FINANCE DECISIONS
advertisement

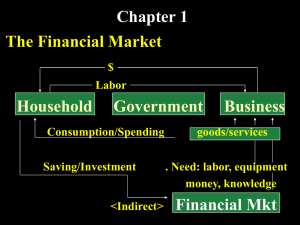
THE CORPORATION Legal entity created to sell goods and/or services. Owned by shareholders who purchase its stock. Possible returns to shareholders: – 1) dividends – 2) stock price appreciation FINANCE DECISIONS Investment Financing Dividend Investment What assets does the company need to accomplish its mission? Buildings, machinery, equipment? (Ch 7 and Ch 8) Cash, accounts receivable, inventory? (Ch 9) Financing How should firm’s assets be financed? Liabilities (debt) or Equity (selling new stock or reinvesting profits)? What is best mix of debt and equity? Valuation (Ch 5); Cost of Capital (Ch 6) Dividend What to do with Earnings After Taxes (profit, net income)? Pay dividends to stockholders? Reinvest into company (retained earnings)? Some combination of both? Goal of Financial Management Most people would say goal is to maximize profits Profits when? - this quarter, this year, next 5 years… Which measure of profit to use? - net income, income before extraordinary items, EPS… Better Goal Who owns firm? Stockholders. Why do they buy stock? To gain financially when stock price goes up (buy low, sell high) Goal: MAXIMIZE STOCK PRICE Advantages of Stock Price Maximization as a Goal Easy to measure Readily available Provides immediate feedback on how market values decisions of firm’s managers Disadvantage of Stock Price Maximization as a Goal Majority of stocks owned by institutional investors Managers of institutional funds push for short-term returns When corporate managers focus on short-term stock price maximization, they may make decisions harmful to the corporation in the long-run. Examples of Institutional Investors Mutual Funds Hedge Funds Private Equity Funds Sovereign Wealth Funds Pension Plans Insurance Companies Endowment Funds Stakeholders in a corporation Shareholders (individuals + institutions) Employees, including managers Customers Suppliers Community Creditors Government Stakeholder Theory Says that managers should make decisions that maximize interests of all stakeholders Example: UAW got BIG 3 Auto Makers to give big concessions in 1970s Look how that turned out in long-run for everyone! Agency Theory Managers are agents of stockholders (principal) Managers sometimes act in own interest instead of stockholders’ Adelphia, Enron, Global Crossing, Qwest, Tyco, WorldCom, to name a few Agency costs – making sure that managers are acting appropriately; e.g. auditing Long-term Decision Making All stakeholders, including employees, managers, and stockholders, have an interest in the continued operation of a corporation Managers should make decisions that maximize stock price in the long-run Taking the long view benefits all stakeholders 3 Steps to Follow in Making Financial Decisions Estimate impact of decision on future cash flows Adjust future cash flows for time value of money (Ch 3) Adjust future cash flows for risk (chance that actual cash flow will not be what is expected) (Ch 4) Where We Are Headed Ch 2: Overview of Financial Markets Ch 3: Time Value of Money Ch 4: Risk Ch 5 and Ch 6 – Financing Decision Ch 7, 8, 9 – Investment Decision Ch 10 – Financial Statement Analysis Ch 11 – Financial Planning