Depth of Knowledge Review
advertisement

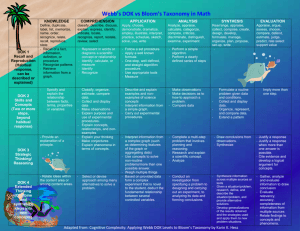
Depth of Knowledge and Rigor: Improving Instruction and Assessment What is DoK? Depth of Knowledge (DoK), a model developed by Norman Webb in 1997, reflects a different level of cognitive expectation required to complete a task. Webb called the DoK nominative, meaning it names ways of going into the content. Characteristics of Webb’s DoK Model Defines levels to align and analyze curriculum, objectives, standards, and assessments Names four different ways that students interact with content Relates closely to the depth of content understanding and scope of a learning activity—focuses on skills required to complete the task from inception to finale (e.g., planning, researching, drawing conclusions). Repo DoK and the Rigor/Relevance Framework Levels of complexity of cognitive demand: Level 1: Quad A Recall and Reproduction Requires eliciting information such as a fact, definition, term, or a simple procedure, as well as performing a simple algorithm or applying a formula. Level 2: Quad B Basic Skills and Concepts Requires the engagement of some mental processing beyond a recall of information. Level 3: Quad C Strategic Thinking and Reasoning Requires reasoning, planning, using evidence, and explanations of thinking Level 4: Quad D Extended Thinking Requires complex reasoning, planning, developing, and thinking most likely over an extended period of time You’re not going to live in Quad D, but you need to visit it on a regular basis! DoK 1/Quad A: Recall and Reproduction DoK 1 involves basic recall of concepts, definitions, facts, and processes. A Level 1 item can involve following a simple, well-known procedure or formula. Simple skills and abilities or recall characterize DOK 1. DoK 1/Quad A Examples Locate or recall facts. Apply a well-known formula. Identify the complete subject and complete predicate in a sentence. Represent math relationships in words, pictures, or symbols. Perform a simple science process or a set of procedures. DoK 2/Quad B: Basic Application of Skills & Concepts Engages mental processes beyond recalling or reproducing a response Requires students to makes decisions about how to approach a question or problem Implies more than ONE cognitive process/step DoK 2/Quad B Examples Identify & summarize the major events, problem, solution, conflicts in literary text. Predict a logical outcome based on information in a reading selection. Explain causes/effects of historical events. Retrieve information from a table, graph, or figure and use it to solve a problem requiring multiple steps. DoK 3/Quad C: Strategic Thinking • • • Requires deep understanding as exhibited through planning, using evidence, and more demanding cognitive reasoning Taps complex and abstract cognitive demands Assessment items have more than one possible answer and require students to justify their response DoK 3/Quad C Examples Justify a response when more than one answer is possible. Compare consumer actions & analyze how these actions impact the environment. Analyze or evaluate the choice and effectiveness of figurative language. Solve a multiple-step problem and provide support with a mathematical explanation that justifies the answer. DoK 4/Quad D: Extended Thinking Requires high cognitive demand Requires time to research, think, or process multiple facets of a problem Due to the complexity of the task, often requires an extended period of time Necessitates real-world, unpredictable applications of knowledge DoK 4/Quad D Examples Gather, analyze, organize, & synthesize information from multiple sources to draft a well-organized essay. Analyze & explain multiple perspectives or issues within or across time periods, events, or cultures. Specify a problem, identify solution paths, solve the problem, and report the results. Why emphasize DoK? Ensures that the intent of the standard and the level of students’ tasks required matches the assessment Ensures that teachers are teaching to a level that promotes student achievement DoK Level? The total cost for an order of shirts from a company consists of the cost for Grade 8 each shirt plus a one-time design fee. The cost for each shirt is the same no matter how many shirts are ordered. The company provides the following examples to customers to help them estimate the total cost for an order of shirts. • 50 shirts cost $349.50 • 500 shirts cost $2370 Part A: Using the examples provided, what is the cost for each shirt, not including the one-time design fee? Explain how you found your answer. Part B: What is the cost of the one-time design fee? Explain how you found your answer. What Level DoK? Select all of the 8 expressions that have a value between 0 and 1. Grade 87 8–12 74 7–3 1 2 3 (–5)6 (–5)10 1 3 9 DoK Level? A cylindrical Grade 8tank has a height of 10 feet and a radius of 4 feet. Jane fills this tank with water at a rate of 8 cubic feet per minute. How many minutes will it take Jane to completely fill the tank without overflowing at this rate? Round your answer to the nearest minute. DoK Level? Grade 8 During the task, the student assumes the role of an architect who is responsible for designing the best plan for a park with area and financial restraints. The student completes tasks in which he/she compares the costs of different bids, determines what facilities should be given priority in the park, and then develops a scale drawing of the best design for the park and an explanation of the choices made. This investigation is done in class using a calculator, an applet to construct the scale drawing, and a spreadsheet. Bloom’s and Webb’s Bloom's Taxonomy focuses on the tasks that students complete to deepen student understanding. However, Webb's DoK centers on the thinking process, not just the product. Webb’s Depth of Knowledge is about the cognitive demands (thinking process) of instruction, tasks, and/or assessments. While Bloom's Taxonomy relies on the verb, Webb's DoK extends beyond the verb to what follows--beyond the 'what' to the 'how'. Karin Hess Video http://schools.nyc.gov/Academics/Com monCoreLibrary/Videos/default.htm# A verb alone can vary in terms of difficulty & complexity. “Create,” for example, is a high level on Bloom’s taxonomy. If you ask students to “create a model of the human eye based on a textbook model,” students may not need additional background knowledge to complete the task. There is little transfer of knowledge. But. . . If you ask students to create a threedimensional model of one hole for a miniature golf course utilizing a parallelogram, a rectangle, a circle, a triangle, and a rhombus, they must use critical thinking skills. Look what our HS geometry students designed last year! DoK Verb Activity: #1 Describe a model that you might use to represent the relationships that exist within the rock cycle. (requires deep understanding of the rock cycle and a determination of how best to represent it) What level is this task and why? DoK Activity #2 Describe the difference between metamorphic and igneous rocks. (requires cognitive processing to determine the differences in the two rock types) What level is this and why? DoK Activity #3 Describe three characteristics of metamorphic rocks (requires simple recall) What level is this task and why? It’s about more than the verb! “Just because we ask students to create or analyze doesn’t necessarily mean that we are providing a deep level of thinking (nor does it mean we haven’t provided it either). We must consciously ask students to extend their thinking in order to improve their thinking.” ~Karin Hess As we continue our journey of curriculum review into CCSS curriculum alignment, We must remain conscious of our questioning, our modeling, and our guidance to teach students how to extend their thinking. We must ask our students to extend their thinking on the new SBAC assessments. We must prepare them to be college and career ready! Why MUST we change? Condeleesa Rice said 70% of students in American are no longer accepted into the military because they lack a diploma. They must take the ASVAB, now an admissions exam that is being recalibrated every year to add rigor. (Daggett, 2013) College and Career Ready? 86% of high school teachers say their kids are ready for college-; only 21% of college teachers agree. Nationally, college retention rates are 55.5% in 2-year colleges and 36.6% in 4-year colleges. 13 million are unemployed but 3.8 million jobs remain unfilled. (Daggett, 2013) Kansas is comparable How will we apply this knowledge to change instruction, expectation, assessment, and preparation for the SBAC, college, and career? Even if we shoot high and slightly miss the mark, haven't we developed our students to be better, independent thinkers? Sounds like a win-win to me. Rigor. Text complexity. Difficulty. Thinking. Teaching. Learning. Broas, Sarah. http://littlebitofliteracy.blogspot.com/2012 /09/webbs-depth-of-knowledge.html. Daggett, Bill. (July, 2013). Begin with the End in Mind. Keynote address presented at Model Schools Conference, Washington, D.C.