Classification
advertisement

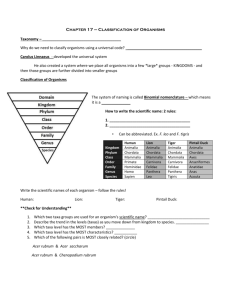
1 Classification is the grouping of objects based on similarities. Examine the evolutionary basis of modern classification systems. (six kingdoms) 2 Classification Classification is an important – In understanding how organisms are related and how they are different. – So that we can work with the diversity of life Taxonomy is the branch of biology that studies the grouping and naming of organisms. 3 Aristotle His classification system was based on structural differences that were seen. 4 Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) Swedish Botantist •Based his classification on characteristics of organisms that were similar. Developed the two word system used to identify species: binomial nomenclature. 5 Clip 6 Binomial Nomenclature Because scientists speak many different languages and common names for organisms may vary from place to place, a universal system for naming organisms is used. The scientific name of an organism is based on a two-word system called binomial nomenclature. 7 Quercus alba: is the name for white oak (alba is Latin for “white”) Quercus rubra: is the name for the red oak (rubra is Latin for “red”) Micropterus salmoides is the name for a largemouth bass 8 Binomial nomenclature •The two words, genus and species, are always italicized (or underlined). •The first word in a scientific name, genus, is always capitalized and the second word, species, is never capitalized. •For example the scientific name of the largemouth bass would be Micropterus salmoides (or Micropterus salmoides). 9 In addition to (1) appearance and (2) behavior, (3) molecular structure (e.g., DNA) and(4) evolutionary relationships are also considered when classifying organisms. Organisms that share more similarities are more closely related and are grouped together. 10 Eight levels of classification Least alike Domain Taxon: Group or level of classification Most alike Species is the most specific 11 Taxon Level HUMAN CHIMPANZEE HOUSE CAT LION HOUSEFLY KINGDOM Animalia Animalia Animalia Animalia Animalia PHYLUM Chordate Chordate Chordate Chordate Arthropoda CLASS Mammal Mammal Mammal Mammal Insect ORDER Primates Primates Carnivora Carnivora Diptera FAMILY Hominidae Pongidae Felidae Felidae Muscidae GENUS Homo Pan Felis Felis Musca SPECIES sapiens troglodytes domestica leo domestica Scientific Name ORGANISM Homo sapiens Pan troglodytes Felis domestica Felis leo Musca domestica 12 Example: Human Classification How would you write the scientific name? a. homo Sapiens b. Homo sapiens c. Homo Sapiens 13 CLASSIFICATION OF THE LARGEMOUTH BASS Domain Eukarya Kingdom Animalia (multicellular organisms that eat food) Phylum Chordata (animals with a backbone) Class Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes) Order Perciformes (perch-like fishes) Family Centrarchida (sunfishes) Genus Micropterus (types of bass) Species salmoides (largemouth bass) Largemouth Bass: Micropterus salmoides 14 15 KINGDOMS OF LIFE 16 Six Kingdoms of Life Plantae Protista EuBacteria Archaebacteria OLD NAME: MONERA Fungi Animalia Three Domains and Six Kingdoms: Three Domains: Bacteria- Unicellular and prokaryotic. 17 Autotrophic and Heterotrophic. Cell walls have peptidoglycan. Kingdoms: Eubacteria Archaea- Unicellular and prokaryotic. Cell walls do not have peptidoglycan. Kingdoms: Archaebacteria Eukarya- Eukaryotic. Kingdoms: Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia. 18 Bacteria •Eubacteria (true bacteria) & Archaebacteria contain prokaryotes, cells without membranebound organelles. •Microscopic & unicellular. •Archaebacteria are mainly found in extreme environments like the deep oceans, hot springs, and swamps. •Heterotropic & autotrophic Protista •unicellular and multicellular organisms with a variety of characteristics •eukaryotic organisms that lack complex organ systems and live in moist environments. •Heterotropic and autotrophic •Most are microscopic. Fungi •Consumers that stay put. •Unicellular or multicellular heterotrophic eukaryotes that absorb nutrients from dead and decaying matter by decomposing dead organisms and wastes in the environment. 19 Plantae Multicellular eukaryotes that photosynthesize. Most have cellulose cell walls and tissues that have been organized into organs and organ systems. Autotrophic-some parasitic- some carnivore. Animalia Multicellular consumersheterotrophic Cells do not have cell walls. Their tissues have been organized into complex organ systems; the nervous system, muscle system and digestive system, as well as others. 20 6 Kingdoms of Life Clip 22 Evolutionary relationship between the kingdoms. Clip A cladogram is a tree-like diagram showing evolutionary relationships. Any two branch tips sharing the same immediate node are most closely related. Cladogram 22.3 Illustrate relationships • Bacteria, Archaebacter ia, & the Prokaryotic Domains Video (8:51) 22.1 1a Two feet 2 1b Some other number of feet 3 2a Does not look at all human 4 2b Looks a lot like a human 5 3a One leg 6 3b Three or four legs 7 4a Fly-like Mosk Cara 4b Not fly-like 8 5a Seems to be a girl Rita Nita 5b Not a girl 9 6a Leg is curled , two feet Ru-ela.Brella 6b Leg is straight, one foot Giggles 7a Three legs 10 7b Four legs 11 8a Has webbed feet Hex Oculate 8b Clawed feet 12 9a Curly hair, no toes Lugio Wirum 9b Wiggly looking mouth, three toes on feet C. Nile 10a Very long nose, open mouth Elle E. Funk 10b Some other appearance 13 11a Has duck bill, two pinchers Tri D. Duckt 11b No arms or pinchers 14 12a Has ears, tail, and beak Grif Leon 12b Four eyes on stalks Eggur Ondy 13a One eye, webbed feet Cue Kide 13b Four stalked eyes, four pinchers Quadrumenox 14a Three toed feet, nose like a flower Tunia petalos 14b Spider-like, has spots Patterned mulywumpus 23 EOCT ALERT!!!! A multicellular organism that obtains its food by absorbing nutrients belongs to the kingdom A Animalia B Fungi C Plantae D Protista 24 The study of animals is known as A B C D botany ecology taxonomy zoology 25 In 1988, the tiger swallowtail, Papilio glaucus, was proclaimed Georgia’s state butterfly. The tiger swallowtail shares the most characteristics with members of which taxonomic level? A class B family C order D phylum 26 One main difference between members of the Kingdoms Plantae and Animalia is the ability to A obtain energy B reproduce C move D exchange gases 27 The table shows an early method of classifying animals. Which of the following best illustrates why the modern Linnaean classification system has replaced the system developed by Aristotle? A) Flying insects fly over both land and water. B) Eating habits of reptiles and some land mammals are different. C) Sea snake bones are similar to those of reptiles that live on land. D) Birds are warm-blooded like mammals. A group of prokaryotes that live in extreme environments are the A viruses B protists C eubacteria D archaebacteria 28 The complexity of body systems differs greatly among organisms. Which of the following organisms has developed organ systems for obtaining and utilizing energy? A B C D bacterium mushroom mouse virus 29 Ms. Wall, may I be excused? My brain is full.