712209 - Other postemployment benefits obligations
advertisement

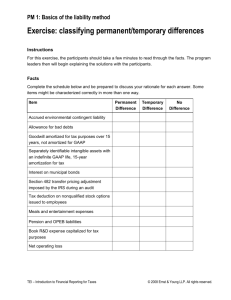
. CHAPTER 4.3.9 GAAP ADJUSTMENTS AND RECLASSIFICATION ENTRIES LIABILITIES: OTHER POSTEMPLOYMENT BENEFITS OBLIGATION 1 GAAP POLICIES AND PROCEDURES The Other Postemployment Benefits (OPEB) obligation includes the CSU’s estimated funding liability of the State administered and sponsored plan as of the fiscal year end. The State’s actuary has employed methods and assumptions considered reasonable and appropriate given the information currently available. Given the inherent uncertainty in the nature of such estimates, future amounts may deviate from those estimates. In accordance to GASB pronouncements, CSU is required to recognize the cost of OPEB on an accrual basis. Postretirement Healthcare Plan The State provides retiree healthcare benefits to statewide employees, including the University employees, through the programs administered by CalPERS. The State’s substantive plan represents a substantive single-employer defined benefit OPEB Plan, which includes medical and prescription drug benefits (collectively, healthcare benefits) to the retired University employees. The University provides dental benefits to eligible University’s retirees. Eligible retirees receive healthcare and dental benefits upon retirement at age 50 with 5 years of service credit. For healthcare benefits, CalPERS offers Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), and Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs) (limited to members in certain California counties); for dental benefits, a Dental Maintenance Organization (DMO) and dental indemnity plans to the University’s retirees. Health plans offered, covered benefits, monthly rates, and copayments are determined by the CalPERS Board, which reviews health plan contracts annually. The contribution requirements of retirees and the State are established and may be amended by the State legislature. For healthcare benefits, the State makes a contribution toward the retiree’s monthly health premiums, with the retirees covering the difference between the State’s contribution and the actual healthcare premium amount. The State contribution is normally established through collective bargaining agreements. No retiree contribution is required for dental benefits. 4.03.9-1 GAAP Manual | GAAP Adjustments and Reclassification Entries – Liabilities: Other Postemployment Benefits Obligation | June 30, 2015 . Funding Policy For healthcare benefits, responsibility for funding the cost of the employer share of premiums is apportioned between the State and the University based on “billable” and “nonbillable” accounts. Billable accounts have special revenue sources such as fees, licenses, penalties, assessments, and interest, which offset the costs incurred by a State department during the year. The University reimburses the State for retiree’s health benefit costs allocated to billable accounts but not for costs allocated to nonbillable accounts. The University is responsible for funding the costs of the billable accounts on a pay-as-you-go basis as part of the statewide general administrative costs charged to the University. The State is responsible for funding the cost of the employer share of healthcare premiums of retirees for all nonbillable accounts. The University is responsible for paying the cost of dental benefits for all University retirees using funds provided by the State through general fund appropriations. The University makes payments directly to Delta Dental for the retiree’s monthly dental premiums. The University is paying these benefits on a pay-as-you-go basis. 2 RELEVANT ACCOUNTING LITERATURE GASB Statement No. 43, Financial Reporting for Postemployment Benefit Plans and Other than Pension Plans GASB Statement No. 45, Accounting and Financial Reporting by Employers for Postemployment Benefits Other Than Pensions 3 OBJECTIVES OF GAAP ADJUSTMENTS To reverse accrual of other postemployment benefits obligation made in prior year. To accrue other postemployment benefits obligation as of year-end. 4 GAAP ACCOUNTING T REATMENT AND JOURNAL ENTRIES 4.1 RELATED GAAP ACCOUNT(S) 712209 - Other postemployment benefits obligations 722002 – Benefits 4.2 BILLABLE VERSUS NONBILLABLE ACCOUNTS The OPEB obligation includes the employer’s share of health and dental benefits for retirees, and are classified as billable and nonbillable accounts. Billable accounts are State funds that (1) have special revenue sources, such as fees, licenses, penalties, assessments, interest, etc., and (2) support a State department. For nonbillable accounts, the State is responsible and pays for the cost of the employer’s share of health benefits for retirees. The State also pays for the cost of the employer’s share of health benefits for retirees for billable accounts but allocates the cost to the CO through the State’s pro 4.03.9-2 GAAP Manual | GAAP Adjustments and Reclassification Entries – Liabilities: Other Postemployment Benefits Obligation | June 30, 2015 . rata process. The CO then allocates this cost to the campuses, which only includes the health benefits portion for the billable accounts. The CO pays for the cost of the employer share of dental benefits for retirees for both billable and nonbillable accounts, and does not allocate this cost to the campuses. Because of this, only the health benefits portion of the OPEB obligation for the billable accounts is allocated to and accrued by the campuses. OPEB Obligation Health Benefits Dental Benefits Billable Accounts The State allocates to the CSU. Cost is allocated to and accrued by campuses. Accrued by the CO. No allocation to campuses. Nonbillable Accounts Paid by the State. No accrual by the CSU. Accrued by the CO. allocation to campuses. No As an agency of the State, the CSU is included in the State’s OPEB actuarial study. Therefore, the amounts of annual required contribution (ARC), employer contributions, and net OPEB obligation (NOO) are all provided by the State Controller’s Office (by State fund). The CO estimates the portion of the OPEB obligation related to health benefits based on the percentage of each campus’ health benefits contributions compared to the total employer contributions. The CO allocates this estimated health benefits portion of the OPEB obligation to campuses based on the campuses’ retirement expenses (object code 603005) for the billable funds recorded in the legal-basis accounting records. The following CSU funds are considered billable: CSU Fund 441 442 443 444 452 462 471 472 473 474 496 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 560 561 4.03.9-3 CSU Fund Description Type Program TF CERF Extended Education TF CERF-Construction TF CERF-Maintenance and Equipment TF CERF-Campus Partners TF Facility Revenue Fund-Health Facilities Fee TF Campus Union Operating Revenue Trust TF Parking Revenue Fund-Fines and Forfeitures TF Parking Revenue Fund-Parking Fees TF Parking Revenue Fund-Construction TF Parking Revenue Fund-Maintenance and Equipment TF Miscellaneous Trust TF Housing-Operations and Revenue TF Housing-Maintenance and Repair TF Housing-Construction TF Campus Union-Operations and Revenue TF Campus Union-Maintenance and Repair TF Campus Union-Construction TF Auxiliary Org.-Operations and Revenue TF Cal State Online TF Cal State Online Program Reinvestment Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable CERF CERF CERF CERF Health Union Parking Fines Parking Fees Parking Fees SCO Fund 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Billable Parking Fees Trust Housing Housing Housing Union Union Union Auxiliary Operations CERF CERF 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 0948 GAAP Manual | GAAP Adjustments and Reclassification Entries – Liabilities: Other Postemployment Benefits Obligation | June 30, 2015 . The allocation entries to record the OPEB obligation as of year-end per campus will be provided by the CO. Campus should record the OPEB obligation journal entry based on the GASB 45 template provided by the CO. The schedule is posted on the CO website and emailed via SFSR_GAAP@calstate.edu as discussed in Chapter 5 GAAP Adjustments of Reclassifications that Require Information from the Office of the Chancellor. EXAMPLE The current year ARC $3,000,000, employer contribution $2,000,000, and NOO $1,000,000 are allocated to the State fund and CSU fund 0948.XXX of the campus. In prior year, ARC is $2,000,000, employer contribution $1,500,000, and NOO $500,000 are allocated to the state fund and CSU fund 0948.XXX of the campus. Reverse Prior Year Balance NOTE: Campuses should NOT reverse the prior year OPEB obligations accrual until the current year-end accrual from the CO is ready for posting. This is to avoid an out-ofbalance situation in the initial reporting package in TM1, which is typically due before the current year’s OPEB obligation is recorded. Account Account Name 712209 Other postemployment benefits obligations 722002 Benefits Journal Description To properly reverse 6/30/PY OPEB liability. Fund (Net Position) 881 – Unrestricted 881 – Unrestricted Program Class (CSU Fund) 90 496 Various 496 Program Class (CSU Fund) Various 496 90 496 Amount $500,000 ($500,000) Record Current Year Balance Account Account Name 722002 Benefits 712209 Other postemployment benefits obligations Journal Description To properly reverse 6/30/PY OPEB liability. Fund (Net Position) 881 – Unrestricted 881 – Unrestricted Amount $1,000,000 ($1,000,000) The campus must record a GAAP adjustment to accrue the NOO, which is the difference between the ARC and the employer contribution. Refer to the Legal Manual in Chapter 6 Extended Education (EE), 3.4.1 Centrally Paid Costs for State Overhead (Pro Rata) for more information on recording employer contribution. The ARC and the employer contribution are required for footnote disclosure only and will be entered by the CO in Note 19 Other Post-Employment Benefits Obligation in the YES (TM1) reporting package. The campus needs to validate the numbers in the note in YES with the allocation schedule 4.03.9-4 GAAP Manual | GAAP Adjustments and Reclassification Entries – Liabilities: Other Postemployment Benefits Obligation | June 30, 2015 . provided for recording the GAAP adjusting entries. The ARC, contribution, and NOO should agree between the note in YES and the allocation schedule. NOTE: Campuses should only record OPEB obligations in the CSU funds which have recorded payroll expenses. For instance, the general fund (CSU fund 001) usually does not record payroll expenses and therefore should not have any OPEB obligations recorded. 5 REFERENCE TOOLS 5.1 TABLES OF OBJECT CODE AND CSU FUND DEFINITIONS http://www.calstate.edu/SFSR/standards_and_rules/2014/Tables-of-Object-Code-andCSU-Fund-Definitions-Updated-10-30-14.xls 5.2 PASSDOWN SCHEDULES http://www.calstate.edu/sfsr/gaap/ under Passdown Schedules and by selecting the most recent fiscal year. 4.03.9-5 GAAP Manual | GAAP Adjustments and Reclassification Entries – Liabilities: Other Postemployment Benefits Obligation | June 30, 2015 . REVISION CONTROL Document Title: CHAPTER 4.3.9 – GAAP ADJUSTMENTS AND RECLASSIFICATION ENTRIES – LIABILITIES: OTHER POSTEMPLOYMENT BENEFITS OBLIGATION REVISION AND APPROVAL HISTORY Section(s) Revised General 4.03.9-6 Summary of Revisions Previously in Chapter 5.6. Revision Date April 2015 GAAP Manual | GAAP Adjustments and Reclassification Entries – Liabilities: Other Postemployment Benefits Obligation | June 30, 2015