Physical & Chemical Properties
advertisement

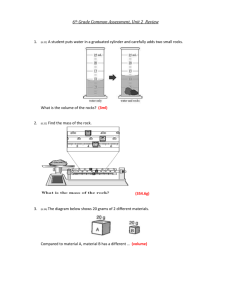
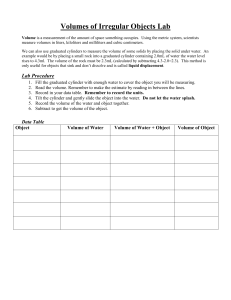
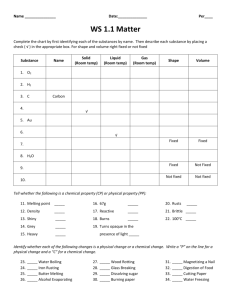
Chapter 4 Lesson 3 PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL PROPERTIES How do you describe physical properties? Color Shape Texture Luster Density: tells how much matter is in a certain space, or volume Density Differences: oil (floats on top) water syrup (has the greatest density of the 3) Chemical Properties What causes a chemical change? reaction to air, heat, & water Examples: Logs can burn. An egg can cook. (heat) Iron can rust. Chapter 4 STUDY GUIDE 1. Anything that has mass and takes up space is called matter. 2. The smallest particle part of any element is an atom. 3. Two or more atoms make a molecule. 4. The 3 states of matter are: solid, liquid, and gas. 5. Solid molecules have a definite shape, are tightly packed, and a fixed size. 6. Liquid molecules do not have a definite shape, they take the shape of their container, and slide past each other; they do have a fixed size. 7. Gas molecules move rapidly, and do not have a fixed size. 8. The amount of space that matter takes up is volume. 9. To measure liquid volume, use a graduated cylinder or beaker. 10. To measure a solid block, use the formula: l x w x h. 11. To measure a solid odd shape (rock), place the rock in water in a graduated cylinder, then place the rock in, and subtract the water. 12.The amount of matter in an object is its mass. 13. A tool to measure mass is a balance. 14. The measure of the pull of gravity on an object is its weight. 15.Name as many physical properties as you can think of: color texture magnetism mass weight volume odor density taste 16.Name as many chemical properties as you can think of: temperature ability to tarnish ability to burn ability to rust 17. How much matter is in a given space is called density (aka thickness). 18. To measure density, you must know is mass and volume.