kingdom_plantae
advertisement

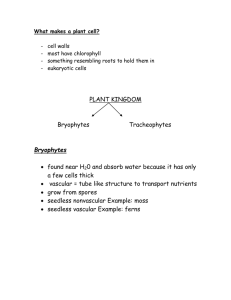
Kingdom Plantae Unit 3 Video: Kingdom Plantae Video Quiz What is a plant? Plants are multicellular eukaryotes that have cell walls made of cellulose. They carry out photosynthesis using the green pigment chlorophyll. Plants include trees, shrubs, grasses, mosses, flowers and ferns. Overview Flowering plants make up almost 90% of all plant species. We will study the 4 main divisions: 1) Non-Vascular Plants 2) Seedless Vascular Plants 3) Gymnosperms 4) Angiosperm Overview Non-Vascular Plants generally small, low to the ground live on land in moist, shaded habitats lack vascular tissue lack true roots, leaves and stems water required for reproduction (do not form seeds) Ex. Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts Mosses Phylum Bryophyta Many mosses can tolerate low temperatures, and grow abundantly in swamps and bogs. "Leaves" are only one cell thick, so they lose water quickly if the air is dry. They do not have true roots, but have rhizoids, which are long, thin cells that anchor them in the ground. Liverworts Phylum Hepaticophyta Some species resemble the shape of a liver. Flat leaf-like structures very close to the ground. Can reproduce sexually and asexually. Hornworts Phylum Anthocerophyta Generally found in soil that is moist year-round. Look very similar to Liverworts. During part of their life cycle, they look like a tiny green horn. Read and Respond 1. Read pages 556-559 in textbook 2. Answer questions #1, 2, 4on page 559. Warm-Up! 1. What are the four division of plants? 2. Plants contain ________ in their chloroplasts. 3. Plant’s cell walls contain ___________. Seedless Vascular Plants Vascular tissue: a type of plant tissue specialized to conduct water and nutrients through the plant Xylem - carries water upward from the roots Phloem - transports solutions of nutrients and carbohydrates Can move fluids through the plant body, even against the force of gravity. Seedless Vascular Plants Lignin makes the cell wall rigid, and together with the transport system, allows plants to reach great heights. Seedless vascular plants include club mosses, horsetails and ferns. Have true roots, leaves and stems. Seedless Vascular Plants Roots are underground organs that absorb water and minerals. Leaves are photosynthetic organs that contain one or more bundles of vascular tissue. This vascular tissue is gathered into veins made of xylem and phloem. Stems are supporting structures that connect roots and leaves, carrying water and nutrients between them. Club Mosses Club mosses are small plants that live in moist woodlands. Members of the genus Lycopodium (common club moss) look like miniature pine trees. Horsetails Non-photosynthetic, scale-like leaves are arranged in distinctive whorls at joints along the stem. Contain crystals of abrasive silica. Horsetails were commonly used to scour pots and pans. Ferns Have true vascular tissues, strong roots, creeping or underground stems called rhizomes and large leaves called fronds. Can thrive in areas with little light; most abundant in wet habitats. Practice Read pages 560-563 Answer questions 1,2,5 on page 563 Warm-Up! 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of plants? a. b. c. d. 2. Eukaryotic Cell walls contain chitin Multicellular Contains chloroplasts The leaves of ferns are called? a. b. c. d. 3. Sori Rhizomes Fronds Spores Water is carried up through the roots to every part in the plant by: a. b. c. d. Cells walls Cuticle Phloem Xylem Seed Plants Two groups of seed plants: Gymnosperms Angiosperms Gymnosperms ("naked seed") bear their seeds directly on the surfaces of cones; includes conifers, palm-like plants. Angiosperms ("enclosed seed") bear their seeds in a protective layer of tissue; grasses, flowering trees and shrubs, all species of flowers. Seed Plants Cones: seed-bearing structures of gymnosperms Flowers: seed-bearing structures of angiosperms Pollen grain: sperm-producing part of the plant Pollen is carried to the female reproductive structure by wind, insects, or small animals. Seed Plants A seed is an embryo that is encased in a protective covering, and surrounded by a food supply. An embryo is the early stage of plant development. Special adaptations that help them to disperse: e.g. textured to stick in fur; "wings"; fruits that are eaten Gymnosperms Gymnosperms include gnetophytes, cycads, ginkgoes and conifers. Conifers Most common gymnosperms; includes pines, spruces, firs, cedars, redwoods, junipers, etc. Thrive in a wide variety of habitats. Leaves are long, thin needles - reduces evaporation. Most are "evergreens" - retain leaves throughout the year. Angiosperms Angiosperms develop unique reproductive organs known as flowers. Evolutionary advantage - attract animals which then transport pollen (more efficient). Flowers contain ovaries, which surround and protect the seeds. 5 Angiosperms After pollination, the ovary develops into a fruit, which protects the seed and helps it disperse. Fruit - wall of tissue surrounding the seed; attracts animals, which digest and spread the seed. Monocots and Dicots Monocots and dicots are named for the number of seed leaves, or cotyledons, in the plant embryo. Monocots = one seed leaf (corn, wheat, lilies, orchids) Dicots = two seed leaves (roses, clover, tomatoes, oaks, daisies) Cotyledon: the first leaf or pair of leaves produced by the embryo. Textbook Time! Warm-Up! Fill in the missing parts 1 3 4 5 2 Flower Dissection Warm-Up List 3 differences between moncots and dicots. Review for Test #4 Warm-Up! 1. What are the 4 animal-like protists? 2. What is the difference between gymnosperms and angiosperms? 3. What is the difference between pollination and fertilization? Grudge Ball Question #1 What is the following organism? What is its classification? (Domain, Kingdom and Phylum) Question #2 What are the two components that make up vascular tissue? What do they do? Question #3 Label the following paramecium Question #4 What are the four divisions of plants? What two are able to produce seeds? Question #5 How do fungi reproduce? Question #6 What are the four animal like protists? How do they move? Question #7 Label the following mushroom 2 1 3 Question #8 Label the following flower Question #9 What are the 3 divisions of Non-Vascular Plants? What kind of environment must they live in? Question #10 What are the 3 divisions of Seedless Vascular Plants? Question #11 What are some differences between Kingdom Fungi and Kingdom Plantae?