Biomedical equipment revision Question I: Define:
advertisement

Biomedical equipment revision
Question I: Define:a. drift
As components age and equipment undergoes changes in temperature
or humidity or sustains mechanical stress, performance gradually degrades. This
is called drift
b. Calibration
Process of comparing an unknown against a reference standard within
defined limits, accuracies and Uncertainties
c. Verification
Process of comparing an unknown against a reference standard at
usually one data point
d. Ultrasound
Mechanical vibration of frequency greater than 20 KHz
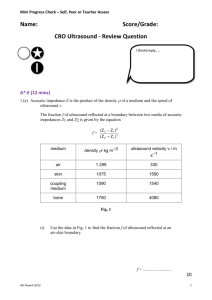
e. Acoustic Impedance
When an ultrasound wave meets a boundary between two different materials
some of it is refracted and some is reflected. The reflected wave is detected by the
ultrasound scanner and forms the image. The proportion of the incident wave that
is reflected depends on the change in the acoustic impedance, Z.
Acoustic Impedance, Z of a medium is defined as:
Z = c
Where = the density of the material, kgm-3
c = speed of sound in that material, ms-1
f. Intensity reflection coefficient,
At a boundary between mediums, the ratio of the intensity reflected, Ir to the intensity
incident, I0 is known as the intensity reflection coefficient, .
α=
𝐼𝑟
𝐼𝑜
The intensity of both the reflected and incident ultrasound waves depend on the acoustic
impedance, Z of the two mediums. Therefore the fraction of the wave intensity reflected
can be calculated for an ultrasound wave travelling from medium 1, (acoustic impedance Z1)
to medium 2 (acoustic impedance Z2).
𝛼=
𝐼𝑟
𝑍1 − 𝑍2 2
={
]
𝐼𝑜
𝑍1 + 𝑍2
If 2 mediums have a large difference in impedance, then most of the wave is reflected. If
they have similar impedance then none is reflected.
Question II: Answer
1-What to TEST for?
2-
3-
4-
5-
g. Performance Testing
h. Safety Testing
When to test equipment
a. prior to being accepted for use
b. During preventative maintenance.
c. After repairs.
Why we Need for Medical Equipment Testing?
a. Medical device incidents resulting in patient injury and death
• Ensure that the equipment is performing to the expected standards of
accuracy, reliability, free of hysteresis and linear (as designed).
• Safe and effective devices need to be available for
patient care
– Downtime costs money
• Regulations, accreditation requirements and standards.
Why do we do electrical safety?
a. Ensure patient safety
i. Protect against macroshock
ii. Protect against microshock
b. Test for electrical internal breakdown / damage to power cord, AC mains
feed, etc.
c. Meet codes & standards
i. Association of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI),
ii. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC),
iii. National Federation of Paralegal Associations (NFPA), etc.
d. Protect against legal liability
i. In case of a patient incident
Compare between Curvilinear, Rectilinear, Pseudo rectilinear chart recorder
6- Mention Writing Methods Used in Strip Chart Recorders.
a. Thermal, and Direct contact
i. Both of these types use a special writing stylus (rather than a pen
and a knife edge, also called writing edge)
ii. The mark on the paper by the contact of the stylus on the paper
along the knife edge,
iii. The stylus tip travels in a curvilinear path, but the resulting trace is
rectilinear because the knife edge is straight.
iv. The stylus can write anywhere along its length, so by keeping the
knife edge straight under the paper, we obtain the rectilinear
recording that shows waveshape as well as amplitude
b.
7- Mention writing systems are commonly used on PMMC recorders
a. direct contact,
b. thermal pen
c. ink pen
d. ink jet
e. Optical
8- Explain circuit for Servo recorders and recording potentiometers
In potentiometeric measurements a three-terminal variable resistor (potentiometer)
is connected to produce an output voltage that is a function of both a reference
potential and position of the variable resistor’s wiper arm.
A galvanometer will read zero when the unknown voltage and potentiometer
voltage are equal.
9- Explain A slide-wire potentiometer
10- Compare between Curvilinear recording, Rectilinear recording and Pseudo rectilinear
writing system
11- Compare between ultrasound and x-ray
ultrasound
Mechanical waves
Speed depends on the medium
safe
Frequency greater than 20 kHz
Cannot penetrate any substantial gas-layer.
Cannot penetrate mature
adult bone
(brain).
X-ray
Electromagnetic waves
Speed of light
Ionizing radiation have physiological effects
3×10 16 Hz to 3×10 19 Hz
Penetrate gas
Penetrate none
12- Explain different Writing Methods Used in Strip Chart Recorders
Question III: Complete:
i- The main components of x-ray unit are X-ray tube, X-ray electrical
power generator, Control unit, Film or digital system and additional
components are Table unit, Bucky film tray and grid system, and
Suspension system
ii- Main components of a modern x-ray tube are Glass Tube, Cathode- (which
consists of three parts Filament, Supporting wires and Focusing cup), and
Anode (two types Stationary and rotating).
iii- Properties of X-rays
b. X-rays travel in straight lines.
c. X-rays cannot be deflected by electric field or magnetic field.
d. X-rays have a high penetrating power.
e.
f.
g.
h.
Photographic film is blackened by X-rays.
Fluorescent materials glow when X-rays are directed at them.
Photoelectric emission can be produced by X-rays.
Ionization of a gas results when an X-ray beam is passed through
it.
iv. Minimum wavelength in the X-ray Spectra
min
hc
eV
v. maximum frequency in the X-ray spectra:
f max
eV
h
vi. Absorption mechanisms convert the energy of an acoustic wave to heat as the wave
propagates through a medium. A plane ultrasonic wave in an absorbing medium will lose
intensity as
I ( x) I 0 e 2x
vii. Ultrasound systems must contain some form of the five system blocks.
–
Display - The system will have some way of displaying the data it acquires.
–
User Interface - It must have a user interface, this may be mechanical or
voice activated.
–
Transducer – Your ultrasound system will have a transducer to convert
electrical impulses to sound and back.
–
Image Processing - The ultrasound machine will have some sort of image
processing. This may be analog or digital.
–
Power Supply - Finally it will have a power supply, again analog or digital.
And Peripherals may include cameras, or printers.
viii. In the case of ultrasound two transducer function are recognized:
–
conversion of ac electric oscillation into acoustic vibration, and
–
Conversion of acoustic vibrations into ac oscillations of the same frequency.
–
These two functions are the transmitter and receiver transducers.
ix. Radiation is generated by means of:–
electromagnetic (EM)
–
ultrasound
–
electrons
And Displayed for interpretation on
–
Film
–
photograph or
–
computer display monitor
x. types of x-ray: diagnostic and therapeutic and diagnostic devices divided into still
picture, continuous picture and scan tomography
Question IV:
Draw a schematic diagram for:
-
Curvilinear recording
-
Rectilinear recording
-
Pseudo rectilinear writing system



![Jiye Jin-2014[1].3.17](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005485437_1-38483f116d2f44a767f9ba4fa894c894-300x300.png)

