Jeopardy Game
advertisement

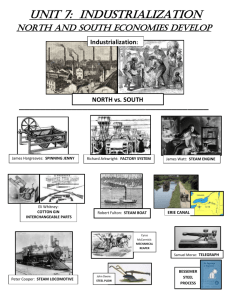
Welcome! The Topic For Today Is… Rules of Jeopardy! • Contestants must wait until the host finishes reading the clue before ringing in • Groups will be assigned numbers (1-4) with group #1 going first. When Group #1 has picked their question, they are the only ones who can answer. They will be given 10 seconds to answer, after that time, it will be open for groups to answer. If no group has the answer, it will be Group #2’s turn to pick a question. • All responses must be phrased in the form of a question – Ex. Write in “Wealth of Nations” about an “invisible hand” that guides a market economy… “who is Adam Smith?” If the answer is not stated in a question, then the answer will not be counted. – Daily Doubles - One clue hidden on the Jeopardy! Round game board is designated a "Daily Double". Only the contestant who selects a Daily Double may respond to its clue • The winning team will be giving 5 extra credit points (each player) Your Topic: The Industrial Revolution Beginnings of Industrializatio n Economic Systems Urbanization/I ndustrializatio n Spreads Technology Reform Movements 200 200 200 200 200 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 Bonus Question: 5000 pts Beginnings of Industrialization: 200 • Question: • A person who organizes, manages, and takes on the risks of a business • Answer • Who is an entrepreneur? • • • • Beginnings of Industrialization: 400 Question: Land, labor, capital, and Entrepreneurship Answer What is factors of production? Beginnings of Industrialization: 600 • Question: • This movement allowed landowners to experiment with new agricultural methods, eventually forcing small farmers to become tenant farmers or to give up farming and move to the cities. • Answer • What is the enclosure movement? Beginnings of Industrialization : 800 • Question: • In addition to a large population of workers, the Great Britain had extensive natural resources in four particular areas. • Answer • What is water power and coal, iron ore, rivers, and harbors? Beginnings of Industrialization: 1000 • Question: • By the seventeenth century, some industries were no longer jealously protected by a few guildsmen trying to keep others out. Any worker and any employer could be driven from his occupation by a competitor who was more capable. Competition, therefore, provided an essential safeguard by assuring this. • Answer • What is the most efficient production of goods possible? Economic Systems/Philoso phy: 200 • Question: • The three basic economic questions that businesses need to answer before they can begin production • Answer • What is “what to produce” “how to produce it” and “for whom to produce it for”? Economic Systems/Philoso phy: 400 • Question: • Economic system that is a form of complete socialism in which the means of production would be owned by the people • Answer • What is communism? Economic Systems/Philoso phy: 600 • Question: • Economic system in which the factors of production are owned by the public and operate for the welfare of all • Answer • What is socialism? Economic Systems/Philoso phy: 800 • Question: • An economic philosophy of capitalism that called for an economy free of government regulation • Answer • What is laissez-faire? Economic Systems/Philsop hy: 1000 • Question: • German journalist named Karl Marx introduced the world to a radical type of socialism called Marxism (later termed communism). Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels outlined their ideas in the Communist Manifesto. In the manifesto, they referred to employers and workers in these terms. • Answer • What is bourgeoisie (employers) and proletariat (workers)? Urbanization/Industrialization Spreads: 200 • Question: • Factories were willing to employ women and children because of this. • Answer • What is cheap labor? Urbanization/Industrialization Spreads: 400 • Question: • This social class was nonexistent during the feudal period but emerged as a result of the Industrial Revolution • Answer • What is the middle class? Urbanization/Industrialization Spreads: 600 • Question: • The rapid growth in population and the continued growth of cities allowed for great benefits (mass production of goods, greater wealth of the nation, etc.) but had some major drawbacks as well. Living conditions struggled in these ways. (name at least two) • Answer • What is no sanitary codes, building controls, lack of adequate housing, education, lack of running water and indoor plumbing? Urbanization/Industrializatio n Spreads: 800 • Question: • Eager to keep the secrets of industrialization to itself, Britain had forbidden engineers, mechanics, and toolmakers to leave the country. In 1789, however, this young British mill worker emigrated to the United States, building a spinning machine from memory • Answer • Who is Samuel Slater? Urbanization/Industrialization Spreads: 1000 • Question: • Industrialization widened the gap between industrialized and non-industrialized countries, even while it strengthened their economic ties. To keep factories running and workers fed, industrialized countries required a steady supply of raw materials from less developed lands. A policy was soon enacted which extended a country’s rule over many other lands, giving even more power and wealth to these already wealthy nations. • Answer • What is imperialism? Technology: 200 • Question: • This mode of transportation spurred industrial growth by giving manufacturers a cheap way to transport materials and finished products • Answer • What is the railroad? Technology: 400 • Question: • In 1701, he invents the “seed drill” that allows for increased crop production • Answer • Who is Jethro Tull? Technology: 600 • Question: • Creates faster, more efficient “steam engine” in 1765 • Answer • Who is James Watt? Technology: 800 • Question: • Invents “cotton gin” in 1793 which separates seeds from cotton thereby boosting production • Answer • Who is Eli Whitney? Technology: 1000 • Question: • Around 1764, a textile worker named James Hargreaves made an invention that named after his daughter. This invention allowed one spinner to work eight threads at a time. • Answer • What is the spinning jenny? Reform Movements: 200 • Question: • William Wilberforce, a highly religious man, was a member of British Parliament who led the fight in this reform movement • Answer • What is the abolition of slavery? Reform Movements: 400 • Question: • In the Union movement, workers and their employers engaged in this negotiation activity in order to get better working conditions and higher pay • Answer • What is collective bargaining? Reform Movements: 600 • Question: • This new reform law made it illegal to hire children under 9 years old, children from the ages of 9 to 12 could not work more than 8 hours a day, young people from 13 to 17 could not work more than 12 hours • Answer • What is the Factory Act of 1833? Reform Movements: 800 • Question: • The Industrial Revolution proved to be a mixed blessing for women. While factory work offered higher wages than work done at home, women factory workers faced this drawback • Answer • What is lower wages than men (roughly 1/3 of what men got paid)? Reform Movements: 1000 • Question: • This man favored free public education for all children. Spending his own childhood working at hard labor, he warned that “if we do not prepare children to become good citizens . . . if we do not enrich their minds with knowledge, then our republic must go down to destruction.” • Answer • Who is Horace Mann? Bonus Question: 5000 pts. • Question: • In An Essay on the Principle of Population, written in 1798,Thomas Malthus argued this • Answer • What is “that without the wars and epidemics to kill off the extra people, most were destined to be poor and miserable” Daily Double The Winner Of The Last Round Write Down How Many Points You Are Willing To Risk If You get the Question write you win those points If you get it wrong you Lose that amount of points! Daily Double The Winner Of The Last Round Write Down How Much Money You Are Willing To Risk If You get the Question write you win that money If you get it wrong you Loss the money!