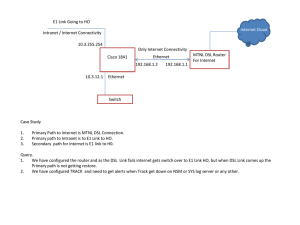
Assignment3-LeonardEhalt
advertisement

Assignment 3 Networking Devices Leonard Ehalt • Click to edit Master subtitle style Before beginning… • The slides that you are about to see are actual slides that I use when teaching my Network+ class at Tarrant County College. • Many of the figures come from the Sybex book that CompTIA recommends for Network+ certification 2 Common Network Devices Here’s a list of the devices we’ll be covering: • Hub • Network Interface Card (NIC) • Bridge • Switch • Router • Firewall • Many of the devices shown are used in the home consumer market and can be procured at your local computer store for less than $100 3 A Basic Hub A hub is the device that connects all the segments of the network together in a star topology Ethernet network. Every device in the network connects directly to the hub through a single cable and is used to connect multiple devices without segmenting a network. 4 Network Interface Card (NIC) • A Network Interface Card (NIC) is installed in your computer to connect, or interface, your computer to the network. • It provides the physical, electrical, and electronic connections to the network media. • A NIC either is an expansion card or is built right into the computer’s motherboard. • The NIC usually connects to the computer through expansion slots located on the motherboard that allow peripherals to be plugged in directly. • In some notebook computers, NIC adapters can be connected to the printer port or through a PC card slot. 5 Network Interface Card (NIC) 6 A wireless NIC 7 A wireless access point 8 Bridge A bridge—specifically, a transparent bridge—is a network device that connects two similar network segments together. Its primary function is to keep traffic separated on either side of the bridge, breaking up collision domains. 9 Switch Switches connect multiple segments of a network together much like hubs do, but with three significant differences—a switch recognizes frames and pays attention to the source and destination MAC address of the incoming frame as well as the port on which it was received. 10 Switch interface Switch#sh running-config interface FastEthernet0/1 interface FastEthernet0/2 interface FastEthernet0/3 interface FastEthernet0/4 Switch(config-if)#duplex ? auto Enable AUTO duplex configuration full Force full duplex operation half Force half-duplex operation Switch(config-if)#speed ? 10 Force 10 Mbps operation 100 Force 100 Mbps operation auto Enable AUTO speed configuration 11 Router A router is a network device used to connect network segments together. A router can make intelligent decisions about the best way to get network data to its destination. 12 Interface Configurations Router(config-if)#ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 Router(config-if)#no shutdown Router(config-if)# *Oct 5 17:26:46.522: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up *Oct 5 17:26:47.522: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up The interface can now be connected to a Layer 2 switch and the connected hosts must set their default gateway address to 1.1.1.1 They can now send packets to the router 13 Firewall • Basically, firewalls are your network’s security guards; and to be real, they’re probably the most important thing to implement on your network. • That’s because today’s networks are almost always connected to the Internet—a situation that makes security crucial! • A firewall protects your LAN resources from invaders that prowl the Internet for unprotected networks, while simultaneously preventing all or some of your LAN’s computers from accessing certain services on the Internet. • You can employ them to filter packets based on rules that you or the network administrator create and configure to strictly delimit the type of information allowed to flow in and out of the network’s Internet connection. 14 Firewall • A firewall will have at least two network connections: one to the Internet (known as the public side) and one to the network (known as the private side). • Sometimes, there is a second firewall • This firewall is used to connect servers and equipment that can be considered both public and private (like web and email servers). • This intermediary network is known as 15 a demilitarized zone (DMZ). Firewall 16 Planning and Implementing a Basic SOHO Network Using Network Segmentation Network design incorporating all device types 17 Planning and Implementing a Basic SOHO Network Using Network Segmentation (Cont) Optimal design 18 A wireless network 19 Wireless access point setup 20