Final Exam Chapters
advertisement

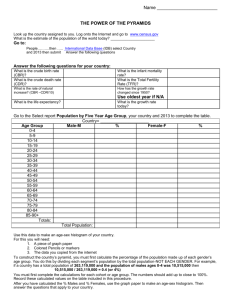
GEOG100 - Chapters for Final Exam: All reading should be completed with respective Power Points and labs Chapter 3: Geographies of population Population distribution and structure: population distribution, population density and composition, age-sex pyramid (dependency ratio; youth, middle, and old-age cohorts), population dynamics and processes (birth, fertility, death rates), natural increase and decrease, infant mortality and reasons, demographic transition theory Population movement and migration, push and pull factors, and factors shaping population distribution and composition Interpreting maps and diagrams: e.g. age-sex pyramid, the influencing factors and consequences Chapter 4: Nature, Society, and Technology Nature as a concept Religious perspective on nature Impacts of scientific and industrial revolutions on nature Energy and climate change Climate Change and vulnerability (you should be able to explain the CC indicators and their impacts on the population) Climate refugees Climate change adaptation versus mitigation Impacts of land-use, changes on the environment: deforestation and agriculture, and the relationship with Climate Change Chapter 8: Agriculture and Food Production Traditional forms of agriculture and major changes Different agricultural revolutions – you should be able to explain time, reasons and emerging factors The impacts of industrialization and technological innovations on our food system Green revolution (what, where, how, why) The three crisis Alternative movements (including permaculture) and solutions Chapter 10: Urbanization The role of the cities Urban origin: you should be able to trace the evolution in time with all the different periods seen in class, and the major factors of change World urbanization today: trends and projections Industrialization (contributing factors and impacts) and shock cities World cities and megacities The Von Thunen model Urban growth processes and economic interdependence: agglomeration effects, external economies, regional cores, cumulative causation, deindustrialization (Chapter 7: pp. 321-330) and, centralization and decentralization (p.471-474) Chapter 11: Urban structure Urban structure and land use: edge cities, gentrification, internal organization and districts Congregation and segregation: examples All the locational theories seen in class Planned urban design (start p.503 with modern movement) The concept of New Urbanism (like seen during the walking tour) Problems found in post-industrial cities: you should be able to provide me with examples seen in class and during the tour Problems found in developing cities (unintended metropolises) Colonial cities What is urban planning and urban design + Power Point on First Nations and Natural Resources in Canada and walking tours (lab 5)