Union-Management Slides
advertisement

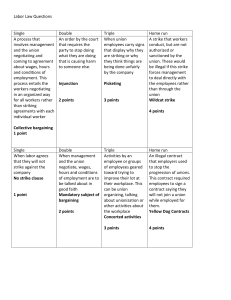
Overall Percent of Union Membership -- United States 35 30 25 20 20.1% 14.5% 15 12.5% 10 5 0 1983 Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics 1996 2005 Union Membership By Certain Industries Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics: http://www.bls.gov/opub/ted/1999/jul/wk3/art04.htm Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics: http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/union2.pdf#search=%22union%20membership%20by%20state%202005%22 Union Membership of 14 European Countries Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics: http://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2006/01/art3full.pdf#search=%22percent%20union%20membership%20by%20countries%22 Selected List of Labor Unions American Federation of Labor-Congress of Industrial Organizations (AFL-CIO) American Federation of State, County, and Municipal Employees Amalgamated Transit Union American Postal Workers Union Association of Flight Attendants Communication Workers of America International Association of Machinists International Brotherhood of Boilermakers National Education Association Screen Actors Guild United Auto Workers United Farm Workers United Mine Workers United Steel Workers Reasons for Union Formation • Economic factors (e.g., pay, promotion opportunity) • Supervision (behavior, attitude, interpersonal style, unfair treatment) • Safety concerns Overview of How Unions Form Campaign (sign cards to endorse an election or not [overseen by representative of NLRB] Greater 30% required for election Election Majority of members of in bargaining vote “yes” required for union to be formed Union Labor Contract --- A formal, written agreement between union and the company regarding the conditions of employment (e.g., pay, benefits, grievance process, performance assessment) over a given period of time Collective Bargaining Mediation --- Assist, facilitate an agreement between parties [share information]. No formal power to impose a decision Federal Mediation & Conciliation Service Fact-Finding --- More formal process. 1) Review relevant facts on the issues 2) Make formal recommendation 3) Make recommendation public Not used very often, most successful in private sector Collective Bargaining (cont.) Arbitration --- Final and binding decision [American Arbitration Association] Arbitration types: Type used if determined by law in the public sector, by agreement in private sector. Voluntary – Agreed upon by both parties (most common in private sector) Compulsory – Mandated by law (common in public sector) Conventional --- Arbitrator decides on best solution; often a compromise between opposing positions Final Offer -- Choose one position or the other Total package vs. Issue by issue Sample Grievance Procedure Step Management Union Form Mgmt. Answer Written 20 Days 20 Days 10 Days Arbitration 5 Union Appeal 4 Industrial Relations Manager Grievance Committee Written 10 Days 3 Division Manager Chief Steward Written 5 Days 5 Days 2 Industrial Relations Manager Shop Steward Written 5 Days 5 Days Grievant Oral 1 Industrial Relations Manager Issue in Dispute Immediate Immediate Factors Impacting Grievances • Employee characteristics More education Greater activity in union More absenteeism More likely to file grievances Lower wages • Shop steward characteristics (e.g., Personality; more dominant = more likely to file a grievance) • Type of work/job performed Not related to number of grievances filed but to type of grievance filed Impasse (failure of collective bargaining process) Union options used -- • Work slow down • Absenteeism (“blue flu”) • Sabotage • Strike (legitimate or “wildcat” strike) Management options used -• Lockout Union Impact Selection (e.g., applicant pool, process) Training (e.g., apprentice programs) Performance Evaluation (e.g., factors to be evaluated, frequency) Job Performance (e.g., scheduling of work, speed of production, type of work allowed) Some Influential Labor Leaders Mary Harris (Mother Jones) 1830-1930 United Mine Workers of America Samuel Gompers 1850-1924 American Federation of Labor Eugene Debs 1855-1926 American Railway Union Pauline Newman 1890-1986 International Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union Frances Perkins 1882-1965 Secretary of Labor Walter Reuther 1907-1970 United Auto Wokers Cesar Chavez 1927-1993 American Farm Workers Union Albert Shanker 19281997 American Federation of Teachers Some Key Events in U.S. Labor History Date Event April 27, 1825 First strike for the 10-hour work-day by carpenters in Boston July 3, 1835 Children at a silk mills company (Paterson, NJ) go on strike for 11 hr. days/6 days week January 13,1874 Tompkins Square Riot (Demonstration of unemployed workers. Police beat demonstrators causing over 100 casualties) June 21, 1877 10 coal miners (The "Molly Maguires") hanged July 14, 1877 National railroad strike. Federal troops called in to end strike. In Chicago ("Battle of the Viaduct“) 30 workers killed over 100 injured September 5, 1882 1st celebration of Labor Day (New York City) September 10, 1897 Lattimer Massacre. Striking coal miners marched in protest of oor mine conditions. 19 miners killed, 50 or more wounded May 1886 Haymarket Protests/Riots [see http://www.chicagohistory.org/dramas/overview/over.htm] Day after police killed 2 protestors, a bomb thrown in Haymarket Square killed 7 police. Eight people found guilty of murder; 4 executed on 11/11/1887. Impetus for May Day (May 1st) as the International Workers’ holiday April 20, 1914 "Ludlow Massacre" State Militia, in response to a strike at the Ludlow Mine Field, attack a union camp with machine guns and set tents on fire. 5 men, 2 women, and 12 children killed May 19, 1920 Battle of Matewan August 3, 1981 Federal air traffic controllers began nationwide strike. Majority of 13,000 controllers who ignored back-to-work order fired by Ronald Reagan October 6, 1986 Female flight attendants (1,700) won an 18-year lawsuit (including $37 million in damages) against United Airlines, which fired them for getting married Law List of Major Labor Laws Main Feature Railway Labor Act (RLA), 1926 Required companies to bargain collectively, prohibited discrimination against unions Davis-Bacon Act, 1931 Construction contracts with the Federal Gov’t need to specify the minimum wage to be paid Norris-LaGuardia Act, 1932 Guaranteed labor unions the right to organize, strike, and use other economic leverage in negotiations with management National Labor Relations Act (NLRA), 1935 (Wagner Act) Guaranteed the right to organize, join labor unions, choose representatives, collective bargain, and strike National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) established Independent Federal agency to enforce violations by organizations: a) interfering with formation of labor unions, b) hampering employees in organizing/collective bargaining, c) imposition of employment conditions to discourage union membership, d) discriminating against employees filing charges under the NLRA, and e) refusing to submit to collective bargaining Anti-Strikebreaker Law (Byrnes Act), 1936 Illegal to employ those to use force/threats against non-violent labor disputes, organizing, or bargaining Walsh-Healy Act, 1936 Guaranteed pay of not less than the "prevailing minimum wage" paid in a locality; restricted regular working hours to 8 hrs./day & 40 hrs./wk., timeand-a-half pay for additional hours; prohibited employment of convicts and children under 18, established sanitation and safety standards Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), 1938 Established minimum wages and maximum hours for workers. Established minimum ages of employment and hours of work for children Taft-Hartley Act, 1947 Set process to delay/avert "national emergency" strikes; prohibited supervisory employees from coverage of Wagner Act; prohibited "closed shops" Child Labor 1836 -- National Trades’ Union Convention make the first formal proposal for states to establish minimum ages for factory work 1836-- 1st state child labor law. Massachusetts mandates children less than 15 working in factories to attend school at least 3 months a year 1876 -- Working Men’s Party proposes abolishing the employment of children under the age of 14 1881 -- American Federation of Labor passes a resolution for states to ban children under 14 from employment 1904 -- National Child Labor Committee forms to campaign for federal child labor law reform Bibb Mill, Macon, GA. 1936 -- Walsh-Healey Act passed. U.S. government will not purchase goods made by underage children 1938 -- Fair Labor Standards Act. Minimum ages of employment and hours of work for children regulated by federal law 11 year old girl. Rhodes Manufacturing Co. N.C. Photos by Lewis Hine. See http://www.historyplace.com/unitedstates/childlabor/index. html Hughestown Borough Coal Co. Pittston, PA
![Labor Management Relations [Opens in New Window]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006750373_1-d299a6861c58d67d0e98709a44e4f857-300x300.png)