THC
advertisement

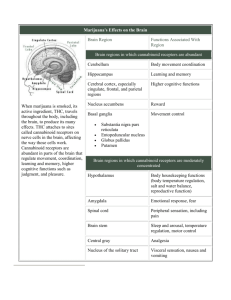
THC Brandon Connor UW-Eau Claire Indian Medicine Treatment of cramps Migraine Convulsions Neuralgia Attenuation of nausea and vomiting Decreased intestinal motility during diarrhea Bronchodialation in asthma Appetite stimulation Isolation of THC Y. Gaoni and R. Mechoulan completed work by R. Adams in 1940’s. Belongs to cannabinoid family Geranyl-pyrophosphate and olivetol Vincenzo Di Marzo THC 1,1’-di-methyl-pyrane ring (B ring) Variedly derivatized aromatic ring (C ring) Variedly unsaturated cyclohexyl ring (A ring) OH O Further Pharmacological Properties 1986-300 analogs and related compounds were available Analgesic Anti-emetic Anti-inflammatory Bronchodilatory Anti-convulsant Reduction of ocular blood pressure Alleviation of neurological disorders Continued Multiple sclerosis, Huntington’s chorea, spinal cord injury associated spasticity and seizures. Abortive and anti-fertiltiy actions Various metabolic effects Modulation of prostaglandins or pituitary and steroid hormones Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) Tetrad of behavioral tests on mice (Martin) 1) Antinociception-tail flick latency 2) Catalepsy-ring stand test 3) Rectal temperature 4) Spontaneous activity in open field test Results of SAR Psychoactive properties are (-) transenatioselective Length, lipophilicity C3 alkyl chain Phenolic hydroxyl-group C9 substitute OH O Discovery of Cannabinoid Receptor Cp-55,940 4-25 times more potent Amino-alkylindoles (WIN 55,212-2) O OH N HO N O Cloning of Receptor 1990-Matsuda clones receptor using “homology screening” approach Oligonucleotide probe “Orphan receptor” Concomitantly Gerard et. al. reports human receptor 98% homology to rat receptor Expressed in Testes SN Substantia Nigra -- the cannabinoid binding is highest here GP Globus Pallidus -- second-highest region of binding Caud Caudate Nucleus -- believed to control repetitive movement Pu Putamen Hip Hippocampus -- where short term memory is processed into long term memory Am Amygdala -- the part of the brain controlling rage, lust, fear and other strong emotions Hy Hypothalmus -- where vital endocrine hormones are released Central Receptors Seven trans-membrane spanning receptor family 1) Seven alpha-helices 2) Three extra- and intra-celluar loops 3) Glycosylated extra-celluar N-terminal domain 4) Intra-celluar C-terminal domain Continued 32-39% homolgy to adrenocorticotropic hormone and melanocortin receptors Lack of disulfide bond between 1st and 2nd extracelluar loop Lack of proline residue between 4th and 5th trans-membrane domain Steve Alexander Peripheral Receptor Three years later a peripheral receptor is cloned 44% identity with central receptor 68% identity within helical regions CB1 and CB2 Not present in thymus, liver, lung, kidneys Steve Alexander Important Findings Distribution correlated well with pharmacological actions Agonists which selectively bind to CB2 Antagonists which do not activate G-protein SR141716A- CB1 antagonist THC- weak antagonist at CB2 Intracelluar effects of THC Inhibition of agonist-induced cAMP formation Inhibition of N-type Ca channels Interference with gamma-aminobutyric acid, acetylcholine, and the catecholamines Pertussis toxin ADP-ribosylation and subsequent inactivation Vincenzo Di Marzo Discovery of Endocannabinoids Lipophilic molecule like THC 1992-Devane isolated brain constituent NMR GC/MS analysis Derivative of arachidonic (prostaglandins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes, etc.) Presence of amidated ethanolamine Cis-5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoyl-N-(2hydroxy-ethyl)-amine Continued Anandamide- Sanskrit for “bliss”, ananda Shared most of the pharmacological properties with THC Located where receptors are present O OH N Physiological Roles Role of cannabinoid system remains elusive Widespread tuning system of finely tuned tasks Modulation of neurotransmitter release/action at autonomic and sensory fibers Control of immunological, gastrointestinal, reproductive, cardiovascular performance Continued Thermoregulatory centers Regulation of perceptive, cognitive, motor functions Suggested roles in synaptic plasticity, brain development Hypothalmic hormone secretion Release of dynorphins-analgesic Lowers blood pressure and heart rate Immune system Autoimmune encephalomyelitis Placebo-95% died; THC-98% lived Antigen-specific effect on macrophages Mitogen-activated protein kinase Suppression of immune system and tumoicidial cells Protection of nerve cells from exitotoxins Reproductive System Control of spermatogenesis and male fertility Receptors found in sea urchin eggs May be used to direct timing and placing of embryo implantation Suggested to mediate communication between uterus and embryo. References nepenthes.lycaeum.org/Drugs/THC/index.html www.nott.ac.uk/physpharm/cannabinoid.html www.druglibrary.org/schaffer/hemp/BRAIN.htm bctv.butte.cc.ca.us/ads/Marijuana%20Chapter/sld0 01.htm www.umds.ac.uk/neupharm/can.htm www.lacbc.org Www.netscijournal.com/97v1/97007/cabb.htm#Introduction