AP Chemistry WS 11.5 Key (a) ) = 8.49 OH- HCN CN
advertisement
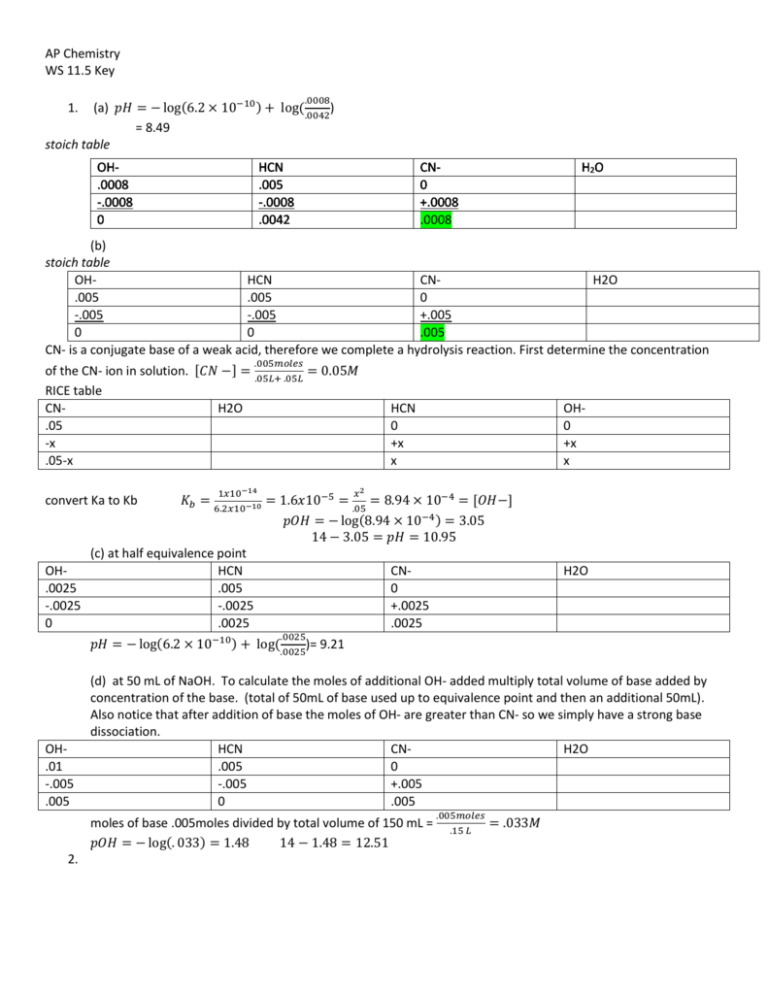
AP Chemistry WS 11.5 Key .0008 (a) 𝑝𝐻 = − log(6.2 × 10−10 ) + log( ) .0042 = 8.49 stoich table 1. OH.0008 -.0008 0 HCN .005 -.0008 .0042 CN0 +.0008 .0008 H2O (b) stoich table OHHCN CNH2O .005 .005 0 -.005 -.005 +.005 0 0 .005 CN- is a conjugate base of a weak acid, therefore we complete a hydrolysis reaction. First determine the concentration .005𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 of the CN- ion in solution. [𝐶𝑁 −] = .05𝐿+ .05𝐿 = 0.05𝑀 RICE table CNH2O HCN OH.05 0 0 -x +x +x .05-x x x convert Ka to Kb OH.0025 -.0025 0 𝐾𝑏 = 1𝑥10−14 6.2𝑥10−10 𝑥2 = 1.6𝑥10−5 = = 8.94 × 10−4 = [𝑂𝐻−] .05 𝑝𝑂𝐻 = − log(8.94 × 10−4 ) = 3.05 14 − 3.05 = 𝑝𝐻 = 10.95 (c) at half equivalence point HCN .005 -.0025 .0025 .0025 −10 ) 𝑝𝐻 = − log(6.2 × 10 + log( )= 9.21 CN0 +.0025 .0025 H2O .0025 OH.01 -.005 .005 (d) at 50 mL of NaOH. To calculate the moles of additional OH- added multiply total volume of base added by concentration of the base. (total of 50mL of base used up to equivalence point and then an additional 50mL). Also notice that after addition of base the moles of OH- are greater than CN- so we simply have a strong base dissociation. HCN CNH2O .005 0 -.005 +.005 0 .005 moles of base .005moles divided by total volume of 150 mL = 𝑝𝑂𝐻 = − log(. 033) = 1.48 14 − 1.48 = 12.51 2. .005𝑚𝑜𝑙𝑒𝑠 .15 𝐿 = .033𝑀 3.