Body Systems
advertisement

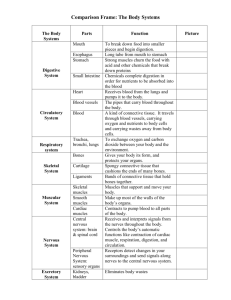
Methacton Elementary Health & Physical Education Department Body Systems Notebook 1 point per completed page Rev 2015-16 Grade 4 Skeletal Respiratory Muscular Nervous Circulatory Urinary My name is _____________________________________ and this is my Health Notebook. It is my responsibility to save and organize all materials and papers from this class in my Health Folder. The following items may be used to measure my progress: classwork and participation notebooks assignments written assessments projects attitude and conduct. PA State Standards 10.1.6.B Identify and describe the structure and function of the major body systems. skeletal muscular circulatory respiratory nervous urinary 10.1.6.B Identify health problems that can occur throughout life and describe ways to prevent them. Competencies Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to: describe the term “body system.” explain the following terms and how they come together to form a body system: - cells - tissues - organs. summarize the function of each of the following body systems: - skeletal muscular circulatory respiratory digestive urinary. identify and know the location of each of the major organs within each system. Health Teachers: Please note that this unit, up through the Respiratory System, should be completed by the end of February to coincide with the elementary Science curriculum. -1- The Human Body The human body is amazing! Directions: Fill in the blanks to complete the sentences below. 1.) Our bodies are made of tiny building blocks called ________________________. 2.) Cells of the same kind work together to form ___________________________. 3.) The heart, stomach and brain are examples of___________________________. 4.) Organs that work together to perform a certain job are called ______________. -2- The Skeletal System The skeletal system supports the body and gives it shape. Another function of the skeletal system is to work with muscles to move the body. A third function of the skeletal system is to protect the soft organs and body parts. For example, the skull protects the brain, while the ribs and breastbone (sternum) protect the lungs and heart. The backbone is made up of tiny bones called vertebrae that protect the spinal cord. The skeleton is made up of 206 bones. Besides bones, the skeleton also has a type of rubbery tissue called cartilage in all places where two bones meet. The cartilage cushions the bones and keeps them from rubbing together. The outer ear and the tip of the nose are very flexible because they are made up of cartilage. The place where two or more bones join together, such as in the elbow or ankle, is called a joint. There are several different types of joints in the body. Ligaments connect the bones in the joints of the body and help to keep them in place. In the very center of the bone is a large space filled with a type of tissue called marrow. Bone marrow is soft tissue that makes new blood cells. Getting plenty of calcium, minerals, vitamins and exercise helps keep your bones strong and healthy. Directions: Answer each of the following questions. 1.) What are the three functions of your skeletal system? a. _______________________________________________________ b. _______________________________________________________ c. _______________________________________________________ 2.) What is cartilage and where can it be found in your body? _______________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3.) What is the purpose of ligaments? ________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4.) What is bone marrow? _________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5.) What can you do to keep your bones strong and healthy? ________________________ __________________________________________________________________ -3- Name That Bone Directions: Use the words from the word bank to label the diagram of the skeletal system. cranium patella ulna mandible vertebrae phalanges ribs sternum tibia radius humerus fibula tarsals carpals -4- femur pelvis clavicle I Did Not Know That! Directions: Use the code to learn more about bones. -5- The Muscular System We can move because of our muscles! The muscular system is made up of all the different muscles that cause movement. There are more than 600 muscles in the body that all control movement in some way. The two main types of muscles in the body are involuntary muscles and voluntary muscles. Involuntary muscles are muscles that cannot be consciously controlled. These are muscles, such as in the heart and stomach, that work without you needing to think about it. Voluntary muscles are muscles, such as in your arms, legs and face, that are under conscious control. This means the movement of voluntary muscles can be controlled. Voluntary muscles are also called skeletal muscles because they attach to the bones of the skeleton. Skeletal muscles move your bones by working in opposing pairs. When a muscle contracts, it pulls the bone in one direction. When the opposite muscle contracts, it pulls the bone in the other direction. Skeletal muscles are attached to the bones by tough bands called tendons. Muscles need to be exercised to stay healthy. Exercise strengthens and stretches the muscles. Without exercise, they become smaller and weaker. Eating foods rich in protein (eggs, meat, fish and beans) promotes the growth and repair of muscles. -6- Directions: Answer each of the following questions. 1.) What is the purpose of the muscular system? _________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2.) What is the difference between a voluntary muscle and an involuntary muscle? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 3.) How do the muscles cause the bones to move? ________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 4.) What muscles are mostly used when you do: pull-ups? ____________________________________________________ curlups? ____________________________________________________ a distance run? _______________________________________________ - 7- Show Your Muscles! Directions: Use the words from the Word Bank to label the muscle groups in the diagram of the muscular system. Word Bank gluteus maximus deltoids biceps triceps abdominals hamstrings quadriceps gastrocnemius pectoralis Here are some fun facts! In the next 24 hours the muscles of both of your eyes will move more than 110,000 times each. Leg muscles are very strong because they are always pushing against the pull of gravity to help the body remain erect. Taking just one step puts about 300 muscles in the body into motion. Keep smiling – it requires 34 muscles to frown, but only 13 to smile! Without your muscles, your heart would not beat, you could not eat, or breathe, and you could not move. -8- The Circulatory System The function of the circulatory system is to carry materials all through the body. The main parts of the circulatory system include the heart, blood vessels and blood. Blood carries food and oxygen to all the cells of the body as it is pumped through the blood vessels by the heart. The circulatory system also helps carry away waste products such as carbon dioxide. The heart is a very hardworking pump that is made up of muscle cells. It has two upper chambers, or hollow spaces, called atria. There are also two lower chambers called ventricles. The atrium and the ventricle on the left side of the heart receive the oxygenrich blood from the lungs and carry it to all parts of the body. The atrium and ventricle on the right side receive the oxygen-poor blood from the body and send it to the lungs. This is where it can get rid of the carbon dioxide and receive oxygen. This cycle continually repeats itself. There are three main types of blood vessels. The largest blood vessels are the arteries which carry the blood away from the heart. The arteries branch into smaller and smaller blood vessels until they are so tiny that only one cell at a time can get pass through them. These tiny blood vessels are called capillaries. The capillaries join together into larger blood vessels called veins which carry the blood back to the heart. Blood has different kinds of cells in it including red blood cells and white blood cells. The red blood cells carry the oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. The white blood cells help the body attack germs and fight diseases. You should have at least 60 minutes of active play each day. Twenty of those minutes should be vigorous. The activity is vigorous if you are breathing hard, sweating and your heart is beating fast. Directions: Please answer each of the following questions. 1.) What is the purpose of the circulatory system? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ -9– 2.) What are the main parts of the circulatory system? ___________________ 3.) _____________________ What are the three main types of blood vessels? ___________________ 4.) ___________________ ___________________ _____________________ What are two of the cells found in the blood? ______________________________ _______________________________ Label the Parts of the Heart Directions: Using the words below, label the parts of the heart. aorta left ventricle right atrium valves right ventricle left atrium From Body To Body - 10 - Pulse You are probably wondering how you can tell how fast your heart is beating. Your heart rate is measured by feeling your pulse. The pulse is caused by the blood being pushed through arteries with each heart beat. There are many places to detect pulses; however, the two most commonly used are the carotid pulse in your neck and the radial pulse in your wrists. To find your radial pulse, put the pads of three fingertips (don’t use your thumb) on the inside part of the wrist near your thumb. Press down slightly until you find a pulse or soft throbbing. Count each pulse for 60 seconds. This will give you your heart rate for one minute. It takes a little practice and coordination, but with the help of your teacher or parent you will be able to learn how to count your radial pulse. Doctors and nurses listen to your heart with a stethoscope. This tells them how healthy your heart is. The heartbeat is the sound the heart makes when the heart valves open and close. Two sounds can be heard during every heartbeat. We call them “lub dub.” Here are some fun facts about your Circulatory System! If your blood vessels were laid end-to-end they would measure 60,000 miles. About 8 million blood cells die in the human body every second. The same number of blood cells are manufactured in the bone marrow each second. Within a tiny droplet of blood, there are some 5 million red blood cells. Red blood cells make approximately 250,000 round trips of the body before returning to the bone marrow to die. Red blood cells may live about four months circulating throughout the body feeding the trillion of other cells. - 11 - Notes - 12 - Notes - 13 - The Respiratory System The respiratory system brings in oxygen from the air and takes away carbon dioxide. The body needs to have oxygen to stay alive. Oxygen is used by all cells of the body to help burn food for energy. Carbon Dioxide is given off as a waste product. Air comes into the body through the nose (or mouth) and travels into the windpipe, or trachea, which is a tube in the throat. As the trachea goes into the chest area, it divides into two branches called bronchial tubes, which lead to the lungs. The bronchial tubes branch into smaller and smaller tubes as they enter each lung. Each of these lungs is made up of hundreds of millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli. Through these air sacs, oxygen passes into the blood, and carbon dioxide passes out of the blood. A dome-shaped muscle under the lungs, called the diaphragm, controls breathing in and out. When the diaphragm flattens out, air rushes in to fill up the lungs. This is called inhaling. When the diaphragm goes back to its dome shape, it pushes the air back out of the lungs. This is called exhaling. Vigorous exercise and not smoking will keep your respiratory system healthy! Directions: Please answer each of the following questions. 1.) What is the purpose of the respiratory system? __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2.) What are the parts of the respiratory system? _____________ 3.) _____________ _____________ _____________ What is the function of the diaphragm? __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 4.) What gas is needed by the body to stay alive? Why? __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ - 14 - Diagram the Respiratory System Directions: Use the number code to label and color the diagram of the respiratory system. 1.) Color the nose and mouth red. 2.) Color the throat (pharynx) blue. 3.) Color the voice box (larynx) green. 4.) Color the windpipe (trachea) purple. 5.) Color the bronchial tubes yellow. 6.) Color the lungs orange. 7.) Color the diaphragm pink. - 15 - Take a Deep Breath Directions: Use the code to learn some interesting facts about the respiratory system. - 16 - The Nervous System The nervous system receives and carries messages all throughout the body. The nervous system controls and coordinates all the body parts. The main organs of the nervous system are the brain, spinal cord and nerves. These organs are made of special nerve cells called neurons. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up what is called the central nervous system. They work together to analyze and store information that comes in from outside the body then pass on instructions to the other body parts about how to respond. The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum and medulla. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It controls all learning, memory and reasoning. It also controls many body parts. The cerebrum is made up of a right half and left half. Each half controls the opposite side of the body. The cerebellum is below the cerebrum. It is the part of the brain that controls balance and coordination. The medulla is the part of the brain that controls body actions such as heartbeat, sneezing and coughing. These are called involuntary actions because they are not consciously controlled. The peripheral nervous system is the network of neurons, or nerve cells, that spread out from the spinal cord to the rest of the body. These nerves carry messages between the central nervous system and all the other parts of the body. Sense organs such as the eyes, ears, nose and skin bring in messages to the brain about conditions outside the body. You can keep your brain healthy by wearing a bike helmet, eating healthy foods, getting regular exercise, getting enough sleep and doing mental activities to challenge your brain. - 17 - Directions: Please answer each of the following questions. 1.) What is the purpose of the nervous system? _____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2.) What are the main organs of the nervous system? ___________________ 3.) ___________________ _____________________ What are the three main parts of the brain and what do they control? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Label the parts of the Brain cerebellum medulla - 18 - cerebrum The Urinary System As the body breaks down extra proteins, it forms a waste called urea. Salt is also given off as a waste product. Small amounts of urea and salt are released from the skin when you sweat, but most of it is released from the main organs of excretion in the body called the kidneys. The two kidneys are at the back of the body, just above the hips. They form a liquid called urine which is made up of wastes and water. Water from the blood goes into the kidney cells along with urea, salt and wastes. Urine forms from these waste products inside the kidney cells and then flows to a collecting area in the kidney. The urine leaves each kidney through a tube called the ureter. After leaving the kidney through the ureters, the urine is collected in a sac-like organ called the bladder where it is stored until it is ready to be released from the body. When urine is released from the body, it passes from the bladder through another tube called the urethra which carries it out of the body. You can keep your urinary system healthy by drinking plenty of water. Lightcolored urine indicates you are not dehydrated. Directions: Please answer each of the following questions. 1.) What is the purpose of the urinary system? _____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2.) What are the four main organs of the urinary system? ______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ 3.) What are the two main products that make up urine? ________________________________ - 19 - _________________________________ Major Organs of the Urinary System Directions: Use the terms from the word bank to label the diagram of the Urinary System. kidney bladder urethra ureter Urinary Factoids - Ever eat kidney beans? They were named after your kidneys which are a similar shape and color! - Your kidneys have about a million tiny structures that filter out liquids and wastes. - About 440 gallons of blood flow through the kidneys each and every day! - 20 - Body Systems Review Directions: Match the body part with the system to which it belongs. BODY PARTS SKELETAL MUSCULAR CIRCULATORY heart ligaments deltoids arteries brain veins lungs biceps kidney tibia bladder diaphragm trachea nerves femur alveoli tendons spinal cord gluteus maximus bronchial tubes - 21 - RESPIRATORY NERVOUS URINARY