Chapter 8 Study Guide
advertisement

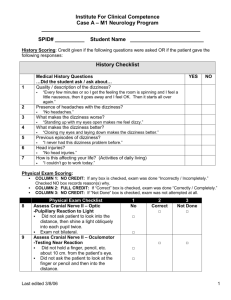
Chapter 8: Special Senses Name____________________ Match the names of muscles, their action, and controlling cranial nerve. Place the correct letter in the space provided. A. Lateral rectus E. Medial rectus B. Inferior rectus F. Superior rectus C. Superior oblique D. Inferior oblique ______ 1. Elevates eye and turns it laterally; controlled by cranial nerve III, the oculomotor. ______2. Elevates eye; controlled by cranial nerve III, the oculomotor. ______3. Moves eye laterally; controlled by the abduscens, cranial nerve VI. ______4. Depresses eye; controlled by the oculomotor, cranial nerve III. ______5. Moves eye medially; controlled by cranial nerve III, the oculomotor. ______6. Depresses eye and turns it laterally; controlled by cranial nerve IV, the trochlear Match the terms at the top with the appropriate description. Place the correct letter in the space provided. A. Accommodation E. Refraction I. Hyperopia B. Accommodation pupillary reflex F. Convergence J. Myopia C. Cataract G. Emmetropia K. Night blindness D. Astigmatism H. Glaucoma L. Photopupillary reflex ______1. Inability to see well in the dark; often a result of vitamin A deficiency ______2. Medial movement of the eyes during focusing on close objects ______3. Nearsightedness ______4. Normal vision ______5. Light bending ______6. Ability to focus for close vision (under 20 feet) ______7. Blurred vision, resulting from unequal curvatures of the lens or cornea ______8. Condition of increasing pressure inside the eye, resulting from blocked drainage of aqueous humor ______9. Reflex constriction of the pupils when viewing close objects ______10. Clouding of the lens, resulting in loss of sight ______11. Inability to focus well on close objects, farsightedness ______12. Reflex-constriction of pupils when they are exposed to bright light Match the terms at the top with the appropriate description. Place the correct letter in the space provided. Choices may be used once, more than once, or not at all. A. Aqueous humor E. Ciliary zonule I. Lens M. Vitreous humor B. Canal of Schlemm F. Cornea J. Optic disk C. Choroid coat G. Fovea centralis K. Retina D. Ciliary body H. Iris L. Sclera ______1. Attaches the lens to the ciliary body ______2. Fluid that provides nutrients to the lens and cornea ______3. The “white” of the eye ______4. Area of retina that lacks photoreceptors ______5. Contains muscle that controls the shape of the lens ______6. Nutritive (vascular) tunic of the eye ______7. Drains the aqueous humor of the eye ______8. Tunic, containing the rods and cones ______9. Gel-like substance that helps to reinforce the eyeball ______10. Heavily pigmented tunic that prevents light scattering within the eye ______11. ______12. Smooth muscle structures (intrinsic eye muscles ______13. Area of acute or discriminatory vision ______14. ______15. ______16. ______17. Refractory media of the eye ______18. Anterior-most part of the sclera—your “window on the world” ______19. Pigmented “diaphragm” of the eye In the following table circle the correct word under the vertical headings that describes events occurring within the eye during close and distant vision. Vision Ciliary muscle Lens convexity Degree of light refraction 1. Distant Relaxed Contracted Increased Decreased Increased Decreased 2. Close Relaxed Contracted Increased Decreased Increased Decreased Match the terms at the top with the appropriate description. Place the correct letter in the space provided. Choices may be used once, more than once, or not at all. A. Anvil (incus) B. External acoustic meatus C. Pinna D. Tympanic membrane E. Auditory (pharyngotympanic) tube F. Hammer (malleous) G. Round window H. Vestibule I. Cochlea J. Oval window K. Semicircilar canals L. Endolymph M. Perilymph N. Stirrup (stapes) ______1. ______2. ______3. Structures composing the outer ear ______ 4. ______ 5. ______6. Structures composing the bony or osseous labyrinth ______ 7. ______ 8. ______9. Collectively called the ossicles ______10. ______11. Ear structures not involved with hearing ______ 12. Allows pressure in the middle ear to be equalized with the atmospheric pressure ______ 13. Vibrates as sound waves hit it; transmits the vibrations to the ossicles ______ 14. Contains the organ of Corti ______ 15. Connects the nasopharynx and the middle ear ______ 16. ______ 17. Contain receptors for the sense of equilibrium ______ 18. Transmits the vibrations from the stirrup to the fluid in the inner ear ______19. Fluid that bathes the sensory receptors of the inner ear ______20. Fluid contained within the osseous labyrinth, which bathes the membranous labyrinth Label the diagram below with the letters of the key choices above. Place the letter at the end of the label line.