Unit 3 study guide
advertisement

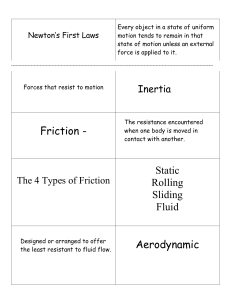
Name: _________________________________ Date: __________ Period: __________ Science 7 Unit 3 Review: Study Guide/Outline of Major Concepts DUE DATE: 12/18/15 TEST DATE: 12/18/15 The following topics will be covered on your exam: Aim 8: How do we describe and calculate motion (Calculating Speed) Aim 9: How do we describe an object’s motion using graphs Aim 10: How is velocity different than speed (calculating velocity) Aim 11: How do we calculate acceleration? Aim 12: What is force and how are forces and motion related? Aim 13: How does Friction, air resistance and gravity affect the motion of an object? Aim 14-16: Newton’s 1st, 2nd and 3rd laws of motion FORMULAS TO KNOW Formula Speed Velocity Acceleration Net force Newton’s 2nd Law Equation S=D T V=D T + Direction A = vf-vi t Forces going in the same direction add forces Forces going in the opposite direction subtract forces F = ma Example of Units 10 m/s 10 m/s East 10 m/s/s OR 10 m/s2 10 N (newtons) 10 N (newtons) Aim 8: Calculating Speed (use your Aim 8 notes and worksheets as a reference) 1. Define Motion: 2. Using the speed triangle below, write the formulas for speed, distance, and time below. T= S= D= 3. A runner jogs 3 miles north, turns left and continues traveling 6 miles east. What was the total distance he traveled? What was the runner’s speed if he completed his run in 60 minutes? Show ALL work below (all units!) 4. After turning the light on, you see a spider run across the floor and under your bed within a 4 second period of time. How far did the spider travel if its speed was 2 m/s? Show all work! Aim 9: Analyzing distance vs. time graphs (use your Aim 9 notes and worksheets as a reference) 5. The speed of an object is determined by the ______________ of a line 6. Match the descriptions below to the corresponding graph 1. Stationary (not moving): _______ 2. Increasing speed: _______ 3. Slow & constant speed: _______ 4. Fast & constant speed: _______ 5. Returning to start: _______ a) Calculate the speed of car B from 0-5 seconds. Show all work b) Calculate the speed of car A from 0-5seconds. Show all work c) Who was faster during this time? _______________ d) Could you have answered question C without making any calculations? Explain WHY! 7. Aim 10: Calculating Velocity (use your Aim 10 notes and worksheets as a reference) 8. What is the difference between speed and velocity? 9. What type of “quantity” is velocity? _______________________ 10. Your dog Spot escaped your backyard and ran 34 meters to his doggie friend’s house. Your dog is so fast it only took him 10 seconds. Spot’s friend’s house is located west of your house. What was Spot’s speed? Show all work! What was Spot’s velocity? What is Spot ran to his other friend’s house who lived in the opposite direction. What would his velocity be? Aim 11: Calculating acceleration (use your Aim 11 notes and worksheets as a reference) 11. Define acceleration: 12. Why is “deceleration” still considered a type of acceleration if deceleration means to “decrease speed”? 13. Match the intervals on the speed vs. time graph that matches each description. You can use more than one interval. 14. object accelerates from rest to a speed of 35 m/s in 25 seconds. What is the acceleration of the object? Show all work! 15. A car accelerated from 50 miles per hour to a stop in 10 seconds. Calculate the cars acceleration. Show all work! Aim 12: Forces (use your Aim 12 notes and worksheets as a reference) 16. Define Force: 17. What type of “quantity” is a force? An 18. List 3 ways that forces affect motion 19. What is a balanced force? Draw an example 20. What is an unbalanced force? Draw an example 21. Does a balanced or an unbalanced force cause motion? Explain why 22. Define net force: 23. Calculate the net force for the following problems. Indicate the net force in Newtons and the direction the object will travel. 24. Draw an object below with a force acting on it of 10 N to the left. If the net force acting on the object is 30 N to the right, what would be the magnitude of an opposite force acting on the object? Aim 13: Friction, air resistance and gravity (use your Aim 13 notes and worksheets as a reference) 25. Define Friction: 26. Briefly describe the 3 types of friction: 27. Which of the 3 types of friction requires the greatest amount of force to move an object? ____________________ 28. Which of the 3 types of friction requires the least amount of force to move an object? _______________________ Explain why! 29. Give 3 ways we can reduce friction: 30. What would happen to a volleyball if it kept rolling and friction did not exist? 31. An object would be (hard/easy) to move along ice because there is (less friction/more friction) 32. If two equal and opposite forces act on an object, can the object accelerate? Explain why or why not 33. Define Air resistance: 34. Define Gravity: 35. An elephant and a pencil are dropped from the top of a building at the same height. Why will they both hit the ground at the same time if air resistance did not exist? Use the words gravitational force and acceleration (9.8 m/s2) in your response. 36. Draw an image below of a falling feather. Draw arrows to represent the forces of gravity and air resistance. 37. What two factors affect gravity? 38. An object with a (small mass/large mass) will have a stronger gravitational pull than an object with a (small/large mass) 39. Two objects that are (close together/far apart) will have a stronger gravitational pull than two objects that are (close together/far apart) Aim 14-16: Newton’s Laws (use your Aim 14-16 notes and worksheets as a reference) 40. Define Newton’s First law: 41. Define Inertia: 42. Which would have more inertia, a paper clip or a dog? Explain why by stating the relationship between mass and inertia. 43. Why would you fly through the windshield of a fast moving car if the car stopped short and you were not wearing a seatbelt? 44. Define Newton’s Second law: 45. Using the force triangle below. Write the formulas for force, mass and acceleration A= F= M= 46. Solve the following problems using the formula for Newton’s second law. Show all work and units! What is the acceleration of the object below? Show all work! (hint: find the net force first!) 47. Define Newton’s Third law: 48. How is your book on your desk or your feet planted on the floor an example of Newton’s third law?