Lab Activity: Special Senses
advertisement

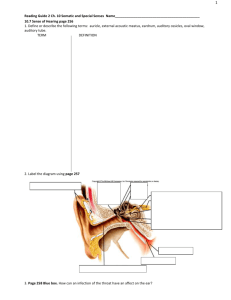
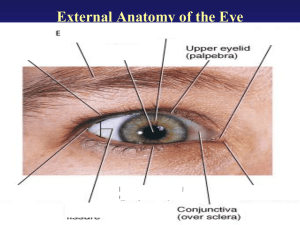
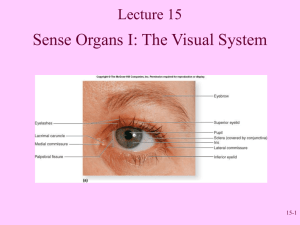
Lab Activity: Special Senses Part A: The Eye and Vision: Anatomy 1. Several accessory eye structures contribute to the formation of tears and/or aid in lubrication of the eyeball. Match the described accessory structures with their secretion by choosing from the choices. Conjunctiva Lacrimal Glands Tarsal Gland a. Mucus b. Oil c. Salt Solution 2. 3. 4. 5. The eyeball is wrapped in adipose tissue within the orbit. What is the function of the adipose tissue? Why may it be necessary to blow one’s nose after having a good cry? What is a sty? Conjunctivitis? What seven bones form the bony orbit? (Think-if you can’t remember, check back to the skeletal system chapter.) 6. Match the key responses with the descriptive statements that follow: Aqueous humor Cornea Lens Sclera Canal of Schlemm Fovea Centralis Optic Disc Suspensory Ligament Choroid Iris Retina Vitreous Humor Ciliary Body a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. Attaches the lens to the ciliary body Fluid filling the anterior segment of the eye The blind spot Contains muscle that controls the size of the pupil Drains the aqueous humor from the eye “sensory” tunic Substance occupying the posterior segment of the eyeball Forms most of the pigmented vascular tunic Tiny pit in the macula lutea; contains only cones Important light-bending structures of the eye; shape can be modified Anterior transparent part of the fibrous tunic Composed of tough, white, opaque, fibrous connective tissue 7. The intrinsic eye muscle are under the control of which of the following? Autonomic Nervous System or Somatic Nervous System Part B: Visual Tests and Experiments 1. Use terms from the key to complete the statements concerning near and distance vision Contracted Decreased Increased Relaxed Taut Lax During distance vision: The ciliary muscle is __ (a)___, the suspensory ligament is ___(b)___, the convexity of the lens is __(c)___, and light refraction is ___(d)__. During close vision: The ciliary muscle is ___(e)__, the suspensory ligament is ___(f)___, lens convexity is ___(g)__, and light refraction is __(h)___. 2. Explain why the part of the image hitting the blind spot is not seen. 3. Match the terms in Column B with the description in Column A: Column A a. Light bending b. Ability to focus for close (under 20 ft) vision c. Normal vision d. Inability to focus well on close objects (farsightedness) e. Nearsightedness f. Blurred vision due to unequal curvatures of the lens or cornea g. Medial movement of the eyes during focusing on close objects Column B accommodation astigmatism convergence emmetropia hyperopia myopia refraction 4. Define astigmatism. 5. How can you explain the fact that we see a great range of colors even though only three cone types exist? 6. Many college students struggling through mountainous reading assignments are told that they need glasses for “eyestrain.” Why is it more of a strain on the extrinsic and intrinsic eye muscles to look at close objects than at far objects?