Vocabulary from Night
advertisement

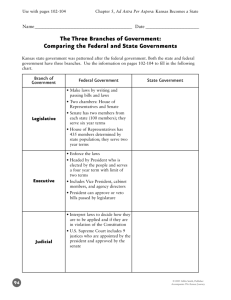
Legislative BranchReview SSCG9 The student will explain the differences between the House of Representatives and the Senate, with emphasis on terms of office, powers, organization, leadership, and representation of each house. SSCG10 The student will describe the legislative process including the roles played by committees and leadership. a. Explain the steps in the legislative process. b. Explain the function of various leadership positions within the legislature. SSCG11 The student will describe the influence of lobbyists (business, labor, professional organizations) and special interest groups on the legislative process. a. Explain the function of lobbyists. b. Describe the laws and rules that govern lobbyists. c. Explain the function of special interest groups. Essential Questions • How does a bill become a law? • What powers does Congress have? • What are some of the leadership positions within the legislature? • How are the House and Senate similar/different? • How do lobbyists and special interest groups influence government? Learning Target • SWBAT review all material covered over Standards 9, 10 and 11!! At least 30 years old • How old do you have to be to be in the Senate? At least 25 years old • How old do you have to be to be in the House of Representatives? 435 • How many members in the House of Representatives? 100 • How many members in the Senate? Majority/Minority Whips • Who is responsible for counting votes and convincing people to vote the way their party wants? Members of Congress • Who is responsible for introducing bills? The House of Representatives • If a bill is started and passed in the Senate, where will it go next? Pocket veto and veto • What 2 ways can the President deny the passage of a bill? Congressional override • What can congress do if the president vetoes a bill? The speaker controls daily activities, refers bills, calls for votes • Why is the Speaker of the House considered the most powerful person in the House of Representatives? The VP is the president of the senate and votes to break a tie • What purpose does the Vice President serve in the Senate? Citizens can write bills • What role can citizens play in the creation of a bill? 7 years • How many years must a member of the House of Representatives been a citizen prior to running for office? House, Senate and President • What 3 groups/individuals must pass a bill before it becomes a law? The president pro tempore • Who usually acts as the Senate’s presiding officer? Every 2 years, 1/3 of the Senate and every member of the House run for election or re-election • When do members of the House and Senate run for election/Re-election? It can veto proposed laws • What check can the executive branch place on Congress? A joint committee • Which committee is always made up of members of both the Senate and the House of Representatives? filibuster • The use of long speeches to prevent a vote on a bill. Constituents • People represented by a Senator or a Representative are known as… 2 years • The term of office for a member of the House of Representatives is cloture • What ends the debate on a bill? 2 senators per state • What is representation in the Senate determined by? Bill • What is a proposed law called? Interest groups • Private organizations whose members share certain views and work to shape public policy Represent interest groups and try to convince legislators of their position • What do lobbyists do? Make laws • What is the main job of the legislative branch? Is vetoed by pocket veto • If the president fails to take action on a bill that has been passed just before the end of a congressional session (within 10 days of the end of a session), the bill… Congress • Term used when referring to the House of Representatives and the Senate. 67% or 2/3 • To override a Presidential veto, what percentage of Congress is needed? 2 • How many Senators does each state have? representatives • A census is taken to determine population every 10 years. After a census is taken, the number of _____________ for a given state may change Single-Issue Group • MADD or Mothers Against Drunk Driving is an example of this type of interest group. Bill of attainder • A law that convicts a person of a crime without a trial The Senate approves presidential appointments, like ambassadors, judges and cabinet members • What is a special duty of the Senate? All bills that deal with raising money (like taxes) must start in the House • What is a special duty of the House of Representatives? A bill can start in either chamber of Congress • Does a bill have to start in the House or Senate in order to go through the legislative process? Markup • Process of making changes to a bill during the legislative process legislate • To write laws LEGISLATIVE PROCESS • MAKE SURE YOU KNOW THE LEGISLATIVE PROCESS!!! STUDY THE LEGISLATIVE PROCESS FLOW CHART! YOU WILL HAVE TO FILL ONE OF THESE OUT!!!!!!