Marijuana - UCSD Cognitive Science
advertisement

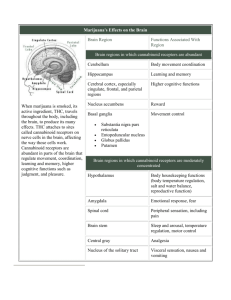
THC/Marijuana By Any Other Name… • Pot, herb, weed, grass, widow, ganja, hash, dank, mota/moto, hierba, pasto, reefer, old man, sinsemilla, bhang, dagga, etc. Marijuana/THC Overview (an intoxicant) • Cannabis Sativa (hemp) and Cannabis Indica native to Central Asia, cultivated for thousands of years for fiber, seeds, medicine, drug use • Main psychoactive ingredient, delta-9tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), from resin on unfertilized flowers (which protects plant from excessive heat) • 483 chemicals (60-70 cannabinoids) • Psychoactive uses: euphoria, sedative, altered state of consciousness STRUCTURE OF THC World Cannabis Highlights • Archaelogical record of hemp cord (~8000 B.C.) • Documentation of medical use in China (~2700 B.C.) • Religious use in India (~2000 B.C.) • Hashish use in Arab world (~1000 A.D.) • Western World learns of psychoactive use (mid 1800s) U.S. Cannabis History • Harvested for hemp in American colonies • Smoking introduced in 1850s by Mexicans and West Indians • Portrayed as evil in 1920s, laws passed to outlaw use • By mid-1930s, considered a “narcotic” • Marijuana Tax Act (1937): made illegal; overturned in 1960s. • By 1940 public convinced that it – Induced violent crimes – Led to heroin addiction – Was a great social menace U.S. Cannabis History (cont) • THC isolated from marijuana (1964) • Hippie era (1960s) • Synthetic marijuana - Marinol (1980) • First cannabinoid receptor isolated and cloned (1990) • Endogenous ligand (anandamide) isolated (1992) • Voters in CA, AZ approve medical use (1996) • Marinol as Schedule 3 (1999) Marijuana Smoke vs. Tobacco Smoke • Which is more harmful? • Each type has more of certain toxins and carcinogens than other • Mitigating factors – Filtration – Additives – Frequency of use – Method of inhalation Normal Lungs and Physiology Lungs are the site of gas exchange: oxygen enters blood and carbon dioxide leaves blood Healthy Lung Diseased Lung Marijuana Use Marijuana Use THC Pharmacokinetics • Absorption – Inhaled (smoked) – Oral (tea, food) • Distribution – Peak blood levels in about 10 minutes – Significant depot binding due to high lipid solubility THC Pharmacokinetics (cont) • Metabolism and Elimination – Metabolized almost entirely by liver – Half-life 20-30+ hours (1-10 days) – More than 24 metabolites, some of which are psychoactive (e.g. 11-hydroxy-delta-9-THC) – Testing done on THC-COOH (an inactive metabolite), can be detected for several weeks – Excreted via feces (2/3) and urine (1/3) Endocannabinoids – First receptor discovered in 1988 • 1992 first endocannabinoid discovered • arachidonyl ethanolamide- named anandamide - CB1 receptors expressed in the brain, especially in the hippocampus, cortex, cerebellum, and the basal ganglia. - CB2 receptors are absent from the brain but are expressed in the immune tissues. - New evidence suggests a “CB3” receptor. THC Pharmacodynamics • Mimics action of endogenous anandamide and sn2 arachidonylglycerol (2-AG) • Direct agonist for cannabinoid (CB) receptors, found in both CNS (CB1) and periphery (CB2) • CB1 receptors are – Metabotropic – Primarily presynaptic heteroreceptors – Mostly inhibitory Devane et al., 1988 • Inhibits Ach, Glu • Complex dose-related effects on reuptake and release of DA and NE • Location-specific effects on DA CB Receptor Localization • • • • • • • • • Cortex Thalamus Hippocampus Cerebellum Striatum Accumbens Amygdala VTA Retina CB(1) receptor is densely distributed in areas of the brain related to motor control, cognition, emotional responses, motivated behavior and homeostasis Depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition (DSI) – short term plasticity DSI was discovered in 1992 by Vincent et al., (1992) DSI: a reduction in inhibitory GABA release DSE: a reduction in excitatory glutamate release; endocannabinoid role not as clear Acute Effects • Analgesia • Euphoria • Disinhibition • Disrupted attention • Sedation • Increased appetite • Impaired short-term memory and learning • Antiemesis • Impaired multi-tasking • Altered control of motor movements/coordination • Altered sensory awareness • Increased heart rate and blood pressure • Hallucinations, loss of control (at high doses) • Anxiety, fear, panic (at stimulation tranquility high doses) Chronic Effects • Respiration – bronchitis, pneumonia, lung cancer • Cardiovascular – speeds heartbeat; risk for those with heart rhythm or blood pressure problems • Immune system – Suppressed; increased likelihood of becoming ill • Reproduction – decreased sperm count; mobility – menstrual irregularities • Emotion – amotivational syndrome • Intellect – impaired thinking/reasoning – difficulty maintaining attention • Psychological – increasing tolerance – drug craving/seeking – addiction Hormone Problems Associated with Marijuana Use • Altered hormone levels (prolactin) • Enlarged breasts in males (gynecomastia) Possible Roles for Anandamide and 2-AG • Broaden Attentional Spotlight – Effects on cortex, thalamus, cerebellum – Wider distribution of resources – More processing of “irrelevant” stimuli • Facilitate Selective Forgetting and promote hippocampal neurogenesis – – – – – Effects on hippocampus Block LTP and gamma synchrony Facilitate rejection of “irrelevant” stimuli Limit memory retention Ensure adequate coping with stressful situations Effects on Performance Leirer et al., 1991 P300 Solowij et al., 1995 Marijuana and Attentional Load Chang et al., 2006 Medical Uses (National Academy of Sciences, 1999) • AIDS – reduces nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite • Glaucoma – reduces intraocular pressure • Cancer – reduces side effects of chemotherapy • Multiple Sclerosis – limits muscle pain and spasticity; relieves tremors • Epilepsy – prevents seizures • Chronic Pain – alleviates pain caused by many disorders Tolerance and Withdrawal • Tolerance to cardiovascular effects in both light and heavy users, but to psych effects more in heavy users • Mechanism: CB receptor downregulation and desensitization • Withdrawal precipitated in animals receiving high doses, seen in chronic heavy users who abstain: – – – – – Restlessness Irritability Agitation Anxiety Depression – – – – – Reduced food intake Insomnia Sleep disturbances Nausea Cramping 1mg/kg cannabinoid 3mg/kg cannabinoid 10mg/kg cannabinoid 10mg/kg THC Inactive cannabinoid vehicle