Final Exam Study Guide Your final exam will either be on Tuesday 1
advertisement

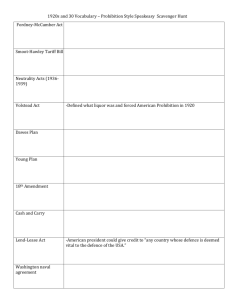
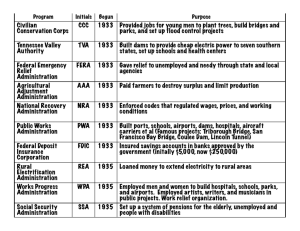
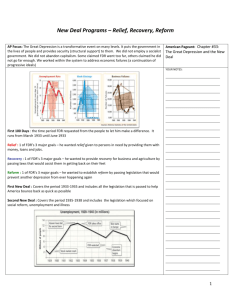
Final Exam Study Guide Your final exam will either be on Tuesday 1/13, Wednesday 1/14, or Thursday 1/15. The exam will be 100 multiple choice questions and will count for 10% of your final semester grade. The exam is cumulative. The content that you are responsible for knowing includes but is not limited to: WESTWARD HO Homestead Act of 1862 Manifest Destiny Morrill Land-Grant Act of 1862 Mining (Placer Method & Hydraulic Method) Boom Town Ghost Town Vigilante Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882 Cattle Drive Nomad Hunting Buffalo Mutilation Dawes Act Colonel George Custer Ghost Dance Battles & Massacres (Sand Creek, Little Bighorn, Wounded Knee) American Indian Chiefs (Crazy Horse, Sitting Bull, Wovoka INDUSTRIALIZATION Pacific Railway Act Union Pacific Central Pacific Continental U.S. Time Zones Robber Barons Corruption (Crédit Mobilier Scandal) Cornelius Vanderbilt John D. Rockefeller Andrew Carnegie Henry Clay Frick Nikola Tesla Philanthropists Kerosene Assembly Line Women’s Unions Homestead Strike IMPERIALISM Monroe Doctrine & the Roosevelt Corollary Yellow Journalism & the Spanish-American War (“Remember the Maine!”) Panama Canal Teddy Roosevelt (Open Door Policy & “Speak softly and carry a big stick”) Taft’s Dollar Diplomacy WORLD WAR I Royal Cousins (Kaiser Wilhelm II – Germany, Czar Nicholas II - Russia, King George V – UK) Causes of WWI (Powder Kegs) o Nationalism o Imperialism o Militarism o Alliances o Balkans Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand (Gavrilo Princip) Trench Warfare o No Man’s Land o Trench Foot o “Shell Shock” Technology of WWI o Airplanes, Tanks, U-Boats, Machine Guns, Artillery, Flamethrower, Poison Gas U.S. Entry into WWI o Sinking of the Lusitania o Unrestricted Submarine Warfare o Zimmerman Telegram o Conscientious Objector Russian Revolution Armistice (11:00am on 11/11/1918) ROARING TWENTIES Influential People of the 1920s o Aviators, Scientists & Inventors o Harlem Renaissance o Pop Culture o U.S. Presidents o “Traditional” vs. “Modern” America “Where Jazz Meets Hip Hop” Prohibition Flappers The Red Scare GREAT DEPRESSION Stock Market Crash of 1929 (Black Tuesday) Bull Market Buying on Margin & Margin Call Speculation Depression Bank Run Overproduction Hawley-Smoot Tariff Causes of the Great Depression Dust Bowl o Okies & their paths of migration o Hoboes o Tenant Farmers Bonus Army Margaret Bourke-White’s The Louisville Flood, 1937 Movies & Music of the 1930s NEW DEAL Moratorium Emergency Banking Relief Act Dole Subsidy Unionization Demagogue Court-Packing Plan 1932 Presidential Election (Hoover vs. FDR) FDR’s 3 R’s o Relief o Recovery o Reform Fireside Chats Demagogues (Father Charles Coughlin & Sen. Huey Long) Act or Program Agricultural Adjustment Act Acronym AAA Year Enacted Significance 1933 Protected farmers from price drops by providing crop subsidies to reduce production, educational programs to teach methods of preventing soil erosion. Declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court. Civilian Conservation Corps CCC 1933 Sent 250,000 young men to work camps to perform reforestation and conservation tasks. Removed surplus of workers from cities, provided healthy conditions for boys, provided money for families. Federal Emergency Relief Act FERA 1933 Distributed millions of dollars of direct aid to unemployed workers. Glass-Steagall Act FDIC 1933 Created federally insured bank deposits ($2500 per investor at first) to prevent bank failures. National Industrial Recovery Act NIRA 1933 Created NRA to enforce codes of fair competition, minimum wages, and to permit collective bargaining of workers. 1935 Response to critics (Dr. Townsend and Huey Long), it provided pensions, unemployment insurance, and aid to blind, deaf, disabled, and dependent children. 1933 Federal government built series of dams to prevent flooding and sell electricity. First public competition with private power industries Social Security Act Tennessee Valley Authority TVA Wagner Act NLRB 1935 Allowed workers to join unions and outlawed union-busting tactics by management. Organized elections by secret ballots to determine if workers wanted to form a union. Works Progress Administration WPA 1935 Employed 8.5 million workers in construction and other jobs, but more importantly provided work in arts, theater, and literary projects.