cost
advertisement

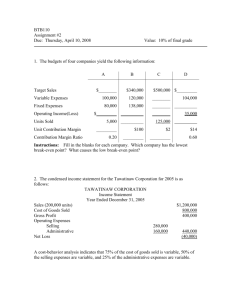
Chapter 2 Financial Aspects of Marketing Management In this chapter, you will learn about… 1. Variable and Fixed Costs 2. Relevant and Sunk Costs 3. Margins Gross Margin Trade Margin Net Profit Margin (Before Taxes) 4. Contribution Analysis Break-even Analysis Sensitivity Analysis Contribution Analysis and Profit Impact 2-2 In this chapter, you will learn about… 4. Contribution Analysis (contd.) Contribution Analysis and Market Size Contribution Analysis and Performance Measurement Assessment of Cannibalization 5. Liquidity 6. Operating Leverage 7. Discounted Cash Flow 8. Preparing a pro forma Income Statement 2-3 Types of Cost Costs Fixed Costs Variable Costs 2-4 Variable Costs are… Expenses that are uniform per unit of output within a relevant time period As volume increases, total variable costs increase 2-5 THERE ARE TWO CATEGORIES OF VARIABLE COSTS 1. Cost of Goods Sold 2. Other Variable Costs 2-6 Variable Costs – Cost of Goods Sold For Manufacturer or Provider of Service Covers materials, labor and factory overhead applied directly to production For Reseller (Wholesaler or Retailer) Covers primarily the cost of merchandise 2-7 Other Variable Costs Expenses not directly tied to production but vary directly with volume Examples include: Sales commissions, discounts, and delivery expenses 2-8 Fixed Costs Expenses that do not fluctuate with output volume within a relevant time period They become progressively smaller per unit of output as volume increases No matter how large volume becomes, the absolute size of fixed costs remains unchanged 2-9 THERE ARE TWO CATEGORIES OF FIXED COSTS 1. Programmed costs 2. Committed costs 2-10 Fixed Costs – Programmed Costs Result from attempts to generate sales volume Examples include: Advertising, sales promotion, and sales salaries 2-11 Fixed Costs – Committed Costs Costs required to maintain the organization Examples include nonmarketing expenditures, such as: rent, administrative cost, and clerical salaries 2-12 Relevant and Sunk Costs 2-13 Relevant Costs are… Future expenditures unique to the decision alternatives under consideration. Expected to occur in the future as a result of some marketing action Differ among marketing alternatives being considered In general, opportunity costs are considered relevant costs 2-14 Sunk Costs are… The direct opposite of relevant costs. Past expenditures for a given activity Typically irrelevant in whole or in part to future decisions Examples of sunk costs: Past marketing research and development expenditures Last year’s advertising expense 2-15 Sunk Cost Fallacy When marketing managers attempt to incorporate sunk costs into future decisions, they often fall prey to the Sunk Cost Fallacy – that is, they attempt to recoup spent dollars by spending even more dollars in the future. Example: Continuing to advertise a failing product heavily in an attempt to recover what has already been spent on it. 2-16 Margins The difference between the selling price and the “cost” of a product or service Margins are expressed in both dollar terms or as percentages on: a total volume basis, or an individual unit basis 2-17 Gross Margin or Gross Profit On a total volume basis: The difference between total sales revenue and total cost of goods sold On a per-unit basis: The difference between unit selling price and unit cost of goods sold 2-18 Gross Margin Total Gross Margin Dollar Amount Percentage Net Sales $100 100% Cost of Goods Sold - 40 Gross Profit Margin $ 60 60% Unit Sales Price $1.00 100% Unit Cost of Goods Sold - 0.40 - 40 Unit Gross Profit Margin $0.60 - 40 Unit Gross Margin 60% 2-19 Trade Margin (Markup) Suppose a retailer purchases an item for $10 and sells it at $20. Retailer Margin as a percentage of cost is: ($10 / $10) x 100 = 100 % Retailer Margin as a percentage of selling price is: ($10 / $20) x 100 = 50 % 2-20 Trade Margin Unit Cost of Goods Sold Unit Selling Price Gross Margin as a % of Selling Price Manufacturer $2.00 $2.88 30.6% Wholesaler $2.88 $3.60 20.0% Retailer $3.60 $6.00 40.0% Consumer $6.00 2-21 Net Profit Margin (before taxes) Net Sales Cost of Goods Sold Dollar Amount Percentage $ 100,000 100% - 30,000 Gross Profit Margin $ 70,000 - 30 70% Selling Expenses - 20,000 - 20 Fixed Expenses - 40,000 - 40 Net Profit Margin $ 10,000 10% 2-22 Kellogg’s Cereal Margins at a Price of $2.72 per box Kellogg’s Direct Unit Manufacturing Cost Grain $.18 Other Ingredients .23 Packaging .31 Labor .18 Mfg. Overheads .34 Cost of Goods Sold $1.24 ––––––– 54.4% Gross Margin ($2.72 - $1.24)/$2.72 Promotions (excluding Advertising) + .20 Total Unit Variable Cost $1.44 Manufacturer Contribution to Fixed Cost and Profit $1.28 ––- 47% Contribution Margin ($2.72-$1.44)/$2.72 Kellogg’s Selling Price to Grocery Store $2.72 Grocery Store Margin .68 ––- 20% Trade Margin ($3.40 - $2.72)/$3.40 Grocery Store Selling Price $3.40 Contribution Analysis Contribution is… The difference between total sales revenue and total variable costs OR on a per-unit basis The difference between unit selling price and unit variable cost 2-24 Break-Even Analysis Break-even point is the unit or dollar sales at which an organization neither makes a profit nor a loss. At the organization’s break-even sales volume: Total Revenue = Total Cost 2-25 Break-even Analysis Chart Dollars Total Revenue BE Point PROFIT Total Cost Variable Cost LOSS 0 Fixed Cost Unit Volume 2-26 Break-even Analysis Example Fixed Costs = $50,000 Price per unit = $5 Variable Cost = $3 Contribution = $5 - $3 = $2 Breakeven Volume = $50,000 $2 = 25,000 units Breakeven Dollars = 25,000 x $5 = $125,000 2-27 Applications of Contribution Analysis Sensitivity Analysis Profit Impact Market Size Performance Measurement Assessment of Cannibalization 2-28 Liquidity Refers to a company’s ability to meet short-term financial obligations Very important for a company’s day-today operations A key factor is Working Capital = Current Assets minus Current Liabilities 2-29 Operating Leverage Extent to which fixed costs and variable costs are used in the production and marketing of products and services. Firms with high total fixed costs relative to total variable costs are defined as having high operating leverage. Higher operating leverage results in a faster increase in profit once sales exceed break-even volume. The same happens with losses when sales fall below break-even volume. 2-30 Discounted Cash Flow Discounted cash flows are future cash flows expressed in terms of their present value Incorporates the time value of money Based on the premise that a dollar received tomorrow is worth less than a dollar today Useful in determining a business’s net cash flows 2-31 Discounted Cash Flow The discount rate can be expressed as follows: Discount factor = ___1___ (1 + r)n Where the r in the denominator is the interest rate and n is the number of years 2-32 The interest or discount rate is often defined as… The opportunity cost of capital, which is the cost of earnings opportunities forgone by investing in a business with its attendant risk as opposed to investing in risk-free securities. 2-33 Discounted Cash Flow Example Suppose you were to collect $1 million in 5 years. If the discount rate used were 10%, the present value of the $1 million would be: 1 PV = ———— X $1,000,000 = $620,921.32 (1 + 0.10)5 2-34 Preparing a pro forma Income Statement A pro forma income statement is a projected income statement Includes: Projected Revenues Budgeted Expenses Estimated Net Profit 2-35 Pro Forma Income Statement – Example Sales Cost of goods sold Gross margin Marketing expenses Sales expenses $170,000 Advertising expenses 90,000 Freight or delivery expenses 40,000 General and administrative expenses Administrative salaries $120,000 Depreciation on buildings and equipment 20,000 Interest expense 5,000 Property taxes and insurance 5,000 Other administrative expenses 5,000 Net profit before (income) tax $1,000,000 500,000 500,000 300,000 155,000 $45,000 Preparing a pro forma Income Statement Sales – forecasted unit volume times selling price Cost of goods sold – costs incurred in buying or producing products and services Gross margin – represents the remainder after cost of goods sold has been subtracted from sales 2-37 Preparing a pro forma Income Statement Marketing Expenses – programmed expenses to be spent on increasing sales General & Administrative Expenses – fixed costs (often referred to as overheads) Net Income before Taxes – sales revenues minus all costs 2-38