What Should You Take?
advertisement

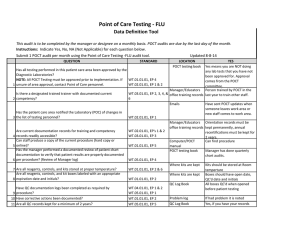
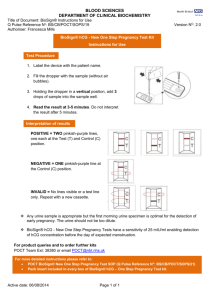
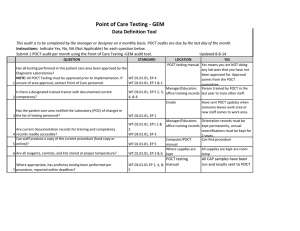
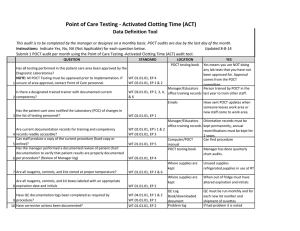
Sandwell and West Birmingham Hospitals NHS NHS Trust Tips For MRCpath Success Loretta Ford Jonathan Berg Clinical Biochemistry City Hospital, Birmingham What To Expect • Three hours long • Afternoon of the second day • Spectrophotometers -you will be given time before practical for familiarisation. If ever used again! • Told this on day one What Should You Take? Essential: Lab coat Gloves Pipettes (at least 1 ml and 5 ml) Pipette tips Marker pen Make sure you Calculator Ruler know how to use Graph paper the equipment! Desirable: Parafilm Stop clock Plain 10 ml Universal Containers Plastic test tubes Pastettes Thermometer Box of consumables at front of room (but you should not really need them) Books & Notes • • • • • Bring any books/notes into exam Tietz obvious choice Little time in exam to read books! Better off compiling own folder Google will provide plenty of ready made notes Practical Folder Suggested Contents • Most past papers involve urine analysis • Far easier for examiners to provide urine than blood • Limits the number of analysis that can be performed think: creatinine proteins drugs of abuse • POCT becoming more popular: glucose meters Practical Folder Suggested Contents • Enzyme kinetics: (km/vmax) Michaelis-Menten, Lineweaver-Burk • Reference intervals (especially urine tests) • Conversion tables for units of common analytes • Chemistry of ATP/NADH • Advantages/disadvantages of POCT • Equations e.g. A=CL, MDRD Before you pick up a pipette! • Spend 10 min reading to the end of the paper (recommend read twice!) • Write notes at front of workbook as you go along • Underline important points • Create a Work Plan • Make sure the work you do answers all the examiners questions Before you pick up a pipette! • Check you have all the reagents listed • Check you have enough reagents for the work you propose • Are reagents in date? • Observations e.g. if reagents are cold and kit insert says they should be used at RT point this out • Check lot numbers • For POCT is device CE Marked? Don’t worry If everyone else has started while you do this it maybe half hour before you start -preparation is everything! Practical work and writing up For each experiment you will need: • Title (aim of experiment) • Methods • Results Always present data in a tabulated form Graphs must have a title and labelled axis Make a note of any observations e.g. colour change • Conclusions Include further work e.g. what the next experiment will be Practical work and writing up Most practicals require: Calibration curve (unless stated use min 3 points) Measurement of standards & unknown samples Investigation of interference Use your initiative (only if time & reagents allow!) What happens if POCT results are read after 5, 10 min instead of 2 Practical work and writing up Short Report to Consultant • Popular inclusion in recent practicals • Create a template for your Practical Folder (especially for POCT device) • Discuss contents of report with supervisor Final Summary Summarise all results on a single page in tabulated form What if it all goes wrong? • Write down any mistakes • If you can explain what went wrong even better • Try to repeat wrong experiments correctly • If you have run out of time/reagents write down what you would of done Remember…. • Marks can only be given for what you have written down! • Write legibly –keep work as neat as possible • Explain clearly everything you do • Write down all observations • Keep an eye on the time • Even if you have not finished leave at least 15 min at the end to make sure you have written everything down! • Always read to the end of the paper before starting!!! Don’t cry…….. Examples Example Questions: Comparison of 2 POCT glucose devices Study of the cross-reactivity of a drugs of abuse POCT device