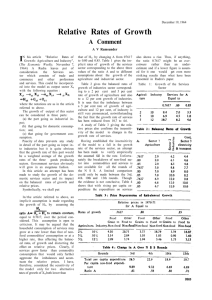
Lysbilde 1 - Norges Bank
advertisement

Charts Inflation Report 3/05 1 Monetary policy assessments and strategy Chart 1.1 CPI. Moving 10-year average1) and variation2). Per cent. Annual figures. 1980 – 20053) 14 14 12 12 10 CPI 10 8 6 8 Inflation target 6 4 4 2 2 0 0 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 The moving average is calculated 7 years back and 2 years ahead. 2) The band around the CPI is the variation in the period, measured by +/- one standard deviation. 3) Projections for 2005 – 2007 from this Report form the basis for this estimate. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 1.2 Estimates for the output gap. Level1) and variation2). Per cent. Annual figures. 1980 – 2005 8 8 4 4 0 0 -4 -4 -8 1980 -8 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 The output gap measures the difference between actual and projected potential mainland GDP. 2) The band shows the variation in the output gap measured by + one standard deviation. The variation is estimated as average standard deviation in a 10-year period, 7 years back and 2 years ahead. 1) Source: Norges Bank Chart 1.3 CPI and CPI-ATE1). 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Sep 05 6 6 4 4 2 0 CPI CPI-ATE 2 0 -2 -2 -4 2002 -4 1) 2003 2004 2005 CPI-ATE: CPI adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products. Source: Statistics Norway Chart 1.4 3-month real interest rate1) and the neutral real interest rate in Norway. Per cent. Quarterly figures. 96 Q1 – 08 Q42) 6 5 Real interest rate 6 5 4 4 3 3 2 1 Interval for neutral real interest rate 0 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 3-month money market rate deflated by inflation measured by the CPI-ATE. 2) The projected real interest rate for the period 05 Q4 – 08 Q4 is based on the baseline scenario. 1) Source: Norges Bank 2 1 0 Chart 1.5a The sight deposit rate in the baseline scenario with fan chart. Per cent. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 8 7 8 30% 50% 70% 90% 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 2004 0 2005 2006 Source: Norges Bank 2007 2008 Chart 1.5b Import-weighted exchange rate (I-44)1) in the baseline scenario with fan chart. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 110 30% 50% 70% 90% 110 100 100 90 90 80 80 70 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 70 1) A rising curve denotes a weaker krone exchange rate. It is assumed that strengthening by a certain percentage is just as likely as weakening by the same percentage. Source: Norges Bank Chart 1.5c Projected CPI-ATE in the baseline scenario1) with fan chart. 4-quarter change. Per cent. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 4 4 30% 50% 70% 90% 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 2004 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 Other measures of underlying inflation are shown in a separate box in Section 2. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 1.5d Estimated output gap in the baseline scenario1) with fan chart. Per cent. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 2 30% 50% 70% 90% 2 1 1 0 0 -1 -1 -2 2004 -2 2005 2006 2007 2008 Uncertainty concerning the current situation is not taken into account in the calculation. 1) Source: Norges Bank Chart 1.6a Interest rate projections for trading partners and interest rate differential. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 5 5 Baseline scenario 2) 4 3 3 Forward interest rates trading partners1) 2 1 4 2 1 Interest rate differential against trading partners3) 0 0 -1 2004 -1 2005 2006 2007 2008 Estimated as a weighted average of trading partners' forward rates. Forward rate at 27 October. 2) As in the two previous reports, the forward rate is adjusted somewhat as from 2007. 3) Interest rate differential against trading partners in the baseline scenario from 05 Q4 (broken line). 1) Source: Norges Bank Chart 1.6b Trading partners' interest rates1) in the baseline scenario with fan chart2). Per cent. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 8 7 8 30% 50% 70% 90% 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 2004 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 1) 3-month money market rate. 2) Fan chart is based on prices for interest rate options. Sources: Reuters and Norges Bank Chart 1.7 Projections for the CPI-ATE and output gap in the baseline scenario. Quarterly figures. Per cent. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 3 3 2 2 CPI-ATE 1 1 Output gap 0 0 -1 -1 -2 2004 -2 2005 2006 2007 2008 Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 1.8a House prices deflated by the house rent index in the CPI, building costs, household disposable income and total wage income. Indices, 1985 = 100. Annual figures. 1985 – 20051) 200 Deflated by house rent 200 Deflated by building costs 150 150 100 100 50 Deflated by disposable income Deflated by total wage income 0 0 1985 1) 50 1990 1995 2000 2005 Projections for 2005. Sources: Statistics Norway, Norwegian Association of Real Estate Agents (NEF), Association of Real Estate Agency Firms (EFF), FINN.no, ECON and Norges Bank Chart 1.8b House prices. Annual rise. Per cent. 1992 ― 20081) 18 18 14 14 10 10 6 6 2 2 -2 -2 -6 -6 -10 -10 1992 1) 1996 2000 2004 2008 Projections for 2005 ― 2008. Sources: Norwegian Association of Real Estate Agents, Association of Real Estate Agency Firms, Finn.no, ECON and Norges Bank Chart 1.8c Credit to households (C2). Annual percentage change in credit. 1992 – 20081) 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 1992 1) 1996 2000 Projections for 2005 ― 2008. Source: Norges Bank 2004 2008 Chart 1.9a Sight deposit rate in the baseline scenario and in the alternatives with stronger trade shifts and lower wage growth (red line) and higher inflation (yellow line). Per cent. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 8 7 8 30% 50% 70% 90% 7 6 5 4 6 Higher inflation 5 4 3 3 2 2 1 0 2004 1 Stronger trade shifts 2005 2006 Source: Norges Bank 0 2007 2008 Chart 1.9b Projected CPI-ATE in the baseline scenario and in the alternatives with stronger trade shifts and lower wage growth (red line) and higher inflation (yellow line). 4-quarter change. Per cent. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 4 4 30% 50% 70% 90% 3 3 2 Higher inflation 2 1 1 0 2004 Stronger trade shifts 2005 2006 2007 2008 Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank 0 Chart 1.9c Estimated output gap in the baseline scenario1) and in the alternatives with stronger trade shifts and lower wage growth (red line) and higher inflation (yellow line). Per cent. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 2 30% 50% 70% 90% 2 1 1 0 0 -1 -2 2004 Stronger trade shifts Higher inflation -1 -2 2005 2006 2007 2008 Uncertainty concerning the current situation is not taken into account in the calculation. 1) Source: Norges Bank Chart 1.10 3-month money market rate in the baseline scenario1) and band with highest and lowest forward interest rate last 10 days.2) Per cent. Quarterly figures. 05 Q4 ― 08 Q4 6 6 5 5 Baseline scenario 4 4 Highest and lowest forward interest rate 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 Oct 05 0 Oct 06 Oct 07 Oct 08 The money market rate is normally about ¼ percentage point higher than the sight deposit rate. 1) Highest and lowest forward interest rate in the period 14 – 27 Oct 2005. 2) Source: Norges Bank Chart 1.11 Sight deposit rate, Taylor rule, Orphanides rule and rule with external interest rates. Inflation as in the baseline scenario. Quarterly figures. Per cent. 00 Q1 ― 06 Q2 8 Taylor rate (blue line) 6 4 2 8 6 Orphanides’ rule (yellow line) Sight deposit rate (red line) Rule with external interest rates (green line) 0 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Source: Norges Bank 4 2 0 Chart 1.12 Sight deposit rate and interest rate developments that follow from Norges Bank's average pattern for the setting of interest rates.1). Per cent. Quarterly figures. 00 Q1 – 06 Q2 Interest rate movements that follow from Norges Bank's average pattern with a 90% confidence interval (grey area) 8 6 4 Sight deposit rate (red line) 8 6 4 2 2 0 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 0 The interest rate movements are explained by developments in inflation, mainland GDP growth, wage growth and 3-month interest rates among trading partners. See Inflation Report 3/04 for further discussion. 1) Source: Norges Bank Chart 1.13 CPI and scaled money supply (M2)1). Index, 2000 = 1. Annual figures. 1960 – 2004 1.4 1.4 M2 (red line) 1.2 1.2 1.0 1.0 0.8 0.8 CPI (blue line) 0.6 0.6 0.4 0.4 0.2 0.2 0.0 1960 0.0 1) 1970 1980 1990 M2 is scaled by GDP at constant prices. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank 2000 Chart 1.14 Money supply (M2). 12-month growth, estimated trend growth and intervals.1) Per cent. Monthly figures. Jan 93 ― Aug 05 14 14 30% 50% 70% 90% 12 12 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 0 0 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 1) Actual M2 growth is smoothed. Trend growth is estimated using a Hodrick-Prescott filter (λ = 100 000). The confidence intervals are based on the standard deviation calculated using the deviation between actual M2 growth and trend growth. Source: Norges Bank 2 The economic situation Chart 2.1 GDP growth in the US, the euro area and Japan. Seasonally adjusted volume growth on previous quarter. Per cent. 03 Q1 – 05 Q2 3 3 US 2 Japan 2 1 1 0 0 Euro area -1 -1 -2 -2 2003 2004 Sources: EcoWin and Norges Bank 2005 Chart 2.2 Consumer prices. 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Sep 05 5 5 US 4 4 Euro area 3 3 2 2 1 UK 0 2002 1) 1 Sweden1) 0 2003 UND1X. Source: EcoWin 2004 2005 Chart 2.3 Core inflation1). 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Sep 05 3 3 Euro area US 2 2 1 1 UK Sweden 0 2002 0 2003 2004 2005 US: CPI excl. food and energy. Euro area, UK and Sweden: CPI excl. energy, food, alcohol and tobacco. 1) Source: EcoWin Chart 2.4 Oil price. Brent Blend spot and light crude oil for future delivery. USD per barrel. Daily figures. 1 Jan 02 – 27 Oct 05 65 65 Spot 55 55 45 45 35 35 25 15 2002 Delivery in 6-7 years 25 15 2003 2004 Sources: Reuters and EcoWin 2005 Chart 2.5 Petrol and crude oil prices. Index, Jan 02 = 100. Daily figures. 1 Jan 04 – 27 Oct 05 500 500 Unleaded petrol 400 400 300 300 200 200 Crude oil 100 Jan 04 100 Jul 04 Source: EcoWin Jan 05 Jul 05 Chart 2.6 Crude oil production in the Gulf of Mexico shut down due to hurricanes. Share of total production capacity. Per cent. Daily figures. 29 Aug – 30 Nov in 2004 (Ivan) and 2005 (Katrina, Rita and Wilma) 100 100 Katrina 80 80 Rita 60 Wilma Ivan 60 40 40 20 20 0 0 Aug Sep Oct Source: Energy Administration Information Nov Chart 2.7 Interest rate expectations. Actual and expected key rate1) at 27 Oct 05 and 24 Jun 05. Daily figures. 2 Jan 03 – 1 Nov 06 6 6 5 5 UK Norway 4 4 3 3 2 2 Euro area 1 0 2003 Sweden US 1 0 2004 2005 2006 Broken lines show expectations at 27 October 2005. Dotted lines show expectations at 24 June 2005 (IR 2/05). Based on FRAs and futures contracts adjusted for the estimated difference between 3month money market rates and the key rate. 1) Sources: Reuters and Norges Bank Chart 2.8 The krone exchange rate (I-44)1). Monthly figures. Jan 00 – Oct 052). Relative labour costs in common currency3). Annual figures. Per cent. 2000 – 20054) 85 15 90 Relative labour costs in manufacturing (right-hand scale) 10 5 95 0 100 105 -5 I-44 (left-hand scale) 110 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 1) A rising -10 -15 curve denotes a stronger krone exchange rate. 2) Figures for Oct 05 are the average for the period 1 – 27 Oct 2005. 3) Deviation from average 1970 -2004. 4) 2005 is based on wage growth in the baseline scenario and TWI from 1 Jan – 27 Oct 2005. Source: Norges Bank Chart 2.9 Non-oil government budget deficit and petroleum investment. In billions of NOK. Annual figures. 2000 – 20061) 200 150 200 Non-oil deficit Petroleum investment 150 100 100 50 50 0 0 2000 1) 2003 2006 Projections for 2005 -2006. Sources: Statistics Norway, Ministry of Finance and Norges Bank Chart 2.10 Developments in some sub-indices on the Oslo Stock Exchange. Index, 2 Jan 96 = 100. Daily figures. 2 Jan 96 – 27 Oct 05 550 550 Financial 450 ICT 1) OSEBX 350 350 250 450 Energy 250 150 150 50 1996 Manufacturing 2) 1) Average 2) Average 1998 2000 50 2002 2004 of IT and telecommunications indices. of industrials and materials indices. Sources: Bloomberg and Norges Bank Chart 2.11 Demand. Average quarterly growth (annualised) in the upturn of the last 9 quarters1). Per cent 30 25 30 First 5 quarters Last 4 quarters 25 20 20 15 15 10 10 5 5 0 0 Priv. cons. 1) Public Mainl. Petr. Exp. cons. investm. investm. trad. goods 03 Q2 – 05 Q2. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 2.12 Credit to households1) and enterprises2). 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Aug 05 15 15 Households 12 12 9 9 6 Enterprises 6 3 3 0 0 -3 2002 -3 1) 2003 2004 From domestic sources (C2). credit to mainland Norway (C3). 2) Total Source: Norges Bank 2005 Chart 2.13 Turnover rate1) for new dwellings in Eastern Norway. Per cent. Feb 02 – Oct 05 15 15 10 10 5 5 0 2002 0 2003 2004 2005 Dwellings sold in last 2 months as a percentage of total number of new dwellings for sale in building projects. 1) Source: ECON Chart 2.14 Imports (total) and exports of traditional goods and services1). Volume index, 02 Q1 = 100. Quarterly figures. 02 Q1 – 05 Q2 130 130 Imports 120 110 120 110 Exports 100 90 2002 1) 100 90 2003 Travel and other services. Source: Statistics Norway 2004 2005 Chart 2.15 Mainland GDP. Seasonally adjusted, annualised quarterly growth. Per cent. 02 Q1 – 05 Q41) 6 6 3 3 0 0 -3 -3 02 Q1 1) 03 Q1 04 Q1 05 Q1 Projections for 05 Q3 and 05 Q4. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 2.16 Mainland GDP, employment and productivity1). Average quarterly growth (annualised) in the upturn of the last 9 quarters2). Per cent 5 5 First 5 quarters 4 Last 4 quarters 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 0 Mainland GDP No. employed Personhours worked Productivity Gross product per person-hour. 2) 03 Q2 – 05 Q2. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 2.17 Number employed. Developments after the start of a cyclical upturn. Index, quarter 0 = 100 110 110 82 Q4 91 Q4 03 Q1 106 106 102 102 98 98 -3 0 3 6 9 12 Quarters Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank 15 Chart 2.18 Unemployed. LFS unemployment, registered unemployed and persons on ordinary labour market programmes. In thousands. Seasonally adjusted. Monthly figures. Jan 00 – Oct 05 125 125 Registered unemployed and on labour market programmes 100 75 100 LFS unemployment Registered unemployed 50 75 50 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Sources: Statistics Norway and the Directorate of Labour Chart 2.19 Estimates for the output gap. Per cent. Annual figures. 1983 – 2005 5 5 3 3 1 1 -1 -1 -3 -3 -5 1983 1987 1991 1995 1999 2003 -5 Source: Norges Bank Chart 2.20 Capacity utilisation in manufacturing. Trend. Per cent. Quarterly figures. 90 Q1 – 05 Q2 85 85 83 83 81 81 79 Average 79 77 77 75 1990 75 1994 1998 2002 Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 2.21 Employment and person-hours worked. Percentage deviation from trend1). Quarterly figures. 82 Q2 – 05 Q2 5 3 5 Man-hours gap 3 1 1 -1 -1 -3 Employment gap -5 1982 1986 1990 1994 1998 2002 Trend calculated using HP filter. See Staff Memo 2005/2 (www.norges-bank.no) for further information. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank -3 -5 Chart 2.22 CPI-ATE1). Seasonally adjusted monthly change. 3-month moving average (centred), annualised. Jan 05 – Dec 052) 4 4 2 2 0 0 -2 -2 Jan 05 1) CPI-ATE: Apr 05 Jul 05 Oct 05 CPI adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products. 2) Projections for Sep 05 – Dec 05. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 2.23 Share of imports of clothing and footwear from low-cost countries1). Per cent. Monthly figures. Jan 01 – Sep 05 100 100 90 90 80 80 Volume 70 70 60 60 50 40 2001 50 Value 40 2002 2003 2004 2005 Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Poland, Romania, Slovenia, Czech Republic, Turkey, Hungary, Bangladesh, Philippines, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Cambodia, China, Malaysia, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, Taiwan and Vietnam. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 2.24 Share of imports of audiovisual equipment from low-cost countries1). Per cent. Monthly figures. Jan 01 – Sep 05 60 60 50 50 Volume 40 40 30 30 20 20 10 0 2001 Value 10 0 2002 2003 2004 2005 Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Poland, Romania, Slovenia, Czech Republic, Turkey, Hungary, Bangladesh, Philippines, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Cambodia, China, Malaysia, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, Taiwan and Vietnam. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 2.25 Share of imports of furniture and white goods from low-cost countries1). Per cent. Monthly figures. Jan 01 – Sep 05 40 30 40 Volume 30 20 20 Value 10 0 2001 10 0 2002 2003 2004 2005 Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Poland, Romania, Slovenia, Czech Republic, Turkey, Hungary, Bangladesh, Philippines, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Cambodia, China, Malaysia, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, Taiwan and Vietnam. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 2.26 CPI-ATE1). Total and by supplier sector2). With projections from IR 2/05 (broken line). 12month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Sep 05 6 6 Goods and services produced in Norway 4 2 4 2 CPI-ATE 0 0 -2 -2 -4 -4 Imported consumer goods -6 2002 2003 2004 -6 2005 1) CPI-ATE: 2) Norges CPI adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products. Bank's projections. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 2.27 CPI-ATE1) and estimates for the output gap2). Quarterly figures. Per cent. 00 Q1 – 05 Q43) 4 4 2 CPI-ATE 0 2 0 Output gap -2 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 -2 CPI-ATE: CPI adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products. Quarterly figures for the output gap have been derived from the annual figures. 3) CPI-ATE projection for 05 Q4. 1) 2) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank 3 Developments ahead Chart 3.1 Private consumption as a share of mainland GDP. Constant and current prices. Annual figures. Per cent. 1978 – 20081) 62 60 62 Share of consumption, value 60 58 58 56 56 54 Share of consumption, volume 54 52 52 1978 1983 1988 1993 1998 2003 2008 1) Projections for 2005 – 2008. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 3.2 Real growth in household disposable income1) and consumption. Annual figures. Per cent. 1990 – 20082) 8 Real income growth Real growth in consumption 6 8 6 4 4 2 2 0 0 -2 -2 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 1) Adjusted 2) for estimated reinvested share dividends since 2001. Projections for 2005 – 2008. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 3.3 Household saving ratio and net lending as a share of disposable income.1) Annual figures. 1980 – 20082) 10 10 Saving ratio 5 5 0 0 -5 -5 -10 Net lending -15 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 1) Adjusted -10 -15 for estimated reinvested share dividends since 2001. 2) Projections for 2005 – 2008. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 3.4 Underlying spending growth in the government budget and nominal growth in mainland GDP. Growth on previous year. Per cent. 1985 – 20061) 15 15 12 12 9 Underlying spending growth 6 3 6 Nominal growth in mainland GDP 0 3 0 1985 1988 1991 1994 1997 2000 2003 2006 1) 9 Projections for 2005 and 2006 from the Ministry of Finance. Sources: Ministry of Finance (National Budget 2006) and Statistics Norway Chart 3.5 Structural non-oil deficit and expected real return on the Government Petroleum Fund. In billions of 2006-NOK. Annual figures. 2001 – 2010 120 Use of petroleum revenues over and above the 4 per cent rule Expected real return 100 120 100 80 80 60 60 40 40 20 20 0 0 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 Source: Ministry of Finance (National Budget 2006) Chart 3.6 Oil price (Brent Blend) in USD per barrel. Futures prices from 24 Jun 05 and 27 Oct 05. Daily figures. 2 Jan 02 – 27 Oct 08 65 27 October 2005 55 24 June 2005 IR 2/05 65 55 45 45 35 35 25 25 15 2002 15 2004 Source: Reuters 2006 2008 Chart 3.7 Investment intentions survey for oil and gas activities incl. pipeline transport. Estimated and actual investment. In billions of NOK 80 2005 80 2004 2006 60 2003 60 2002 40 40 20 20 0 May Aug Nov Estimate published previous year Feb May Aug Nov Estimate published same year Source: Statistics Norway Feb 0 Final figures Chart 3.8 Investment in oil and gas recovery incl. pipeline transport. Investment level in billions of NOK (constant 2002-prices) and annual growth in per cent. 1995 – 20081) 30 100 Annual growth (left-hand scale) 20 90 10 80 0 70 -10 Investment level (right-hand scale) -20 50 -30 1995 1) 60 1998 2001 2004 Projections for 2005 – 2008. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank 2007 Chart 3.9 Investment intentions survey for power supply sector. Estimated and actual investment. In billions of NOK 12 10 12 2006 2005 10 2004 8 8 2003 6 2002 6 4 4 2 2 0 May Aug Nov Feb May Estimate published previous year Source: Statistics Norway Aug Nov Estimate published same year Feb Final figures 0 Chart 3.10 GDP and fixed investment. Mainland Norway. Percentage deviation from trend1). Quarterly figures. Per cent. 80 Q1 – 08 Q22) 20 GDP (right-hand scale) 4 10 2 0 0 -10 -2 Fixed investment, (left-hand scale) -20 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 Trend calculated using HP filter. See Staff Memo 2005/2 (www.norges-bank.no) for further details. 2) Based on annual projections for 2005 – 2008. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank -4 Chart 3.11 Oil price in NOK and terms of trade. Export price index relative to import price index, 1990 = 1. Quarterly figures. 90 Q1 – 05 Q2 400 Oil price in NOK (left-hand scale) 1.4 Total goods and services (righthand scale) 300 1.2 200 Traditional goods and services (right-hand scale) 100 0 1990 1 0.8 1993 1996 1999 2002 Sources: EcoWin and Statistics Norway 2005 Chart 3.12 International prices for industrial commodities in USD. Indices, 2000 = 100. Weekly figures. Week 1 2002 – Week 42 2005 160 160 140 Agricultural products excl. food 140 120 120 100 80 60 2002 Total industrials 100 80 Metals 60 2003 Source: EcoWin 2004 2005 Chart 3.13 Change in employment on previous year. Per cent. Unemployment1) as a percentage of labour force. Annual figures. 1980 – 20082) 4 8 LFS unemployment rate (right-hand scale) 2 6 0 4 -2 2 Number employed (left-hand scale) 0 -4 1980 1) 2) 1985 1990 1995 2000 LFS unemployment. Projections for 2005 – 2008. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank 2005 Chart 3.14 Labour force as a percentage of population aged 16 – 74 (labour force participation rate). Per cent. Annual figures. 1980 – 20081) 75 75 73 73 71 71 69 69 67 67 65 65 1980 1984 1988 1992 1996 2000 2004 2008 1) Projections for 2005 – 2008. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 3.15 Composition of the population. Change for various age groups from 2004 to 2008. Percentage points. Labour force participation rates for 2004 in brackets 2 2 1 1 0 0 -1 -1 -2 (49.1) (76.5) (87.1) (87.3) (62.3) (18.7) 16-19 20-29 30-39 40-54 55-66 67-74 Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank -2 Chart 3.16 Annual wage growth1) and LFS unemployment. Per cent. Annual figures. 1993 – 20082) Annual wage growth 6 6 4 4 Unemployment rate 2 2 0 0 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 1) Average for all groups. Including estimated costs of increase in number of vacation days and introduction of compulsory occupational pension. 2) Projections for 2005 – 2008. Sources: Technical Reporting Committee on Income Settlements, Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 3.17 CPI and CPI-ATE1). 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Dec 082) 6 4 6 4 CPI 2 2 CPI-ATE 0 0 -2 2002 -2 2004 2006 2008 CPI-ATE: CPI adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products. 2) Projections for Oct 05 – Dec 08. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 3.18 Consumer prices adjusted for tax changes1). Imported consumer goods. 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 90 – Sep 05 6 6 4 4 2 2 0 0 -2 -2 -4 -4 -6 1990 -6 1) 1993 1996 1999 2002 Norges Bank's calculations up to December 2003. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank 2005 Chart 3.19 Indicator of external price impulses to imported consumer goods measured in foreign currency. Annual figures. Per cent. 1995 – 20081) 2 2 1 1 0 0 -1 -1 -2 -2 -3 -3 1995 1) 1998 2001 Projections for 2005 – 2008. Source: Norges Bank 2004 2007 Chart 3.20 CPI-ATE1). Total and by supplier sector2). 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Dec 083) 6 Goods and services produced in Norway 4 2 0 6 4 2 CPI-ATE 0 -2 -2 Imported consumer goods -4 -4 -6 2002 -6 2004 2006 2008 CPI-ATE: CPI adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products. 2) Norges Bank's calculations. 3) Projections for Oct 05 – Dec 08. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Boxes Uncertainty surrounding future interest rate developments Chart 1 3-month money market rate and forward rates at time of publication of the Inflation Report. Per cent. Quarterly figures. 99 Q1 – 05 Q3 8 8 IR 2/01 IR 2/02 IR 2/00 6 6 IR 1/03 4 IR 2/99 IR 2/03 Forward interest rates 2 IR 2/04 3-month money market rate 0 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Source: Norges Bank 4 2 0 Chart 2 Average deviation between forward interest rates and actual 3-month money market rate in the period 1999 – 2005. Absolute value. Percentage points 3.0 3.0 2.5 2.5 2.0 2.0 1.5 1.5 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.5 0.0 0.0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Quarters ahead Source: Norges Bank Chart 3a Sight deposit rate in the baseline scenario with fan chart based on historical interest rate developments. Per cent. Quarterly figures. 05 Q1 – 08 Q3 8 30% 50% 70% 90% 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 0 2005 0 2006 Source: Norges Bank 2007 2008 Chart 3b Sight deposit rate in the baseline scenario with fan chart based on interest rate options1). Per cent. Half-yearly figures. 05 H1 – 08 H2 8 30% 50% 70% 90% 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 0 2005 0 1) 2006 2007 2008 Based on options prices at 27 October 2005. Source: Norges Bank Chart 4a US. 3-month money-market rate and forward interest rate with fan chart based on options prices calculated in June 2002. Per cent. Half-yearly figures. 01 H1 – 05 H1 12 12 30% 50% 70% 90% 10 10 8 8 Forward interest rate 6 6 4 4 2 2 0 2001 Actual interest rate 2002 2003 Source: Norges Bank 0 2004 2005 Chart 4b Norway. 3-month money-market rate and forward interest rate with fan chart based on options prices calculated in June 2002. Per cent. Half-yearly figures. 01 H1 – 05 H1 12 30% 50% 70% 90% 10 12 Forward interest rate 10 8 8 6 6 4 2 0 2001 4 Actual interest rate 2 0 2002 2003 Source: Norges Bank 2004 2005 Chart 5 The sight deposit rate in the baseline scenario with fan chart. Per cent. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 8 7 8 30% 50% 70% 90% 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 2004 0 2005 2006 Source: Norges Bank 2007 2008 Chart 6 Projected CPI-ATE in the baseline scenario1) with fan chart. 4-quarter change. Per cent. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 4 4 30% 50% 70% 90% 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 2004 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 Other measures of underlying inflation are shown in a separate box in Section 2. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Accuracy of short-term interest rate expectations Chart 1 Interval for the sight deposit rate at the end of each strategy period and actual developments. Daily figures. Per cent. 1 Jan 03 – 27 Oct 05 8 8 3/02 6 4 Strategy period 6 1/03 2/03 4 3/03 2 0 2003 1/04 2/04 2/05 1/05 3/04 Sight deposit rate 2 0 2004 Source: Norges Bank 2005 Monetary policy since 30 June 2005 Chart 1 Interval for the sight deposit rate at the end of each strategy period and actual developments. Daily figures. Per cent. 1 Jan 03 – 27 Oct 05 8 8 3/02 6 4 Strategy period 6 1/03 2/03 4 3/03 2 0 2003 1/04 2/04 2/05 1/05 3/04 Sight deposit rate 2 0 2004 Source: Norges Bank 2005 Price developments Chart 1 CPI, CPI-AT1) and CPI-ATE2). 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Sep 05 6 6 4 4 2 0 CPI CPI-ATE -2 -4 2002 2 0 -2 CPI-AT -4 2003 2004 2005 CPI-AT: CPI adjusted for tax changes. CPI-ATE: CPI adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products. 1) 2) Source: Statistics Norway Chart 2 CPI-ATE1) incl. and excl. prices for clothing and footwear2). Monthly change. Per cent. Jun 03 – Sep 05 1.0 1.0 CPI-ATE 0.5 0.5 0.0 0.0 -0.5 CPI-ATE excluding clothing and footwear -0.5 -1.0 Jun 03 Dec 03 Jun 04 Dec 04 Jun 05 -1.0 CPI-ATE: CPI adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products. 2) Norges Bank's calculations. 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 3 Prices for some imported consumer goods. 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Sep 05 5 5 Cars 0 0 -5 -5 Audiovisual equipment -10 -10 Clothing and footwear -15 2002 -15 2003 Source: Statistics Norway 2004 2005 Chart 4 Prices for goods and services produced in Norway1). 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Sep 05 7 Services with wages as a dominant factor (7) 7 5 5 3 3 1 -1 House rents (18) 1 Consumer goods produced in Norway2) (20) -3 2002 Other services (20) -1 -3 2003 2004 2005 1) Adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products. Percentage share of CPI-ATE in brackets. Norges Bank's calculations up to December 2003. 2) Excluding energy and agricultural and fish products. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 5 Three indicators of underlying inflation. 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 02 – Sep 05 5 4 5 Weighted median1) 4 Trimmed mean2) 3 3 2 2 1 1 CPI-ATE 0 0 -1 2002 -1 2003 2004 2005 Estimated on the basis of 93 sub-groups of the CPI. Price changes accounting for 20 per cent of the weighting base are eliminated. 1) 2) Source: Statistics Norway Chart 6 Oil price1) and components of the CPI that are particularly affected by the oil price. 12-month change. Per cent. Sep 05 40 40 30 30 20 20 10 10 0 0 Oil price 1) Petrol in Transport CPI services in CPI Brent Blend spot. Sources: Statistics Norway and Reuters CPI Output gap uncertainty Chart 1 Estimate and uncertainty for the output gap. Per cent. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 05 Q2 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 0 -1 -1 -2 -2 -3 Mar 04 -3 Sep 04 Source: Norges Bank Mar 05 Increased imports from low-cost countries Chart 1 Cumulative change in share of imports from various segments since 2000. Percentage points 10 Furniture and household articles 0 10 30 0 0 Audiovisual equipment 0 -10 -30 -10 2001 2002 2003 2004 EU15 and EFTA Asia ex. Jap. and China 30 15 Clothing and footwear 0 0 -30 -15 2001 2002 2003 2004 China Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank US and Japan 15 -15 2001 2002 2003 2004 Europe excl. EU 15 and EFTA Chart 2 Former and new indicators of external price impulses. Index, 01 Q1 = 100. Quarterly figures. 98 Q1 – 05 Q2 105 105 100 IPC former 100 95 95 IPC new 90 1998 90 2000 Source: Norges Bank 2002 2004 Chart 3 Former and new indicators of external price impulses to some product groups. Index, 01 Q1 = 100. Quarterly figures. 01 Q1 – 05 Q2 110 Furniture and household articles 110 Audiovisual equipment 110 Clothing and footwear 110 IPC former 100 100 100 IPC new 90 90 IPC former IPC former 90 100 90 IPC new 80 80 70 70 2001 2003 Source: Norges Bank 2005 2001 IPC new 2003 2005 80 80 70 2001 70 2003 2005 Effects of high oil prices on the world economy Chart 1 Oil price and estimates of the output gap (per cent) in the OECD countries and G7. Oil price in USD per barrel. Annual figures. 1971 – 2004 5.0 2.5 G7 (left-hand scale) 40 Oil price (right-hand scale) OECD (left-hand scale) 30 0.0 20 -2.5 10 -5.0 0 1970 1980 1990 2000 Sources: OECD Economic Outlook, EcoWin, Reuters and Norges Bank Chart 2 Oil intensity. Kilos oil per unit of real GDP adjusted for purchasing power parity. Index, 1971 = 100. Annual figures. 1971 – 2004 120 120 Non-OECD countries 100 100 80 80 60 60 OECD 40 40 20 20 0 0 1970 1980 1990 Sources: IMF and Norges Bank 2000 Chart 3 Real oil price and nominal oil price. USD per barrel. Real price in 2004-USD, deflated by the CPI in the US. Monthly figures. Jan 70 – Sep 05 120 120 Real oil price 100 100 80 Nominal oil price 80 60 60 40 40 20 20 0 1970 0 1980 1990 2000 Sources: EcoWin, Reuters and Norges Bank The projections in Inflation Report 2/05 and 3/05 Chart 1 CPI-ATE1). Total and by supplier sector2). Actual inflation and projections in IR 2/05 (broken line). 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 04 – Dec 05 4 4 Goods and services produced in Norway 2 2 CPI-ATE 0 0 -2 -2 -4 Jan 04 1) 2) Imported consumer goods -4 Jul 04 Jan 05 Jul 05 CPI-ATE: CPI adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products. Norges Bank's calculations. Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 2 CPI-ATE. Projections in IR 2/05, projections from a time series model and actual price movements. 12-month change. Per cent. Jan 05 – Sep 05 1.5 Projections IR 2/05 1.3 1.3 Time series model 1.1 0.9 1.5 Actual CPI-ATE 1.1 0.9 0.7 0.7 0.5 0.5 Jan 05 Mar 05 May 05 Jul 05 Sep 05 Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 3 3-month money market rate1) in baseline scenario in IR 2/05 and 3/05. Fan around interest rate from IR 2/05. Per cent. Quarterly figures. O4 Q1 – 08 Q4 8 7 6 5 8 30% 50% 70% 90% 7 Interest rate in IR 3/05 Interest rate in IR 2/05 6 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 2004 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 The money market rate is normally about ¼ percentage point higher than the sight deposit rate. 1) Source: Norges Bank Chart 4 Krone exchange rate (I-44)1) in baseline scenario in IR 2/05 and 3/05. Fan around exchange rate from IR 2/05. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 110 30% 50% 70% 90% 100 110 I-44 in IR 3/05 I-44 in IR 2/05 100 90 90 80 80 70 2004 70 2005 1) A rising 2006 2007 2008 curve denotes a weaker krone exchange rate. It is assumed that strengthening by a certain percentage is just as likely as weakening by the same percentage Source: Norges Bank Chart 5 Estimates for output gap1) in IR 2/05 and 3/05. Fan2) around estimate in IR 2/05. Per cent. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 2 2 1 1 0 0 30% 50% 70% 90% -1 -2 2004 Output gap in IR 3/05 Output gap in IR 2/05 2005 2006 2007 -1 -2 2008 The output gap measures the difference between actual and trend mainland GDP. 2) Uncertainty concerning the current situation is not taken into account in the calculation. 1) Sources: Norges Bank Chart 6 Projections for CPI-ATE1) in IR 2/05 and 3/05. Fan around projection in IR 2/05. Per cent. Quarterly figures. 04 Q1 – 08 Q4 4 4 30% 50% 70% 90% 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 -1 2004 CPI-ATE in IR 3/05 CPI-ATE in IR 2/05 0 -1 2005 2006 2007 2008 CPI-ATE: CPI adjusted for tax changes and excluding energy products 1) Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Chart 7 Mainland GDP. The last two projections published for 20061). Percentage growth 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 0 May Oct FIN 1) All Jun Sep SN Jun Oct CF Jun Nov NB projections published in 2005. Sources: Revised National Budget 2005, National Budget 2006, Economic Survey 2/05 and 3/05, Inflation Report 2/05 and 3/05 Consensus Forecasts June and October 2005 Chart 8 CPI-ATE. The last two projections published for 20061). Percentage rise 2.5 2.5 2.0 2.0 1.5 1.5 1.0 1.0 0.5 0.5 0.0 1) All May Oct FIN Jun Sep SN Jun Nov NB projections published in 2005. Sources: Revised National Budget 2005, National Budget 2006, Economic Survey 2/05 and 3/05, Inflation Report 2/05 and 3/05 0.0 Annex I Regional network Chart 1 Norges Bank’s regional network: demand and production. Index1). Oct 02 – Sep 05 5 Suppliers to the petroleum industry 3 3 Construction 1 5 Export industry -1 1 -1 All industries -3 -3 -5 -5 2002 2003 2004 2005 The scale runs from -5 to +5, where -5 indicates a large fall and +5 indicates strong growth. See article "Norges Bank's regional network" in Economic Bulletin 3/05 for further information. 1) Source: Norges Bank Chart 2 Norges Banks regional network: investment plans. Change in investment in next 6 – 12 months. Index1). Oct 02 – Sep 05 5 3 5 3 Municipal and hospital sector Retail trade 1 -1 1 Services -1 Manufacturing -3 -3 -5 -5 2002 2003 2004 2005 The scale runs from -5 to +5, where -5 indicates a large fall and +5 indicates strong growth. See article "Norges Bank's regional network" in Economic Bulletin 3/05 for further information. 1) Source: Norges Bank Annex II Charts Chart 1 Norwegian interest rates. 3-month money market rate, sight deposit rate and 10-year government bond yield. Monthly figures. Jan 95 – Sep 05 10 10 8 10-year government bond yield 3-month money market rate 8 6 6 4 4 2 Sight deposit rate 0 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Source: Norges Bank 2 0 Chart 2 3-month interest rates in the US, the euro area and Japan. Monthly figures. Per cent. Jan 95 – Sep 05 10 10 8 8 US 6 4 6 Euro area1) 4 2 2 Japan 0 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 1) Theoretical ECU rate up to and including December 1998. Source: EcoWin 0 Chart 3 3-month interest rates in the UK, Sweden and among trading partners. Per cent. Monthly figures. Jan 95 – Sep 05 10 8 10 Sweden 6 8 UK 4 2 4 Trading partners 0 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Sources: EcoWin and Norges Bank 6 2 0 Chart 4 Trade-weighted exchange rate index (TWI) and import-weighted exchange rate (I-44).1) Monthly figures. Jan 95 – Sep 05 115 115 Trade-weighted exchange rate index, TWI (1990 = 100) 110 110 105 105 100 100 95 Import-weighted exchange rate, I-44 (1995 = 100) 90 85 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 1) A rising curve denotes a weaker krone exchange rate. Source: Norges Bank 95 90 85 Chart 5 Bilateral exchange rates1). Monthly figures. Jan 95 – Sep 05 10 NOK/USD (left-hand scale) NOK/EUR (left-hand scale) 9 110 100 8 90 7 NOK/SEK (right-hand scale) 80 6 70 5 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 60 1) A rising curve denotes a weaker krone exchange rate. Source: Norges Bank Chart 6 The credit indicator (C2), credit to households and total credit to the nonfinancial private sector and municipalities, mainland Norway (C3). 12-month rise. Per cent. Jan 97 – Aug 05 20 20 15 15 Credit to households 10 C2 5 C3 Mainland Norway 0 1997 10 5 0 1998 1999 Source: Norges Bank 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005