Slides - High School Economics - Council for Economic Education
advertisement
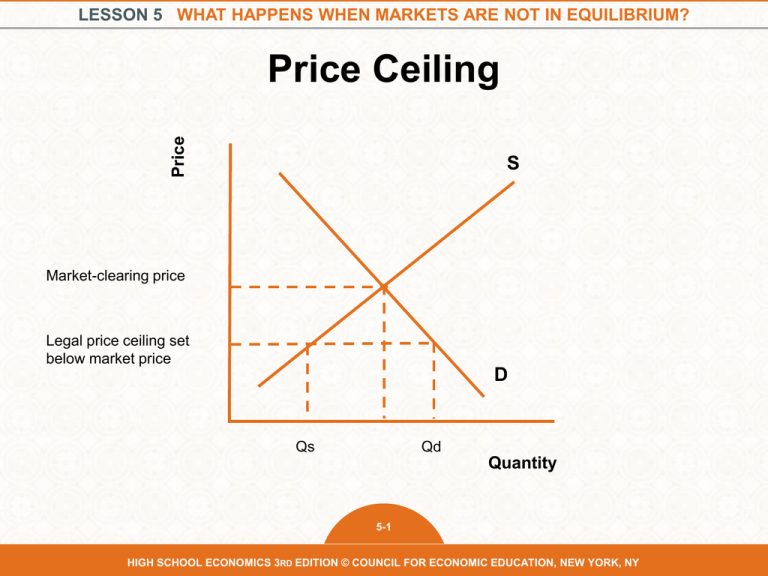
LESSON 5 WHAT HAPPENS WHEN MARKETS ARE NOT IN EQUILIBRIUM? Price Price Ceiling S Market-clearing price Legal price ceiling set below market price D Qs Qd Quantity 5-1 HIGH SCHOOL ECONOMICS 3RD EDITION © COUNCIL FOR ECONOMIC EDUCATION, NEW YORK, NY LESSON 5 WHAT HAPPENS WHEN MARKETS ARE NOT IN EQUILIBRIUM? Price Price Floor S Legal price floor set above market price Market-clearing price D Qd Qs Quantity 5-2 HIGH SCHOOL ECONOMICS 3RD EDITION © COUNCIL FOR ECONOMIC EDUCATION, NEW YORK, NY LESSON 5 WHAT HAPPENS WHEN MARKETS ARE NOT IN EQUILIBRIUM? Class Activity • Minimum wage • Agriculture price minimums • Rent control • “Usury” laws on credit card loans, setting maximum interest rates • Price controls on gasoline in the 1970s Instructions: • Decide whether each is a price floor or price ceiling. • Decide whether consumers or producers would favor the control. • Produce a market graph illustrating the result of this price control. 5-3 HIGH SCHOOL ECONOMICS 3RD EDITION © COUNCIL FOR ECONOMIC EDUCATION, NEW YORK, NY











