Ecology Distribution and Adaptations of Organisms
advertisement

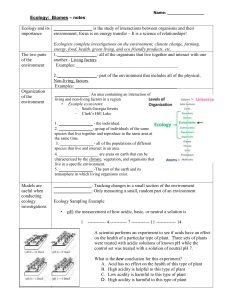
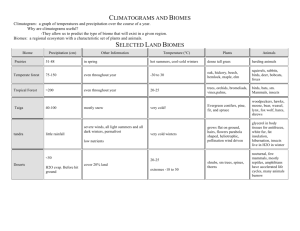
2.d.1 – All biological systems from cells and organisms to populations, communities, and ecosystems are affected by complex biotic and abiotic interaction involving exchange of matter and free energy (52.2). The study of the interactions between organisms and their environment All living beings (animals, plants, fungi, etc) Studied at many different levels 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Organismal Ecology Population Ecology Community Ecology Biome Ecology Biosphere Ecology Abiotic Factors: nonliving factors Ex: Temperature, water, wind, humidity Biotic Factors: living factors Ex: Competition, Predation (plants, animals, fungi, etc) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Temperature Water Sunlight Wind Rocks and Soil Disturbance Effects cell contents Ex: ◦ Cold – cells will rupture if temperatures drop below a certain point ◦ Hot – many proteins and DNA will denature Point – life can only exist over a fairly narrow temperature range Review the properties of water from Chapter 3. Cells must maintain a certain water potential level (keep from exploding or drying out). Provides energy for Ps, which drives most food webs. Plants often compete for light because of shading or absorption of light by deep columns of water. Effects temperature and water conditions for many organisms. May carry abrasive particles that limit plant growth by killing the SAM areas. ◦ SAM??? Shoot apical meristem areas Physical structure, pH, mineral composition of rocks and soil limit where plants can grow. Ex. Se soils. Plants limit what animals can be found in an area. Disturbance is often an important part of an environment. Allows organisms to re-colonize an area. Ex: Fire Humans Wind Yellowstone Fire Shapes environments and what organisms can live in a particular area. Climatic factors: ◦ Solar radiation and latitude ◦ Axis tilt/seasons ◦ Air/Water circulation patterns Changes the amount of light and energy delivered per surface area. Result: ◦ Poles: less light ◦ Equator: more light ◦ Unequal heating causes air and water to circulate Caused by the Earth's tilt. Day length changes over time. Many organisms are restricted in range by how well they adapt to changing seasons. Air rises when heated, sinks when cools. Zones of rising/sinking are created. Earth's rotation causes zones to "twist”. Result: ◦ Air circulation patterns ◦ Rain fall patterns Rising air: wet areas Descending air: dry areas Broad geographical regions with characteristic communities of organisms. Biomes are controlled by: ◦ Temperature ◦ Water amount and proximity ◦ Geography Areas covered with dense/lush growth of trees and vines. Climate: ◦ Warm temperatures. ◦ Constant day length. ◦ High water. Vertical layers of autotrophic growth Have the greatest diversity of species of any area on Earth. Soil is usually very infertile. Most of the nutrients are in the plant life. One of the most endangered Biomes. Grasslands with a few trees. Climate with three growing seasons: ◦ Cool and dry ◦ Hot and dry ◦ Warm and wet Rich in herbivores and predator species Only major biome not found in North America Characterized by plants adapted to dry growing conditions. ◦ Cacti, succulents Climate: ◦ Dry (<30cm/yr). ◦ May be cold or hot. Often found in areas of descending air masses. Low productivity, but still fairly diverse in species. Characterized by spiny evergreen shrubs. Climate: ◦ Mild rainy winters ◦ Hot summers Ex: Southern California Maintained by fires Plants adapted to periodic fires by seeds or re-growing from the roots Grasses and other herbs are the dominant vegetation. Indiana could be considered a temp. grassland Climate: ◦ Intermediate water ◦ Relatively cold winters Very productive for agriculture. (wheat, corn) Need disturbance (fires) to keep trees out. Come in several types: ◦ Tall grass ◦ Short grass Deciduous trees dominate (often called deciduous forest) Climate: ◦ Relatively high rain ◦ Cold winters Very little natural area left. Good diversity of species. Coniferous forest: ◦ Tall stands of cone-bearing tress Coniferous trees dominate (also called coniferous forests) Climate: ◦ Long cold winters ◦ Short wet summers ◦ Long summer daylength Relatively low species diversity Being logged at an alarming rate (disappearing rapidly!) Grasses and sedges dominate. Climate: ◦ Very cold and dry ◦ Low light in winter Permafrost present Plants low in height Poor species diversity Mirror each other. Their Biomes are similar because the environments are similar. Ex: Alpine = Tundra Have <1% salt concentration. Strongly influenced by temperature and light. Classification – based on water flow patterns. Flowing: rivers, creeks Non-flowing: ponds, lakes Cover 3/4 of the Earth's surface. Average 3% salt. Controlled by light and the distance to the shore. Photic - Enough light for Ps. Red light lost rapidly as depth increases. Aphotic - Lacks enough light for Ps and depends on food made in photic zone for energy. Part of the most extensive biome on the planet. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Estuaries Intertidal Coral Reefs Pelagic Benthos Where a freshwater river meets the ocean. Salinity variable. Very productive Biome. Complex flow patterns Characterized by coral. Found in shallow warm waters. Very productive. High species diversity. Very sensitive to temperature changes Bottom area. Usually fed by nutrients drifting down from upper levels. Fairly rich in life. Know what is involved with the study of “Ecology”. Know the major factors of planet Earth that shape climate. Know the major terrestrial biomes and the factors that control them. Know the major types of aquatic biomes and the factors that control them.