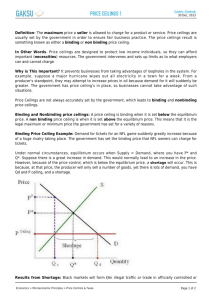
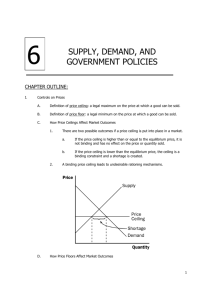
Price Ceilings and Price Floors!
advertisement

Price Ceilings and Price Floors! Supply, Demand, and Government Policies u In a unregulated market system with open entry and exit, market forces establish equilibrium prices and quantities. u While equilibrium conditions may be efficient, not everyone will be satisfied with the outcomes. Consumers Producers Price Controls… u Are usually enacted when policymakers believe the market price is unfair to buyers or sellers. u Result in government-created price ceilings or price floors. Price Ceiling and Price Floor Price Ceiling u A legally established maximum price at which a good can be sold. Price Floor u A legally established minimum price at which a good can be sold. Price Ceiling Two outcomes are possible when the government imposes a price ceiling: The price ceiling is not binding if set above the equilibrium price. The price ceiling is binding if set below the equilibrium price, leading to a shortage. Price Ceiling that is NOT Binding Price of Oranges-lb Supply Price ceiling 4 $3 Equilibrium price Demand 0 100 Quantity of Oranges lbs Price Ceiling that IS Binding Price of Oranges-lb Supply Equilibrium price $3 Price ceiling 2 Shortage Demand 0 75 Quantity supplied 125 Quantity demanded Quantity of Oranges-lbs Effects of Price Ceiling A binding price ceiling creates… shortages because QD > QS u Gasoline shortage of the 1970s nonprice rationing u u Long lines Discrimination by sellers Rationing Resources u Price Rationing Efficient Impersonal u Non-price Rationing Long lines Waste buyers time Inefficient Discrimination by sellers: Goods may not go to buyer who value it most highly Inefficient Potentially unfair Lines at the Gas Pump In 1973, OPEC raised the price of crude oil in world markets. Because crude oil is the major input used to make gasoline, the higher oil prices reduced the supply of gasoline. What was responsible for the long gas lines? Economists blame government regulations that limited the price oil companies could charge for gasoline. Initially … Price of Gasoline Supply 1. The price ceiling is not binding . . . Price ceiling P1 Demand Q1 Quantity of Gasoline Then … Price of Gasoline S2 2. supply falls ... S1 P2 Price ceiling 3. . . . the price ceiling becomes binding . . . P1 4. . . . resulting in a shortage. Demand QS QD Q 1 Quantity of Gasoline Rent Control u Rent controls are ceilings placed on the rents that landlords may charge tenants u Goal: to help the poor by making housing more affordable u New York City rent controls were enacted as a WWII emergency measure u u Some units still under rent control today Many rich tenants in rich neighborhoods paying low WWII prices. Rent Control in the Long Run... Rental Price of Apartment Supply Controlled rent Shortage Demand 0 Quantity of Apartments