USII.6--FDR's New Deal
advertisement

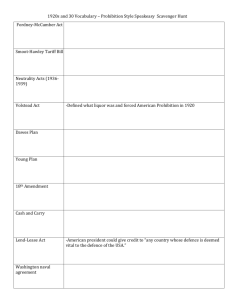
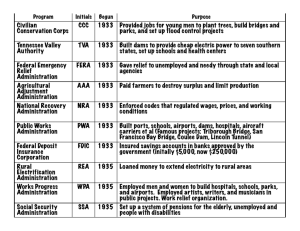
FDR and the NEW DEAL “The only thing we have to fear is…. fear itself” I promise a New Deal! Prosperity is just around the corner The Election of 1932 INTRO to FDR 1. Americans ready for a change 2. Elected with 23 million votes (57% of voting population) 3. More of a quarterback…willing to experiment The New Deal Complete Web: “Impact…” Categorize federal programs: Relief Recovery or Reform Read: WPA article and two letters (the last two letters in the “Letters to Eleanor packet” - Describe the impact of job programs individuals Slide show:Complete Chart Video: Develop an understanding of the AAA Laser Disc: Gather and check info on New Deal programs THE DUST BOWL Causes? Effects? Impact of the Depression on the American People LEGISLATIVE LEADERSHIP 1. THE FIRST 100 DAYS 2. PRESIDENT AND ADVISORS WRITE MAJOR NEW DEAL LAWS 3. CHECKS AND BALANCES 4. INCREASED POWERS OF PRES. Executive Power and the Role of Government Checks and Balances New Deal Themes Farmers Labor Executive Branch Suggests Legislation Congress: Legislates Programs Judicial Branch: Determines Constitutionality FDR – The Great Communicator 1. GREAT COMMUNICATION SKILLS 2. FIRESIDE CHATS – Connection to the people 3. PRESS CONFERENCES 4. NEW ROLES FOR THE FIRST LADY, ELEANOR ROOSEVELT The First 100 Days th 9 th 16 Between March and June 1933 Congress passed more than 15 major pieces of New Deal Legislation Relief Emergency Banking Act, 1933 Federal Emergency Relief Act, 1933 Public Works Administration, 1933 Works Progress Administration, 1935 Civilian Conservation Corps, 1933 Tennessee Valley Authority, 1933 Recovery Reform National Recovery Act, 1933 Glass-Steagall Banking Act, 1933 Home Owners Loan Corp, 1933 Securities Exchange Act, 1934 Federal Housing Administration, 1934 Agricultural Adjustment Act, 1933 and 1937 Social Security Act, 1935 National Labor Relations Act, 1935 Fair Labor Standards Act, 1938 THE NEW DEAL Relief for those suffering Emergency Banking Act Closed the nation’s banks (Bank Holiday) Bank examiners check banks Sound Banks Reopen Civil Works Administration (CWA) Created 3 million work relief jobs repairing roads, parks and public buildings; replaced with Works Progress Administration (WPA) Public Works Administration (PWA) Created jobs on government projects that increased worker buying power and stimulated the economy Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) 1. Provide employment for young men between ages of 1825 conserving natural resources 2. $2.5 million men participated during programs history Federal Emergency Relief Administration Distributed $500,000 to states and cities for direct relief and work projects for the homeless and unemployed Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) 1. Regional Development Project In Southeast 2. Intended to provide jobs, cheap electricity, flood control through construction of dams 3. Dams and power plants government owned THE NEW DEAL Recovery for the sick economy Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA) 1. Sought to control overproduction and increase prices of agricultural products 2. Paid farmers to reduce number of acres they planted and livestock raised 3. funded through a tax on food processors 4. Declared unconstitutional in 1936 (Butler v. U.S) National Industrial Recovery ACT (NIRA) 1. Established National Recovery Administration (NRA) 2. Suspended nation’s anti-trust laws 3. Trade Associations developed codes to regulate wages, working conditions, production, prices 4. Declared unconstitutional (Schecter Poultry v. U.S.) Home Owners Loan Corp Refinanced mortgages of middle income home owners THE NEW DEAL Reform to prevent another Depression Glass-Steagall Banking Act Social Security Act 1. Established Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. (FDIC) 1. Provided old age insurance, unemployment insurance 2. Insured Bank Accounts up to $5,000 2. Gave assistance to dependent children and the elderly, ill and handicapped Securities Exchange Act 1. Required full disclosure of stock offered for sale 2. Established Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to regulate stock market 3. Gave Federal Reserve Board power to regulate purchase of stock on margin National Labor Relations Act (Wagner Act) 1.Guaranteed Labor Right To Organize 2. Guaranteed Right to collective bargaining 3. Outlawed unfair labor practices like blacklisting 4. Created National Labor Relations Board CRITICISMS OF THE NEW DEAL: 1. OPPOSE INCREASED GOV’T ROLE IN ECONOMY (CREEPING SOCIALISM) 2. OPPOSE INCREASED TAXATION 3. OPPOSE DEFICIT SPENDING 4. OPPOSE WELFARE PROGRAMS CRITICISMS OF THE NEW DEAL: COURT PACKING 1. BUTLER V. U.S. & SCHECHTER V. U.S. 2. FDR PROPOSES INCREASING SIZE OF SUPREME COURT FROM 9 TO 15 3. PROPOSAL RAISES SERIOUS CONSITUTIONAL ISSUES 4. CONGRESS REJECTS PLAN (Checks and Balances) NEW DEAL: COURT CASES The United States vs. Schechter Poultry Corporation (1935) The Supreme Court rules the the NRA gave Congress the power to regulate intrastate commerce and violated sep of powers The United States vs. Butler (1936) The Supreme Court declares the AAA is unconstitutional on the grounds that agriculture is a local, not an interstate matter SCHECTHER (1935) BACKGROUND: Schecther Poultry Company bought, slaughtered, and sold chickens only in NYS and was charged with failing to observe minimum wage and hour provisions. ISSUE: Does the NIRA (and the President) have the power to regulate certain aspects of commerce during the Depression? OPINION: Congress, not the President has the power to regulate commerce BUTLER (1936) BACKGROUND: The 1933 AAA implemented a tax on the processing of agricultural commodities. ISSUE: Does the U.S. Congress exceed its power to tax and spend in order to provide for the general welfare of the US? OPINION: The AAA is unconstitutional because it attempted to regulate and control agricultural production, an areareserved to the states