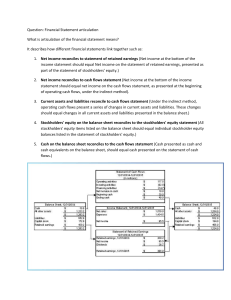
Chapter 14
advertisement

Managerial Accounting Weygandt • Kieso • Kimmel Financial Statement Analysis: The Big Picture Chapter 14 1 Chapter 14 Financial Statement Analysis: The Big Picture After studying Chapter 14, you should be able to: • Describe and apply horizontal analysis. • Describe and apply vertical analysis. • Identify and compute ratios used in analyzing a company’s liquidity, solvency, and profitability. • Understand the concept of quality of earnings. 2 Financial Statement Analysis Three basic tools are used in financial statement analysis : • Horizontal analysis • Vertical analysis • Ratio analysis 3 Horizontal Analysis • Is a technique for evaluating a series of financial statement data over a period of time. • Purpose is to determine whether an increase or decrease has taken place. • The increase or decrease can be expressed as either an amount or a percentage. 4 Horizontal Analysis 5 Horizontal Analysis of Net Sales Current period sales expressed as a percentage of the base period using 1997 as the base period: Kellogg Company Net Sales (in millions) Base Period 1997 2001 2000 1999 $8,853.3 $6,954.7 $6,984.2 129.62% 101.82 % 102.26% 1998 1997 $6762.1 $6,830.1 99% 100.0% 6 Horizontal Analysis of a Balance Sheet KELLOGG COMPANY, INC. Condensed Balance Sheets December 31 (In millions) Increase (Decrease) during 2001 2001 Assets Current Assets Plant assets Other assets Total assets 2000 Amount $ 1,902.0 $1,617.1 $ 284.9 2,952.8 2,526.9 425.9 5,513.8 742.0 4,771.8 $10,368.6 $4,886.0 $5,482.6 Percent 17.6 16.9 643.1 112.2 7 Horizontal Analysis of a Balance SheetIncrease (Decrease) 2001 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Current liabilities $ 2,207.6 Long-term liabilities 7,289.5 Total liabilities 9,497.1 Stockholders' equity Common stock 195.3 Retained earnings and other 1,013.3 Treasury stock (337.1) Total stockholders' equity 871.5 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $10,368.6 2000 during 2001 Amount Percent $2,482.3 1,506.2 3,988.5 $ (274.7) 5,783.3 5,508.6 (11.1) 384.0 138.1 205.8 (10.5) (5.1) 1,065.7 (374.0) (52.4) 36.9 (4.9) 9.9 897.5 (26.0) (2.9) $4,886.0 $5,482.6 112.2 8 KELLOGG COMPANY, INC. Condensed Income Statement For the Years Ended December 31 (In millions) 2001 Net sales $ 8,853.3 Cost of goods sold 4,128.5 Gross profit 4,724.8 Selling & Admin. 3,523.6 Nonrecurring charges 33.3 Income from operations 1,167.9 Interest expense 351.5 Other income (expense), net (12.3) Income before taxes 804.1 Income tax expense 322.1 Net income $ 482.0 2000 $6,954.7 3,327.0 3,627.7 2,551.4 86.5 989.8 137.5 Increase (Decrease) during 2001 Amount Percent $1,898.6 27.3 801.5 24.1 1,097.1 30.2 972.2 38.1 (53.2) (61.5) 178.1 18.0 214.0 155.6 15.4 867.7 280.0 $ 587.7 (27.7) (179.9) (63.6) (7.3) 42.1 15.0 $ (105.7) (18.0) 9 Vertical Analysis • Is a technique for evaluating financial statement data that expresses each item in a financial statement as a percent of a base amount. • Total assets is always the base amount in vertical analysis of a balance sheet. • Net sales is always the base amount in vertical analysis of an income statement. 10 KELLOGG COMPANY, INC. Condensed Balance Sheets December 31 (In millions) 2001 Assets Amount Percent Current Assets $ 1,902.0 18.3 Property Assets 2,952.8 28.5 Other assets 5,513.8 53.2 Total assets $10,368.6 100.0% 2000 z Amount Percent $1,617.1 33.1 2,526.9 51.7 742.0 15.2 $4,886.0 100.0% 11 KELLOGG COMPANY, INC. Condensed Balance Sheets December 31 (In millions) 2001 Liabilities and Amount 2000 Percent* Amount Percent* Stockholders' Equity Current liabilities Long-term liabilities Total liabilities Stockholders' equity Common stock Retained earnings and other Treasury stock Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity $ 2,207.6 7,289.5 9,497.1 91.6 21.3 $2,482.3 70.3 1,506.2 3,988.5 81.6 50.8 30.8 195.3 1.9 205.8 4.2 1,013.3 (337.1) 9.8 (3.3) 1,065.7 (374.0) 21.8 (7.6) 8.4 897.5 18.4 100.0 $4,886.0 100.0 871.5 $10,368.6 *Percentages may be rounded up or down 12 KELLOGG COMPANY, INC. Condensed Income Statement For the Years Ended December 31 (In millions) 2001 Amount Percent* $8,853.3 100.0 Net sales Cost of goods sold 4,128.5 Gross profit 4,724.8 Selling & admin. 3,523.6 Nonrecurring chgs. 33.3 Income operations 1,167.9 Interest expense 351.5 Other income (expense),net (12.3) Income before income taxes 804.1 Income tax ex. 322.1 Net income $ 482.0 *Percentages may be rounded up 46.6 53.4 39.8 0.4 13.2 4.0 (0.1) 9.1 3.6 5.5 or down 2000 Amount Percent* $6,954.7 100.0 3,327.0 3,627.7 2,551.4 86.5 989.8 137.5 47.8 52.2 36.7 1.3 14.2 2.0 15.4 0.2 867.7 280.0 $ 587.7 12.4 4.0 8.4 13 Condensed Income Statements For the Year Ended December 31, 2001 (in millions) Kellogg Company, Inc. Amount Percent* Net sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit Selling and administrative expenses Nonrecurring charges Income from operations Other expenses and revenues (including income taxes) Net income General Mills,Inc Amount Percent* $8,853.3 100.0 4,128.5 46.6 4,724.8 53.4 $7,949.0 100.0 4,767.0 60.0 3,182.0 40.0 3,523.6 39.8 33.3 0.4 1,167.9 13.2 1,909.0 24.0 190.0 2.4 1,083.0 13.6 685.9 $ 482.0 7.7 5.5 622.0 $ 461.0 7.8 5.8 *Percentages may be rounded up or down 14 Ratio Analysis 15 Ratios • Three types: Liquidity ratios Solvency ratios Profitability ratios • Can provide clues to underlying conditions that may not be apparent from an inspection of the individual components. • Single ratio by itself is not very meaningful. 16 Liquidity Ratios Measure the short-term ability of the enterprise to pay its maturing obligations and to meet unexpected needs for cash. WHO CARES? Short-term creditors such as bankers and suppliers 17 Liquidity Ratios • • • • • • • Working capital Current ratio Current cash debt coverage ratio Inventory turnover ratio Days in inventory Receivables turnover ratio Average collection period 18 Working Capital Indicates immediate short-term debtpaying ability Current Assets - Current Liabilities 19 Current Ratio Indicates short-term debt-paying ability Current Assets Current Liabilities 20 Current Cash Debt Coverage Ratio Indicates short-term debt-paying ability (cash basis) Cash provided by operations Average current liabilities 21 Inventory Turnover Ratio Indicates liquidity of inventory Cost of Goods Sold Average Inventory 22 Days in Inventory Indicates liquidity of inventory and inventory management 365 days Inventory Turnover Ratio 23 Receivables Turnover Ratio Indicates liquidity of receivables Net Credit Sales Average Gross Receivables 24 Average Collection Period Indicates liquidity of receivables and collection success. 365 days Receivables Turnover Ratio 25 Solvency Ratios Measure the ability of the enterprise to survive over a long period of time WHO CARES? Long-term creditors and stockholders 26 Solvency Ratios • • • • Debt to total assets ratio Cash debt coverage ratio Times interest earned ratio Free cash flow 27 Debt to Total Assets Ratio Indicates % of total assets provided by creditors Total Liabilities Total Assets 28 Cash Debt Coverage Ratio Indicates long-term debt-paying ability (cash basis) Cash provided by operations Average total liabilities 29 Times Interest Earned Ratio Indicates company’s ability to meet interest payments as they come due Net Income Before Interest Expense & Income Tax Interest Expense 30 Free Cash Flow Indicates cash available for paying dividends or expanding operations Cash Provided By Operations - Capital Expenditures - Dividends Paid Free Cash Flow 31 Profitability Ratios Measure the income or operating success of an enterprise for a given period of time WHO CARES? Everybody WHY? A company’s income affects: • its ability to obtain debt and equity financing • its liquidity position • its ability to grow 32 Profitability Ratios • • • • • • • • Earnings per share (EPS) Price-earnings ratio Gross profit rate Profit margin ratio Return on assets ratio Assets turnover ratio Payout ratio Return on common stockholders’ equity ratio 33 Earnings Per Share (EPS) Indicates net income earned on each share of common stock sales Net Income - Preferred Stock Dividends Average common shares outstanding 34 Price Earnings Ratio Indicates relationship between market price per share and earnings per share Stock Price Per Share Earnings Per Share 35 Gross Profit Rate Indicates margin between selling price and cost of good sold Gross profit Net sales 36 Profit Margin Ratio Indicates net income generated by each dollar of sales Net income Net sales Higher value suggests favorable return on each dollar of sales. 37 Return On Assets Ratio Reveals the amount of net income generated by each dollar invested Net income Average total assets Higher value suggests favorable efficiency. 38 Asset Turnover Ratio Indicates how efficiently assets are used to generate sales Net sales Average total assets 39 Payout Ratio Indicates % of earnings distributed in the form of cash dividends Cash dividends decl. on common stock Net income 40 Return on Common Stockholders’ Equity Ratio Indicates profitability of common stockholders’ investment Net income - preferred stock dividends Average common stockholders’ equity 41 Limitations Of Financial Analysis • Horizontal, vertical, and ratio analysis are frequently used in making significant business decisions. • One should be aware of the limitations of these tools and the financial statements. 42 Quality of Earnings Indicates the level of full and transparent information that is provided to users of the financial statements. 43 Alternative Accounting Methods • One company may use the FIFO method, while another company in the same industry may use LIFO. • If the inventory is significant for both companies, it is unlikely that their current ratios are comparable. • In addition to differences in inventory costing methods, differences also exist in reporting such items as depreciation, depletion, and amortization. 44 Pro Forma Income A measure of the net income generated that usually excludes items that the company thinks are unusual or nonrecurring. 45