Area and volume - Education Scotland
advertisement

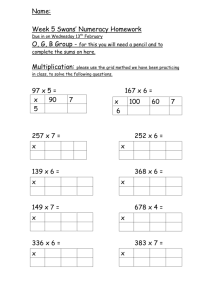
Scottish Survey of Literacy & Numeracy Support material for Measurement Third Level - Area and Volume Produced by Education Scotland Transforming Transforming lives lives through through learning learning Scottish Survey of Literacy and Numeracy 2011 Performance of Measurement at Third Level Based on the recent SSLN 2011 survey, evidence indicates that over a third of S2 pupils answered correctly, questions based on the measurement organiser, which involves the following Es and Os. I can solve practical problems by applying my knowledge of measure, choosing the appropriate units and degree of accuracy for the task and using a formula to calculate area or volume when required. MNU 3-11a Having investigated different routes to a solution, I can find the area of compound 2D shapes and the volume of compound 3D objects, applying my knowledge to solve practical problems. MNU 3-11b Scottish Survey of Literacy and Numeracy 2011 Evidence from this survey also suggests that pupils have difficulty with other aspects of measurement at S2 : • Calculations involving perimeter, area and volume as well as how to use one value to calculate the other • Problem solving in context of length, perimeter, area and volume • Where smaller items do not fit exactly into larger items relating to volume and area. • Fractions, decimal fractions and percentages as a secondary organiser • Conversion of units for length, weight and volume ( also second level). Prior Learning from Second Level Building on prior learning from second level experiences and outcomes relating to measurement: Pupils should be confident and competent with… • Identifying shapes in and around their environment • Using an appropriate measuring device and then apply them for use in real life situations. • Making an estimate of measure • Finding the perimeter and area of a simple 2D shape or volume of a simple 3D object • Converting between related units of the metric system • Using the vocabulary associated with the metric system. Building on prior learning from Es and Os relating to number processes: Pupils should be confident in using whole numbers, fractions and decimal fractions using a range of methods in a range of contexts. Scottish Survey of Literacy and Numeracy 2011 Measurement at Third Level Based on the recent SSLN 2011 survey, evidence indicates that over a third of S2 pupils answered correctly, questions based on the measurement organiser, which involves the following Es and Os. I can solve practical problems by applying my knowledge of measure, choosing the appropriate units and degree of accuracy for the task and using a formula to calculate area or volume when required. MNU 3-11a Having investigated different routes to a solution, I can find the area of compound 2D shapes and the volume of compound 3D objects, applying my knowledge to solve practical problems. MNU 3-11b Scottish Survey of Literacy and Numeracy 2011 In particular, a question focusing on a practical problem involving perimeter : Less than a fifth of pupils answered this question correctly. Question: Perimeter problem solving Farmer Brown wants to make a rectangular chicken run. He bought 18 meters of fencing wire and fixes the wire to posts 1 meter apart. What is the longest run that he can make for his chickens? Learners’ responses include A 8m B 9m C 17m D 18m E 16m Scottish Survey of Literacy and Numeracy 2011 In a similar question from the 2011 SSLN survey, one tenth of pupils gave the correct response of 3cm. Question A cube has a volume of 27 cm3. What is the length of one side of the cube? Reflective questions • What other response(s) do you think pupils would have given? • Why do you think this type of question causes difficulties for pupils? • When planning learning and teaching, how could you help pupils overcome any difficulties with this type of question? Third Level - Experiences & Outcomes I can solve practical problems by applying my knowledge of measure, choosing the appropriate units and degree of accuracy for the task and using a formula to calculate area or volume when required. MNU 3-11a Having investigated different routes to a solution, I can find the area of compound 2D shapes and the volume of compound 3D objects, applying my knowledge to solve practical problems. MTH3-11b Linking length, area and volume Volume Area Length Area: Applying my knowledge to solve practical problems Consider the following task… A new business has taken over an existing floor space and wishes to replace the existing floor covering. Area : Strategy 1 “Having investigated different routes to a solution, I can find the area of compound 2D shapes” 3m 5m 8m 9m A B 12m Area A = (8 x 3)m² = 24m² Area B = (9 x 3)m² = 27m² Total Area = 51m² 3m Strategy 2 3m A 5m 9m 8m B 12m Area A = (5 x 3)m² = 15m² Area 2 = (12 x 3)m² = 36m² Total Area = 51m² 3m Strategy 3 3m 9m 5m 8m 3m 12m Area of large rectangle = (12 x 8)m² = 96m² Area of yellow rectangle = (9 x 5)m² = 45m² Area of blue shape = (96 – 45)m² = 51m² How could this problem have been differentiated to meet the needs of all learners? For example, omit some of the lengths… 5m 6m 7m 10m 4m 12m Some alternative compound shapes… Extract from explanations in Principles and Practice paper for Numeracy states that : ‘for young people, with well developed understanding, problems involving circular properties could be introduced and investigated’ MTH 3-11b Perimeter: Prior learning at Second Level I can explain how different methods can be used to find the perimeter and area of a simple 2D shape or volume of a simple 3D object. MNU 2-11c 10m 7m 4m 12m Perimeter =(7 + 4 + 12 + 10 + 5 + 6 )m = 44m Perimeter: Building on from second to third level Should the strategy adopted to calculate the perimeter be different if… • Some of the lengths were omitted? • Varying units of length were used? • More ‘complicated’ numbers were used e.g. decimal fractions or fractions? • The problem also involves algebraic expressions. For example, how could this problem have been made more challenging? Use varying units of length… 350cm 5m 500cm 8m 50cm 8m 3m 1m 50 12m 100cm 1000mm How could this problem have been made more challenging? Use decimal fractions (or fractions)… 2.5m 5m 9.5m 8m 3m 12m Perimeter: Building on from Second to Third Level • Can you provide opportunities for young people to create their own floor coverage ? • Why is calculating area important? • Can you identify any other examples where calculating area is used in real life? How could this problem have been made more challenging? Omit some of the lengths… 5m 6m 7m 4m 12m Perimeter 7m 10m 4m 12m Perimeter =(7 + 4 + 12 + 10 + 5 + 6 )m = 44m Numeracy across learning Tasks which involve the integration of techniques from across the Numeracy Experiences and Outcomes are found to be more challenging by learners than those which require the application of a direct fact. Consider these projects on NAR which link numeracy across learning Carleith primary: (prior learning for perimeter and area) https://www.narscotland.org.uk/virtual_file_path/68/20110628092647/inde x.html Westhill Academy: Area of compound 2D shapes https://www.narscotland.org.uk/virtual_file_path/171/20110812133016/ind ex.html Key features to consider when planning CPD for learning and teaching • There is a clear developmental sequence throughout the lesson, learners recognise links with earlier work, build on prior learning in numeracy and confidently use their knowledge within familiar and unfamiliar contexts. • An appropriate balance between developing and synthesising/using key facts • Programmes of study and practitioners’ lesson plans make effective use of prior learning to build on learners’ numeracy knowledge and skills including second and third level interface • Learners confidently use mental strategies. Key features to consider when planning CPD for learning and teaching • Learners give explanations of their reasoning as well as their methods • Non-routine problems, open ended tasks and investigations are often used by learners to develop their problem solving skills to develop their problem solving skills including reasoning and generalising • Staff introduce new numeracy terms, vocabulary and symbols meaningfully and expect and encourage correct use. The Numeracy Principles and Practice Paper is essential reading for everyone and can be used to prompt discussion amongst staff. www.educationscotland.gov.uk