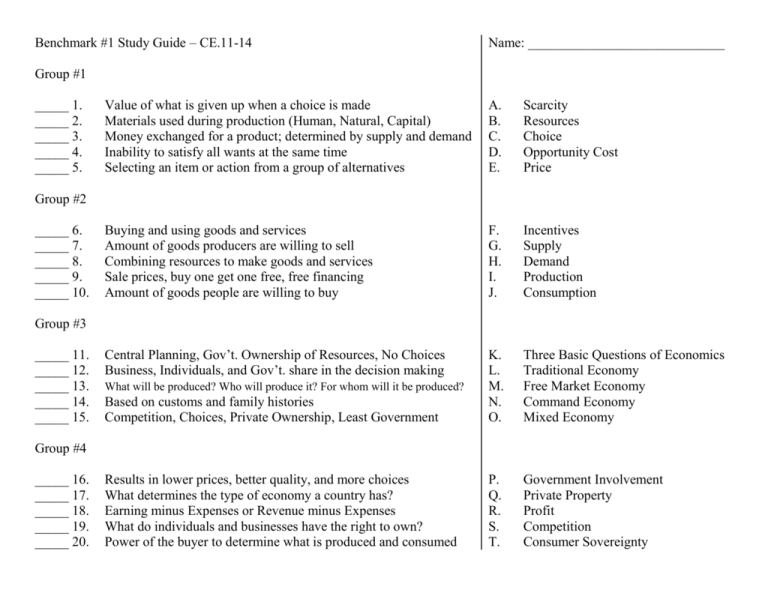
Benchmark #1 Study Guide – CE.11-14 Name: _____________________________ Group #1 _____ 1. _____ 2. _____ 3. _____ 4. _____ 5. Value of what is given up when a choice is made Materials used during production (Human, Natural, Capital) Money exchanged for a product; determined by supply and demand Inability to satisfy all wants at the same time Selecting an item or action from a group of alternatives A. B. C. D. E. Scarcity Resources Choice Opportunity Cost Price Buying and using goods and services Amount of goods producers are willing to sell Combining resources to make goods and services Sale prices, buy one get one free, free financing Amount of goods people are willing to buy F. G. H. I. J. Incentives Supply Demand Production Consumption Central Planning, Gov’t. Ownership of Resources, No Choices Business, Individuals, and Gov’t. share in the decision making Based on customs and family histories Competition, Choices, Private Ownership, Least Government K. L. M. N. O. Three Basic Questions of Economics Traditional Economy Free Market Economy Command Economy Mixed Economy Results in lower prices, better quality, and more choices What determines the type of economy a country has? Earning minus Expenses or Revenue minus Expenses What do individuals and businesses have the right to own? Power of the buyer to determine what is produced and consumed P. Q. R. S. T. Government Involvement Private Property Profit Competition Consumer Sovereignty Group #2 _____ 6. _____ 7. _____ 8. _____ 9. _____ 10. Group #3 _____ 11. _____ 12. _____ 13. _____ 14. _____ 15. What will be produced? Who will produce it? For whom will it be produced? Group #4 _____ 16. _____ 17. _____ 18. _____ 19. _____ 20. Benchmark #1 Study Guide – CE.11-14 Name: _____________________________ Group #5 _____ 21. _____ 22. _____ 23. _____ 24. _____ 25. Business owned by one person who takes all risks and profits Business owned by two or more people who share risks and profits Business with many owners; acts as a legal person; limited liability The continuous movement of money, resources, goods, & services A person who takes a risk in order to make a profit A. B. C. D. E. Proprietorship Partnership Corporation Entrepreneur Economic Flow Banks, Credit Unions, and Savings & Loans What do financial institutions pay on deposits to encourage saving? Buy resources in order to make and sell products Use resources to create income and buy products Use tax revenue to provide public goods and services F. G. H. I. J. Individuals (Households) Businesses Government Private Financial Institutions Interest Buying and selling goods and services around the world Private financial institutions bring together … What is the money called that people borrow from the bank? Increase wealth and create jobs What is the money called that people save in the bank? K. L. M. N. O. Deposits Loans Savers and Borrowers Global Economy Reasons we trade with other nations Laws designed to prevent monopolies Specializing in the production of certain goods and services Buy goods at a lower cost or goods we cannot produce P. Q. R. S. T. Reasons we trade with other nations Innovations in technology (Internet) Using new technology Promotes efficiency and growth Antitrust legislation Group #6 _____ 26. _____ 27. _____ 28. _____ 29. _____ 30. Group #7 _____ 31. _____ 32. _____ 33. _____ 34. _____ 35. Group #8 _____ 36. _____ 37. _____ 38. _____ 39. _____ 40. Contributes to the global flow of information, capital, goods, and services How can companies lower the cost of production? Benchmark #1 Study Guide – CE.11-14 Name: _____________________________ Group #9 _____ 41. _____ 42. _____ 43. _____ 44. _____ 45. Protects the air, water, land, and endangered species Provided by the government and benefits many people Regulates radio and television plus telecommunications Antitrust Legislation, Global Trade, Business Start-Ups Protects the consumer from unsafe and unfair business practices A. B. C. D. E. Ways the gov’t. promotes competition Federal Communications Commission Federal Trade Commission Environmental Protection Agency Public Goods and Services How does the government pay for public goods and services? Government raises taxes Interstate highways, postal service, and national defense Most would not be available if individuals had to provide them Government lowers taxes F. G. H. I. J. Public Goods and Services Examples of Publics and Services Taxes, Borrowed Funds, and Fees Private Spending Decreases Private Spending Increases Allows the government to collect an income tax Demand, Production, and Employment plus Taxes Increase Demand, Production, and Employment plus Taxes Decrease Government borrowing Increases Government borrowing Decreases K. L. M. N. O. Private Borrowing Increases Private Borrowing Decreases When Gov’t. Spending Increases When Gov’t. Spending Decreases The 16th Amendment The central bank of the United States, Banker’s Bank The Federal Reserve regulates banks to keep this safe… The Federal Reserve tries to keep this low and stable… The Federal Reserve tries to maintain the value of this… The Federal Reserve controls the amount of money in this… P. Q. R. S. T. The Economy National Currency (The Dollar) Deposits Inflation The Federal Reserve System Group #10 _____ 46. _____ 47. _____ 48. _____ 49. _____ 50. Group #11 _____ 51. _____ 52. _____ 53. _____ 54. _____ 55. Group #12 _____ 56. _____ 57. _____ 58. _____ 59. _____ 60. Benchmark #1 Study Guide – CE.11-14 Name: _____________________________ Group #13 _____ 61. _____ 62. _____ 63. _____ 64. _____ 65. Government agencies establish guidelines to… Protected by negotiated contracts that are enforceable by the law Anything that is generally accepted as a method of payment If your consumer rights are violated you can take… People have confidence in the gov’t; helps in the exchange of goods & services A. B. C. D. E. Private Property Protect Public Health and Safety Legal Action Money Reasons the Gov’t. Issues Money Career planning starts with looking at your interest and talents Advancements in technology… Attitudes and Behaviors needed to be successful Education, Skills, and Supply/Demand Federal Reserve Notes, Coins, Checks, and Debit Cards F. G. H. I. J. Types of money used Self-Assessment Strong Work Ethic Influence Job Income Creates new jobs Employers seek employees who do this with new technology Create job opportunities and competition for jobs It is important to understand how they protect consumers Making careful spending decisions, saving and investing Keep a budget, having insurance, using credit wisely K. L. M. N. O. Keep Pace Advancements in technology Contracts, Warranties, and Guarantees Being Fiscally Responsible Being Fiscally Responsible Florida State’s Fight Song Georgia Tech’s Fight Song Virginia Tech’s Fight Song Clemson’s Fight Song University of Virginia’s Fight Song P. Q. R. S. T. The V-P-I Victory March Tiger Rag The Good Old Song The War Chant Ramblin’ Wreck Group #14 _____ 66. _____ 67. _____ 68. _____ 69. _____ 70. Group #15 _____ 71. _____ 72. _____ 73. _____ 74. _____ 75. Group #16 _____ 76. _____ 77. _____ 78. _____ 79. _____ 80.







