5 Kingdoms of Life - Cellular
advertisement

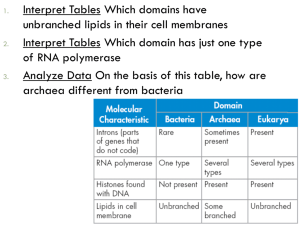
5/6 Kingdoms of Life! The five-kingdom system of classification for living organisms, including the prokaryotic Monera and the eukaryotic Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia is complicated by the discovery of archaebacteria. Living things have certain life processes in common. There are seven things that they need to do to count as being alive. The phrase MRS GREN is a way to remember them: M Movement All living things move, even plants R Respiration Getting energy from food S Sensitivity G Growth Detecting changes in the surroundings All living things grow R Reproduction Making more living things of the same type E Excretion Getting rid of waste N Nutrition Taking in and using food 3 Domains of Life Archaea - These microbes are Prokaryotes, meaning that they have no cell nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles in their cells, but are different to Bacteria Bacteria – are also Prokaryotes were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Eukaryotes - is any organism whose cells contain a nucleus and other organelles enclosed within membranes. 5 Kingdoms of Life Living organisms are divided into five kingdoms: Prokaryotae, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia Characteristics of living things - Living things are made of cells, obtain and use energy, grow and develop, reproduce, respond to their environment, adapt to their environment. Prokaryotae (Monera) - Unicellular and Microscopic. Nonmembrane bound (no nuclear membrane, no ER, no mitochondria). Cell wall made of murein. Examples: Bacteria, Cyanobacteria. 5 Kingdoms of Life Protista - Unicellular (mainly) Many live in aquatic environments. This is usually the kingdom including organisms which aren't animals, plants or fungi that don’t form tissues. Examples: Algae, slime molds and the malaria causing Plasmodium. Fungi - Multicellular, Cell wall made of chitin. The members of this kingdom don't possess photosynthetic pigments and are therefore heterotrophic. Examples: Mushroom, Mold, Puffball 5 Kingdoms of Life + Viruses Plantae - Eukaryotic, Multicellular, Cell wall made of cellulose. Members of the plantae group contain photosynthetic pigment and gain their energy through it and are therefore autotrophic. Animalia - Eukaryotic, Multicellular, Heterotrophic. The members of this kingdom can be split into two groups, vertebrates and invertebrates. Viruses (not living) - Acellular structures composed of nucleic acid enclosed by a protein coat. Not classified as living. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F38Bmg PcZ_I