File
advertisement

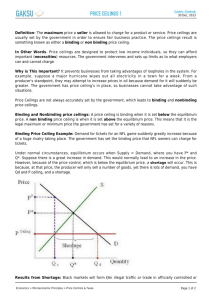
Price Floor and Ceiling Government Intervention At times government will step in and set a limit, high or low on prices. Price Ceiling Legal maximum price that sellers may charge for a product. These are placed on goods that are considered to be too essential for people to be priced out of the market. When the price ceiling is placed BELOW the equilibrium it has a binding effect. The forces of supply & demand want to move the price towards the equilibrium price, but the market price hits the ceiling and cannot rise further. When the government imposes a binding price ceiling in a free market, a shortage of that good/service is created. Sellers must ration the scarce resources among the large number of potential buyers. College Football Tickets CMU prints 30,000 tickets for every game Sells them for $15 each At that price, 60,000 people want to buy the tickets, so there is a shortage of 30,000 tickets. The university can resolve the problem by letting the price of tickets rise until QD and SD meet. But CMU wants to keep tickets affordable to students. The shortage occurs and scalpers are outside selling them for $50 each. Price Floor The legal minimum price that buyers must pay for a product. When the price floor is set BELOW the equilibrium, the price floor is nonbinding, and has no effect. When the price floor is set ABOVE the equilibrium it has a binding effect. The forces of supply & demand want to move the price toward the equilibrium price, but when the market hits the floor, it cannot fall further. When the government imposes a binding price floor in a free market, a surplus of that good/service is created. Sellers are unable to provide all that they want at the market or equilibrium price. Example: Minimum wage. If minimum wage is set above the equilibrium price, employers may decide that paying higher wages is not profitable. As a result, they may choose to employ fewer workers, and unemployment will increase. With a price floor, you now have labor supply exceeding the demand for labor. This causes unemployment. Firms are not willing to hire that many people at that given price (wage).